Erkan Bostanci
A new Video Synopsis Based Approach Using Stereo Camera
Jun 23, 2021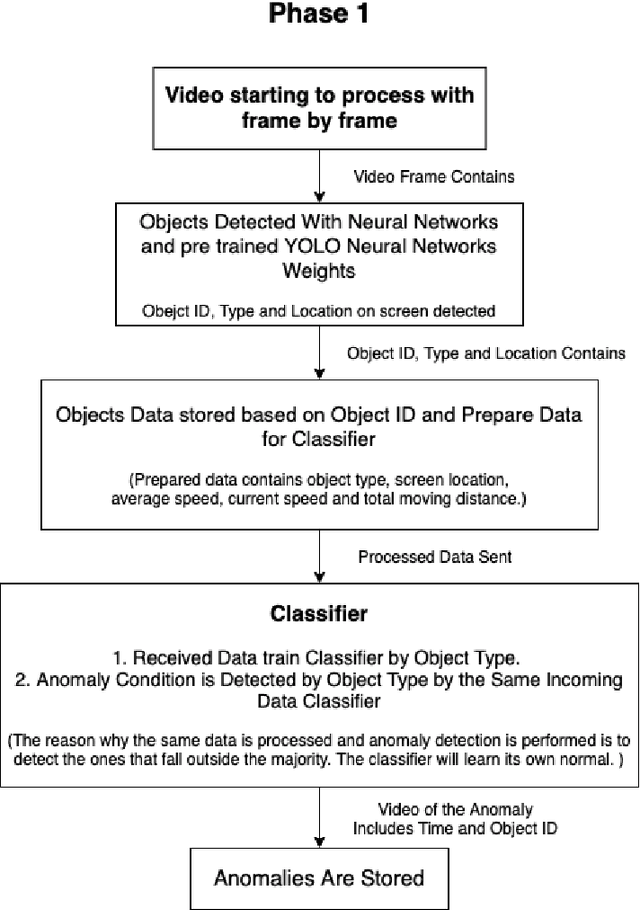
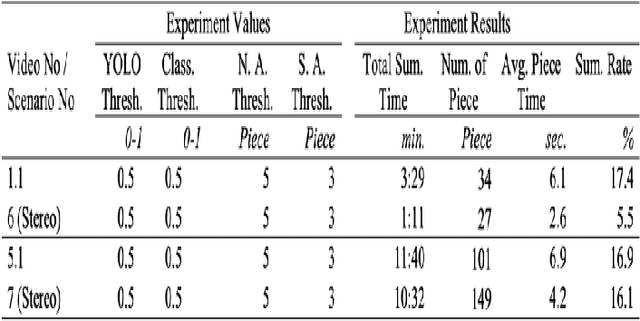
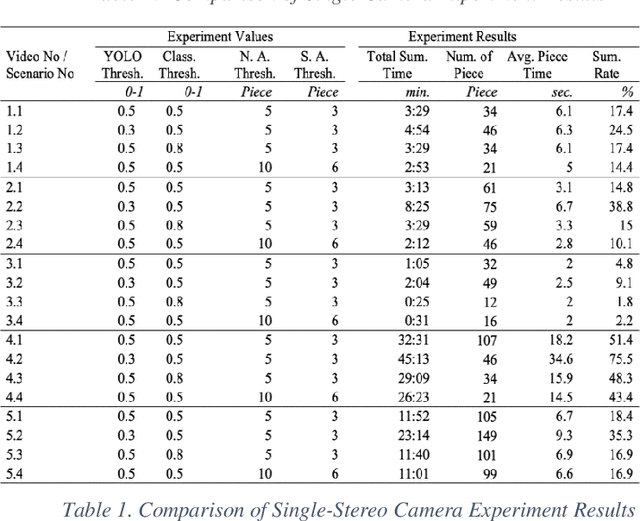
Abstract:In today's world, the amount of data produced in every field has increased at an unexpected level. In the face of increasing data, the importance of data processing has increased remarkably. Our resource topic is on the processing of video data, which has an important place in increasing data, and the production of summary videos. Within the scope of this resource, a new method for anomaly detection with object-based unsupervised learning has been developed while creating a video summary. By using this method, the video data is processed as pixels and the result is produced as a video segment. The process flow can be briefly summarized as follows. Objects on the video are detected according to their type, and then they are tracked. Then, the tracking history data of the objects are processed, and the classifier is trained with the object type. Thanks to this classifier, anomaly behavior of objects is detected. Video segments are determined by processing video moments containing anomaly behaviors. The video summary is created by extracting the detected video segments from the original video and combining them. The model we developed has been tested and verified separately for single camera and dual camera systems.
Analysis of Interpolation based Image In-painting Approaches
Feb 12, 2021
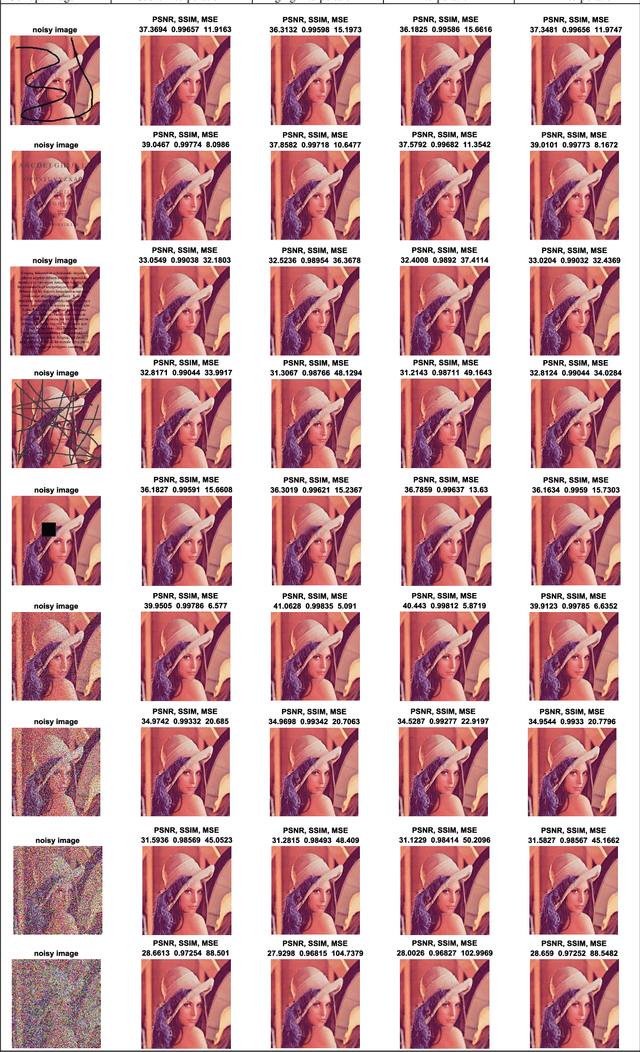


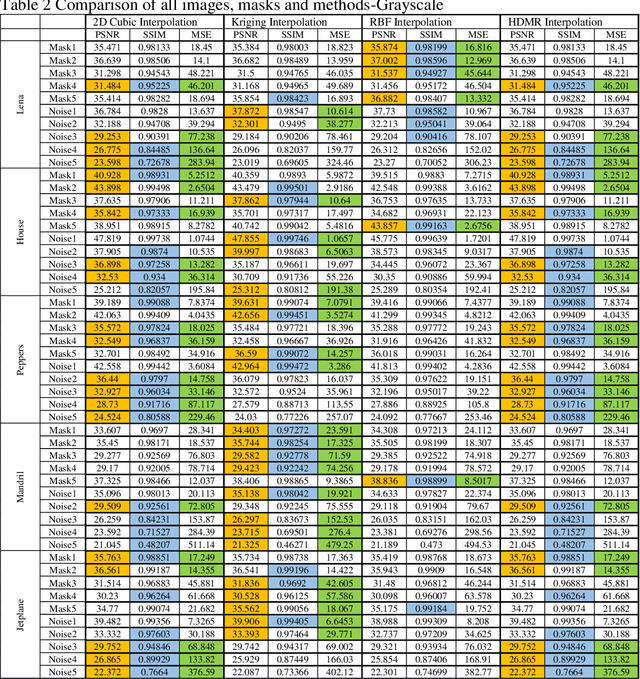
Abstract:Interpolation and internal painting are one of the basic approaches in image internal painting, which is used to eliminate undesirable parts that occur in digital images or to enhance faulty parts. This study was designed to compare the interpolation algorithms used in image in-painting in the literature. Errors and noise generated on the colour and grayscale formats of some of the commonly used standard images in the literature were corrected by using Cubic, Kriging, Radial based function and High dimensional model representation approaches and the results were compared using standard image comparison criteria, namely, PSNR (peak signal-to-noise ratio), SSIM (Structural SIMilarity), Mean Square Error (MSE). According to the results obtained from the study, the absolute superiority of the methods against each other was not observed. However, Kriging and RBF interpolation give better results both for numerical data and visual evaluation for image in-painting problems with large area losses.
A Vehicle Detection Approach using Deep Learning Methodologies
Apr 02, 2018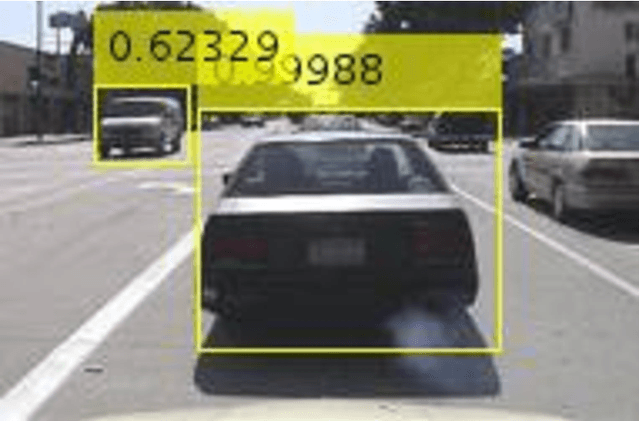
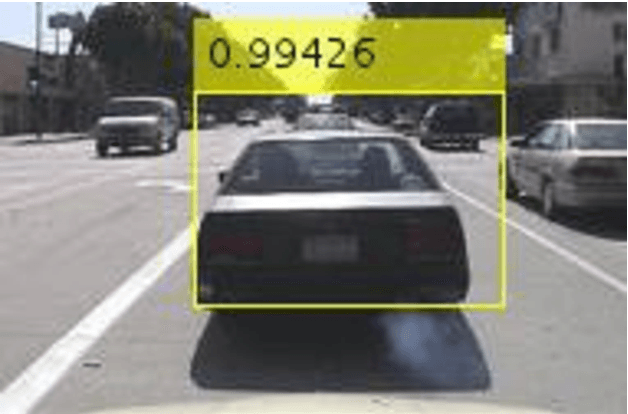
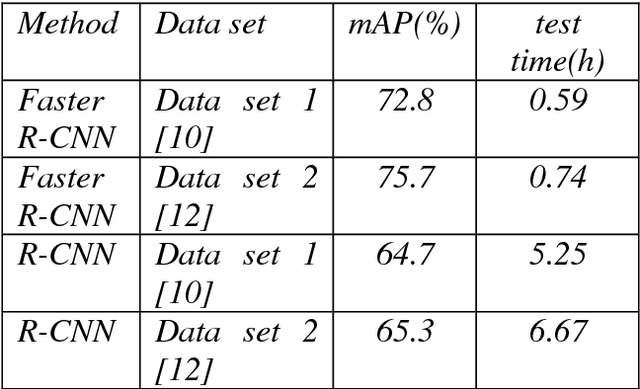

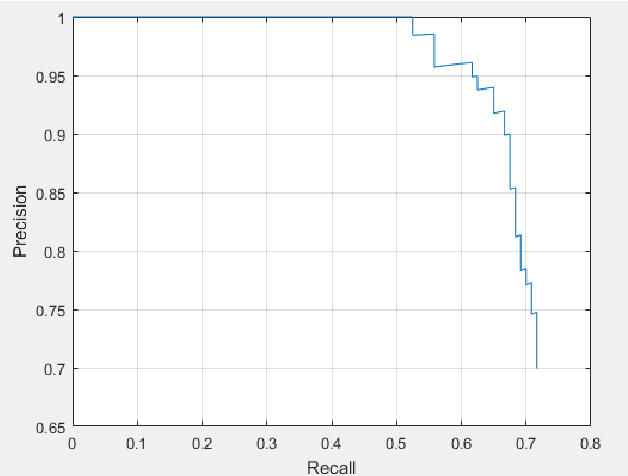
Abstract:The purpose of this study is to successfully train our vehicle detector using R-CNN, Faster R-CNN deep learning methods on a sample vehicle data sets and to optimize the success rate of the trained detector by providing efficient results for vehicle detection by testing the trained vehicle detector on the test data. The working method consists of six main stages. These are respectively; loading the data set, the design of the convolutional neural network, configuration of training options, training of the Faster R-CNN object detector and evaluation of trained detector. In addition, in the scope of the study, Faster R-CNN, R-CNN deep learning methods were mentioned and experimental analysis comparisons were made with the results obtained from vehicle detection.
Live Target Detection with Deep Learning Neural Network and Unmanned Aerial Vehicle on Android Mobile Device
Mar 22, 2018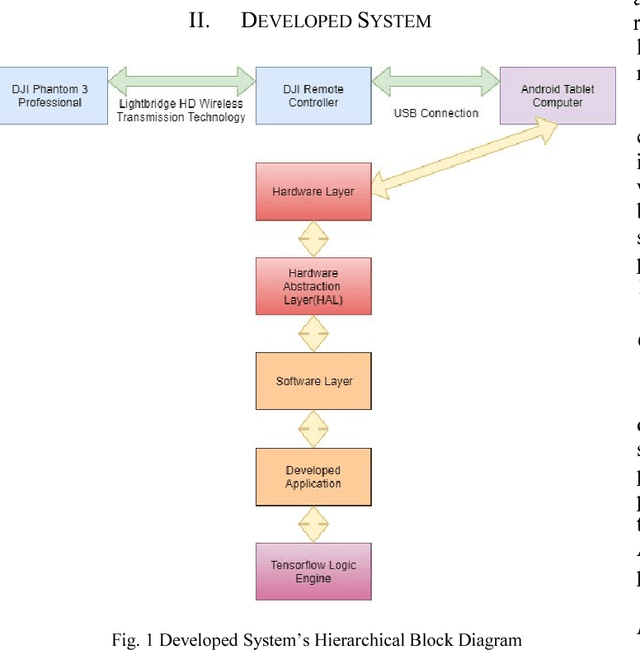
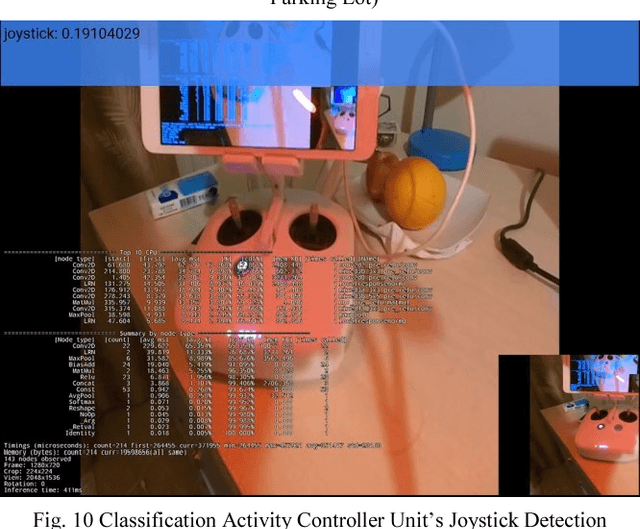
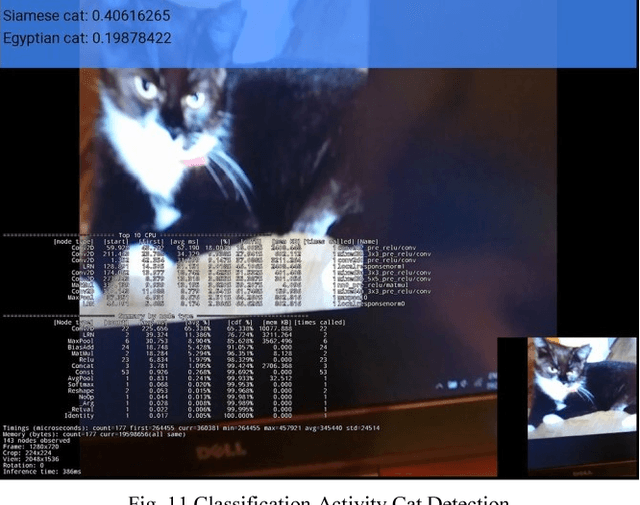
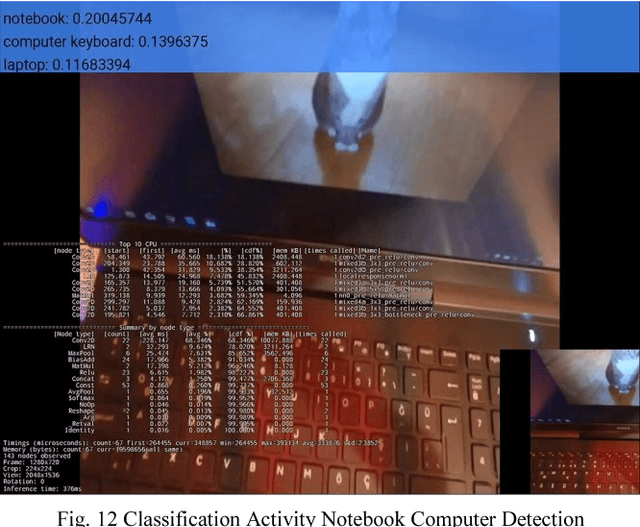
Abstract:This paper describes the stages faced during the development of an Android program which obtains and decodes live images from DJI Phantom 3 Professional Drone and implements certain features of the TensorFlow Android Camera Demo application. Test runs were made and outputs of the application were noted. A lake was classified as seashore, breakwater and pier with the proximities of 24.44%, 21.16% and 12.96% respectfully. The joystick of the UAV controller and laptop keyboard was classified with the proximities of 19.10% and 13.96% respectfully. The laptop monitor was classified as screen, monitor and television with the proximities of 18.77%, 14.76% and 14.00% respectfully. The computer used during the development of this study was classified as notebook and laptop with the proximities of 20.04% and 11.68% respectfully. A tractor parked at a parking lot was classified with the proximity of 12.88%. A group of cars in the same parking lot were classified as sports car, racer and convertible with the proximities of 31.75%, 18.64% and 13.45% respectfully at an inference time of 851ms.
A Fuzzy Brute Force Matching Method for Binary Image Features
Apr 20, 2017
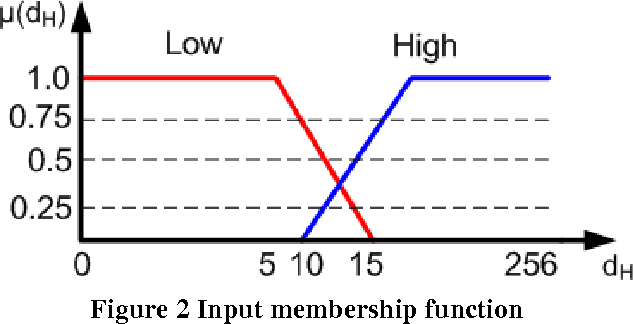
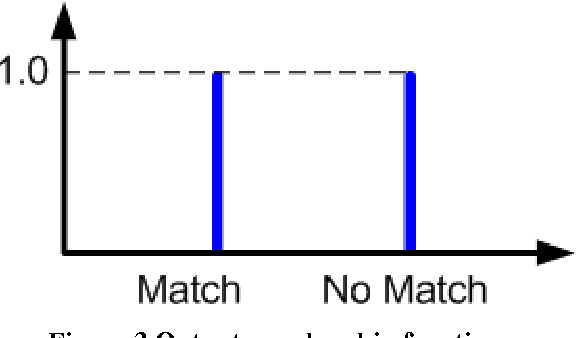
Abstract:Matching of binary image features is an important step in many different computer vision applications. Conventionally, an arbitrary threshold is used to identify a correct match from incorrect matches using Hamming distance which may improve or degrade the matching results for different input images. This is mainly due to the image content which is affected by the scene, lighting and imaging conditions. This paper presents a fuzzy logic based approach for brute force matching of image features to overcome this situation. The method was tested using a well-known image database with known ground truth. The approach is shown to produce a higher number of correct matches when compared against constant distance thresholds. The nature of fuzzy logic which allows the vagueness of information and tolerance to errors has been successfully exploited in an image processing context. The uncertainty arising from the imaging conditions has been overcome with the use of compact fuzzy matching membership functions.
Genetic Algorithm Based Floor Planning System
Apr 20, 2017
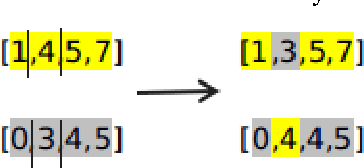
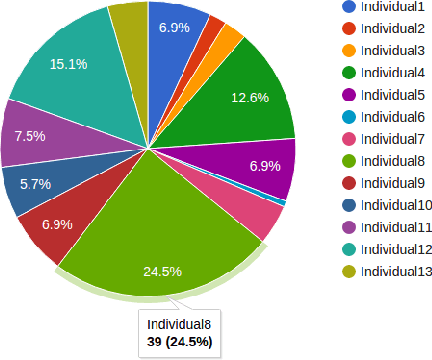
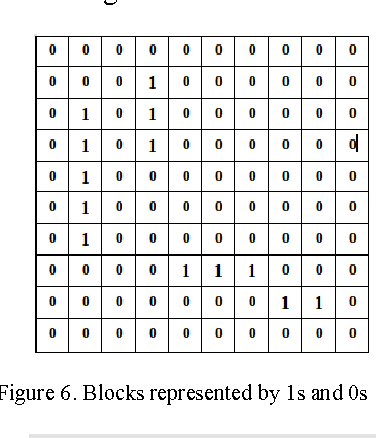
Abstract:Genetic Algorithms are widely used in many different optimization problems including layout design. The layout of the shelves play an important role in the total sales metrics for superstores since this affects the customers' shopping behaviour. This paper employed a genetic algorithm based approach to design shelf layout of superstores. The layout design problem was tackled by using a novel chromosome representation which takes many different parameters to prevent dead-ends and improve shelf visibility into consideration. Results show that the approach can produce reasonably good layout designs in very short amounts of time.
Comparative Study of Instance Based Learning and Back Propagation for Classification Problems
Apr 19, 2016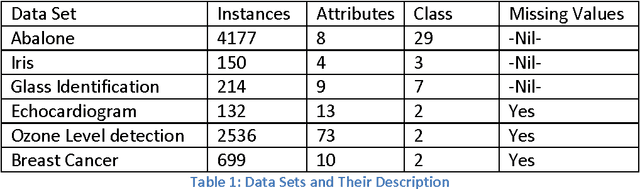
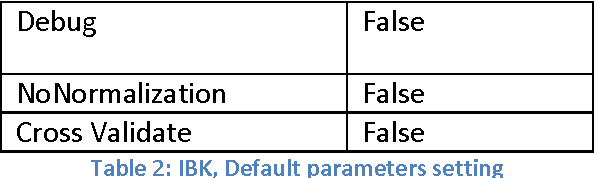
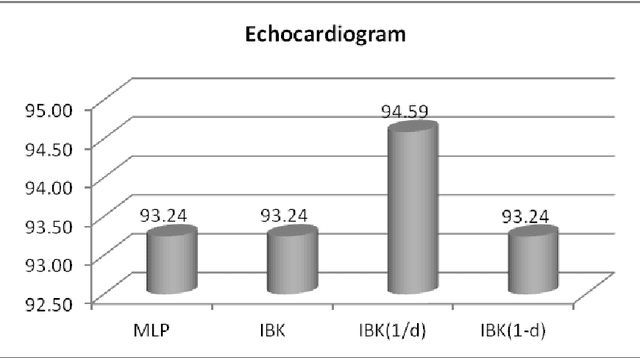

Abstract:The paper presents a comparative study of the performance of Back Propagation and Instance Based Learning Algorithm for classification tasks. The study is carried out by a series of experiments will all possible combinations of parameter values for the algorithms under evaluation. The algorithm's classification accuracy is compared over a range of datasets and measurements like Cross Validation, Kappa Statistics, Root Mean Squared Value and True Positive vs False Positive rate have been used to evaluate their performance. Along with performance comparison, techniques of handling missing values have also been compared that include Mean or Mode replacement and Multiple Imputation. The results showed that parameter adjustment plays vital role in improving an algorithm's accuracy and therefore, Back Propagation has shown better results as compared to Instance Based Learning. Furthermore, the problem of missing values was better handled by Multiple imputation method, however, not suitable for less amount of data.
3D Reconstruction of Crime Scenes and Design Considerations for an Interactive Investigation Tool
Dec 10, 2015
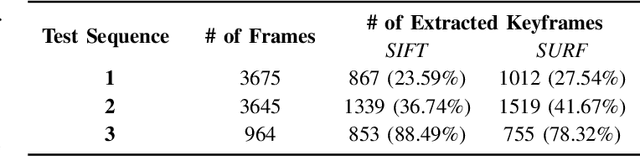
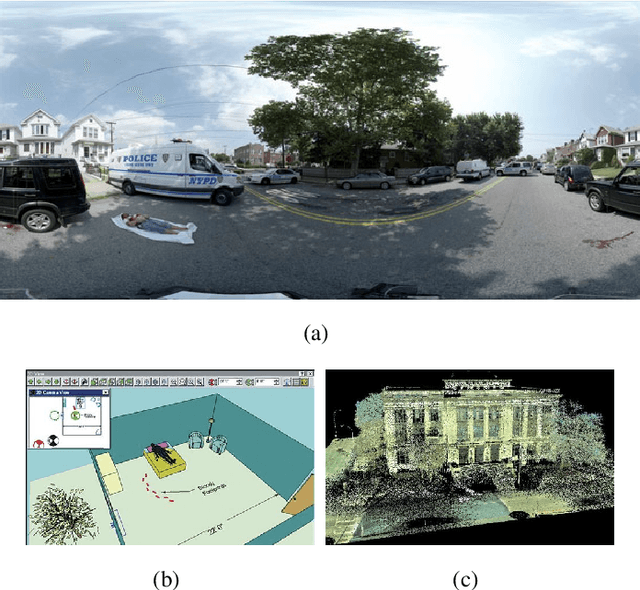
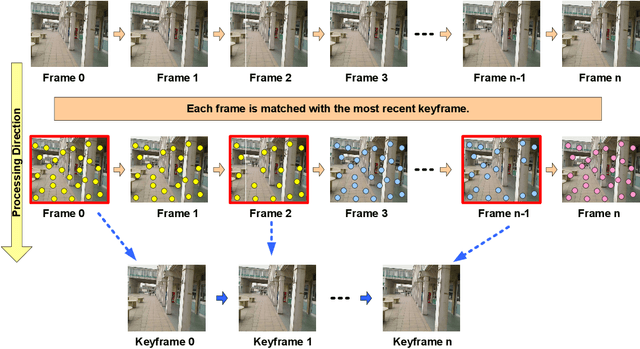
Abstract:Crime Scene Investigation (CSI) is a carefully planned systematic process with the purpose of acquiring physical evidences to shed light upon the physical reality of the crime and eventually detect the identity of the criminal. Capturing images and videos of the crime scene is an important part of this process in order to conduct a deeper analysis on the digital evidence for possible hints. This work brings this idea further to use the acquired footage for generating a 3D model of the crime scene. Results show that realistic reconstructions can be obtained using sophisticated computer vision techniques. The paper also discusses a number of important design considerations describing key features that should be present in a powerful interactive CSI analysis tool.
* 9 pages, journal
Enhanced image feature coverage: Key-point selection using genetic algorithms
Dec 10, 2015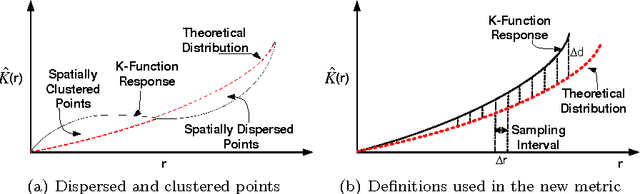
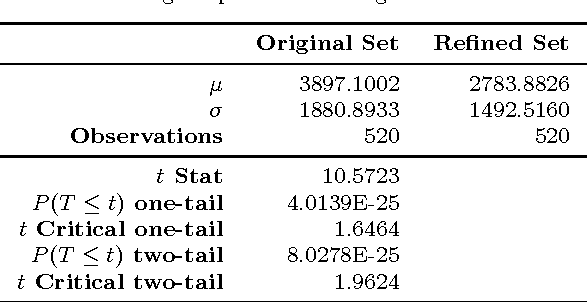
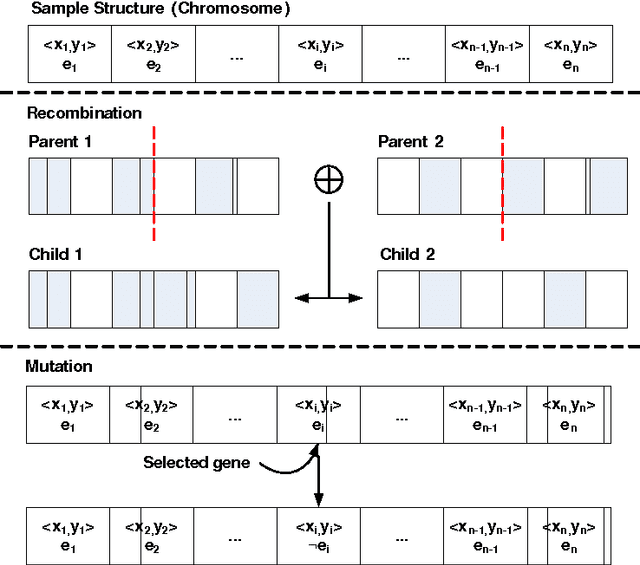
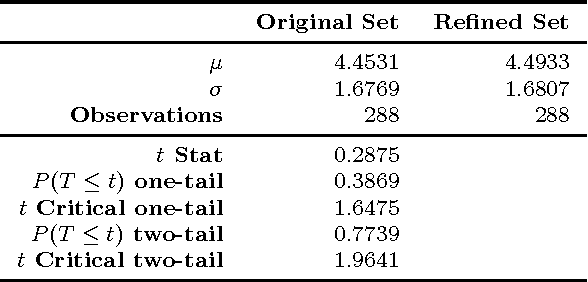
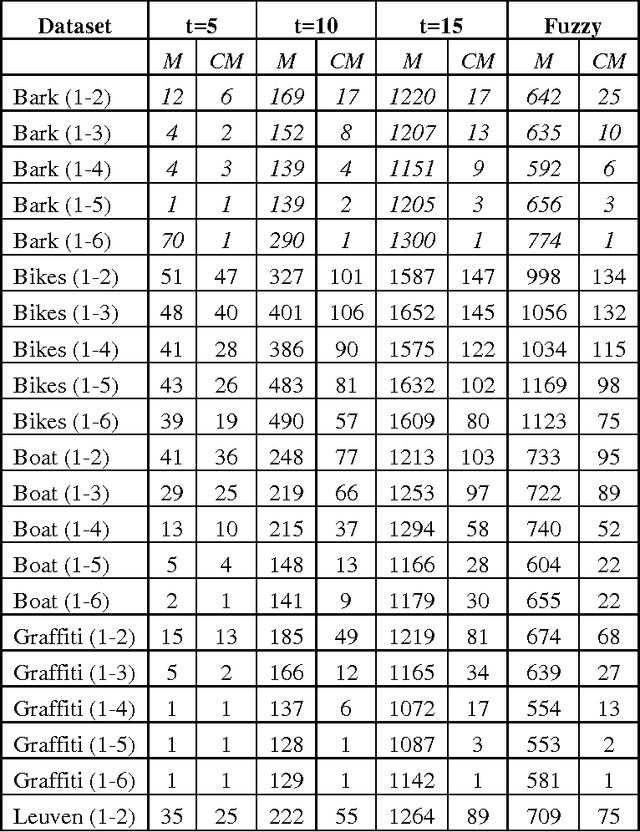
Abstract:Coverage of image features play an important role in many vision algorithms since their distribution affect the estimated homography. This paper presents a Genetic Algorithm (GA) in order to select the optimal set of features yielding maximum coverage of the image which is measured by a robust method based on spatial statistics. It is shown with statistical tests on two datasets that the metric yields better coverage and this is also confirmed by an accuracy test on the computed homography for the original set and the newly selected set of features. Results have demonstrated that the new set has similar performance in terms of the accuracy of the computed homography with the original one with an extra benefit of using fewer number of features ultimately reducing the time required for descriptor calculation and matching.
Sensor Fusion of Camera, GPS and IMU using Fuzzy Adaptive Multiple Motion Models
Dec 09, 2015
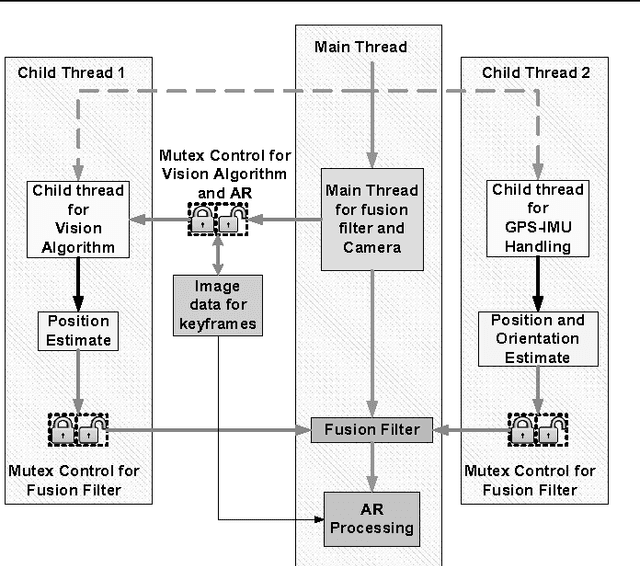
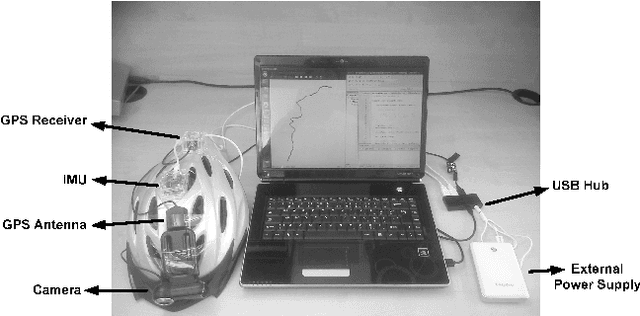
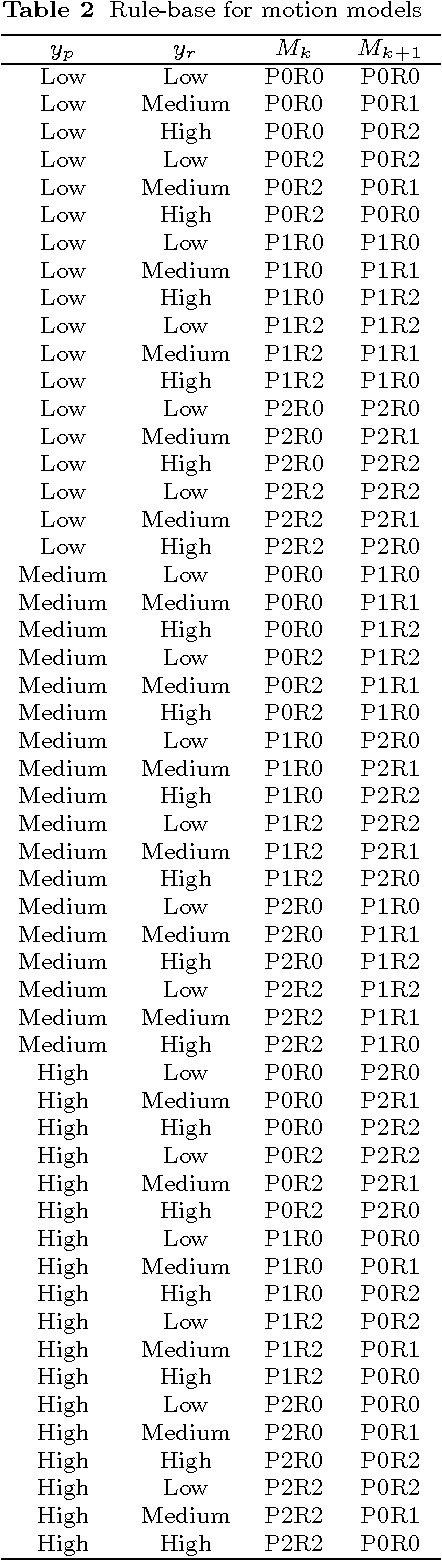
Abstract:A tracking system that will be used for Augmented Reality (AR) applications has two main requirements: accuracy and frame rate. The first requirement is related to the performance of the pose estimation algorithm and how accurately the tracking system can find the position and orientation of the user in the environment. Accuracy problems of current tracking devices, considering that they are low-cost devices, cause static errors during this motion estimation process. The second requirement is related to dynamic errors (the end-to-end system delay; occurring because of the delay in estimating the motion of the user and displaying images based on this estimate. This paper investigates combining the vision-based estimates with measurements from other sensors, GPS and IMU, in order to improve the tracking accuracy in outdoor environments. The idea of using Fuzzy Adaptive Multiple Models (FAMM) was investigated using a novel fuzzy rule-based approach to decide on the model that results in improved accuracy and faster convergence for the fusion filter. Results show that the developed tracking system is more accurate than a conventional GPS-IMU fusion approach due to additional estimates from a camera and fuzzy motion models. The paper also presents an application in cultural heritage context.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge