Eric Sunada
Physics-Informed Machine Learning Towards A Real-Time Spacecraft Thermal Simulator
Jul 08, 2024



Abstract:Modeling thermal states for complex space missions, such as the surface exploration of airless bodies, requires high computation, whether used in ground-based analysis for spacecraft design or during onboard reasoning for autonomous operations. For example, a finite-element thermal model with hundreds of elements can take significant time to simulate, which makes it unsuitable for onboard reasoning during time-sensitive scenarios such as descent and landing, proximity operations, or in-space assembly. Further, the lack of fast and accurate thermal modeling drives thermal designs to be more conservative and leads to spacecraft with larger mass and higher power budgets. The emerging paradigm of physics-informed machine learning (PIML) presents a class of hybrid modeling architectures that address this challenge by combining simplified physics models with machine learning (ML) models resulting in models which maintain both interpretability and robustness. Such techniques enable designs with reduced mass and power through onboard thermal-state estimation and control and may lead to improved onboard handling of off-nominal states, including unplanned down-time. The PIML model or hybrid model presented here consists of a neural network which predicts reduced nodalizations (distribution and size of coarse mesh) given on-orbit thermal load conditions, and subsequently a (relatively coarse) finite-difference model operates on this mesh to predict thermal states. We compare the computational performance and accuracy of the hybrid model to a data-driven neural net model, and a high-fidelity finite-difference model of a prototype Earth-orbiting small spacecraft. The PIML based active nodalization approach provides significantly better generalization than the neural net model and coarse mesh model, while reducing computing cost by up to 1.7x compared to the high-fidelity model.
How to Deploy a 10-km Interferometric Radio Telescope on the Moon with Just Four Tethered Robots
Sep 06, 2022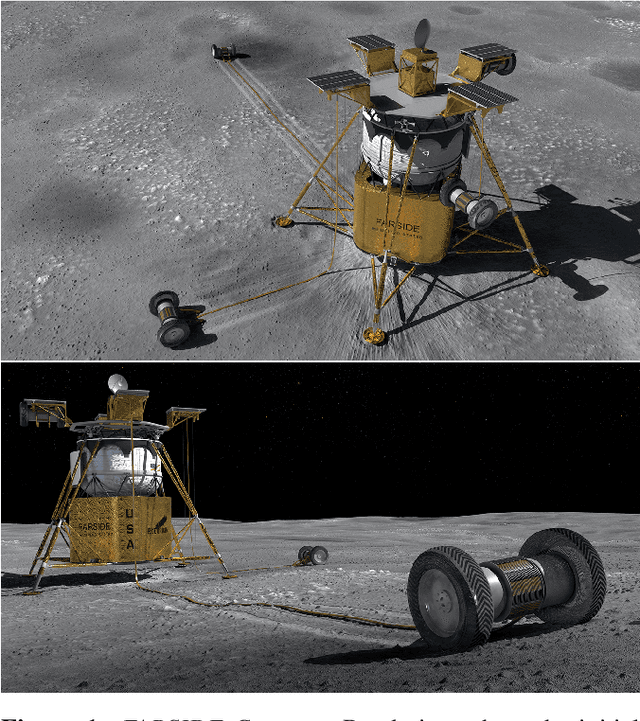

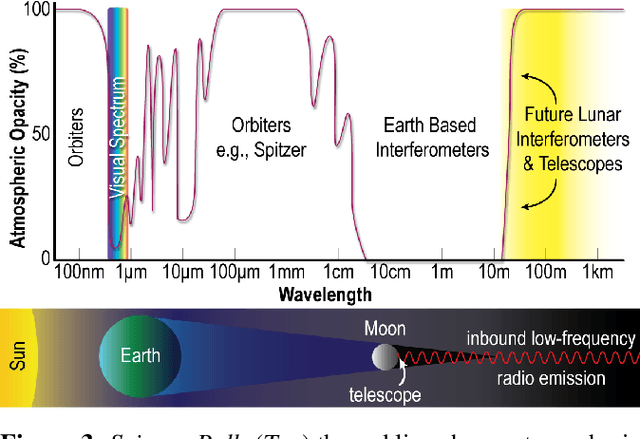
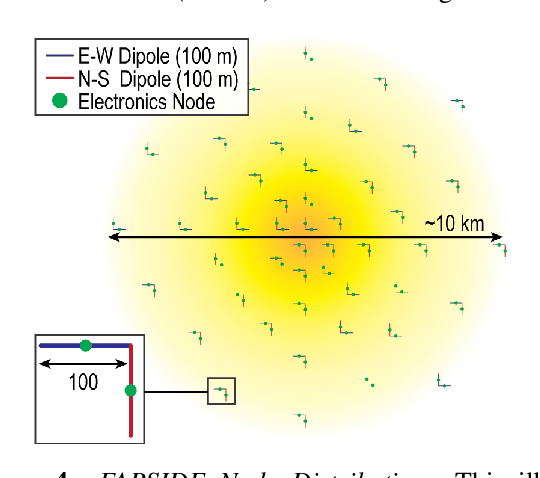
Abstract:The Far-side Array for Radio Science Investigations of the Dark ages and Exoplanets (FARSIDE) is a proposed mission concept to the lunar far side that seeks to deploy and operate an array of 128 dual-polarization, dipole antennas over a region of 100 square kilometers. The resulting interferometric radio telescope would provide unprecedented radio images of distant star systems, allowing for the investigation of faint radio signatures of coronal mass ejections and energetic particle events and could also lead to the detection of magnetospheres around exoplanets within their parent star's habitable zone. Simultaneously, FARSIDE would also measure the "Dark Ages" of the early Universe at a global 21-cm signal across a range of red shifts (z approximately 50-100). Each discrete antenna node in the array is connected to a central hub (located at the lander) via a communication and power tether. Nodes are driven by cold=operable electronics that continuously monitor an extremely wide-band of frequencies (200 kHz to 40 MHz), which surpass the capabilities of Earth-based telescopes by two orders of magnitude. Achieving this ground-breaking capability requires a robust deployment strategy on the lunar surface, which is feasible with existing, high TRL technologies (demonstrated or under active development) and is capable of delivery to the surface on next-generation commercial landers, such as Blue Origin's Blue Moon Lander. This paper presents an antenna packaging, placement, and surface deployment trade study that leverages recent advances in tethered mobile robots under development at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which are used to deploy a flat, antenna-embedded, tape tether with optical communication and power transmission capabilities.
* 8 pages, 17 figures, IEEE Aerospace Conference Proceedings, 2021
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge