Enrique Zuazua
Fair feature attribution for multi-output prediction: a Shapley-based perspective
Feb 26, 2026Abstract:In this article, we provide an axiomatic characterization of feature attribution for multi-output predictors within the Shapley framework. While SHAP explanations are routinely computed independently for each output coordinate, the theoretical necessity of this practice has remained unclear. By extending the classical Shapley axioms to vector-valued cooperative games, we establish a rigidity theorem showing that any attribution rule satisfying efficiency, symmetry, dummy player, and additivity must necessarily decompose component-wise across outputs. Consequently, any joint-output attribution rule must relax at least one of the classical Shapley axioms. This result identifies a previously unformalized structural constraint in Shapley-based interpretability, clarifying the precise scope of fairness-consistent explanations in multi-output learning. Numerical experiments on a biomedical benchmark illustrate that multi-output models can yield computational savings in training and deployment, while producing SHAP explanations that remain fully consistent with the component-wise structure imposed by the Shapley axioms.
Training Together, Diagnosing Better: Federated Learning for Collagen VI-Related Dystrophies
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:The application of Machine Learning (ML) to the diagnosis of rare diseases, such as collagen VI-related dystrophies (COL6-RD), is fundamentally limited by the scarcity and fragmentation of available data. Attempts to expand sampling across hospitals, institutions, or countries with differing regulations face severe privacy, regulatory, and logistical obstacles that are often difficult to overcome. The Federated Learning (FL) provides a promising solution by enabling collaborative model training across decentralized datasets while keeping patient data local and private. Here, we report a novel global FL initiative using the Sherpa.ai FL platform, which leverages FL across distributed datasets in two international organizations for the diagnosis of COL6-RD, using collagen VI immunofluorescence microscopy images from patient-derived fibroblast cultures. Our solution resulted in an ML model capable of classifying collagen VI patient images into the three primary pathogenic mechanism groups associated with COL6-RD: exon skipping, glycine substitution, and pseudoexon insertion. This new approach achieved an F1-score of 0.82, outperforming single-organization models (0.57-0.75). These results demonstrate that FL substantially improves diagnostic utility and generalizability compared to isolated institutional models. Beyond enabling more accurate diagnosis, we anticipate that this approach will support the interpretation of variants of uncertain significance and guide the prioritization of sequencing strategies to identify novel pathogenic variants.
Federated Learning for Pediatric Pneumonia Detection: Enabling Collaborative Diagnosis Without Sharing Patient Data
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Early and accurate pneumonia detection from chest X-rays (CXRs) is clinically critical to expedite treatment and isolation, reduce complications, and curb unnecessary antibiotic use. Although artificial intelligence (AI) substantially improves CXR-based detection, development is hindered by globally distributed data, high inter-hospital variability, and strict privacy regulations (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR) that make centralization impractical. These constraints are compounded by heterogeneous imaging protocols, uneven data availability, and the costs of transferring large medical images across geographically dispersed sites. In this paper, we evaluate Federated Learning (FL) using the Sherpa.ai FL platform, enabling multiple hospitals (nodes) to collaboratively train a CXR classifier for pneumonia while keeping data in place and private. Using the Pediatric Pneumonia Chest X-ray dataset, we simulate cross-hospital collaboration with non-independent and non-identically distributed (non-IID) data, reproducing real-world variability across institutions and jurisdictions. Our experiments demonstrate that collaborative and privacy-preserving training across multiple hospitals via FL led to a dramatic performance improvement achieving 0.900 Accuracy and 0.966 ROC-AUC, corresponding to 47.5% and 50.0% gains over single-hospital models (0.610; 0.644), without transferring any patient CXR. These results indicate that FL delivers high-performing, generalizable, secure and private pneumonia detection across healthcare networks, with data kept local. This is especially relevant for rare diseases, where FL enables secure multi-institutional collaboration without data movement, representing a breakthrough for accelerating diagnosis and treatment development in low-data domains.
A PDE Perspective on Generative Diffusion Models
Nov 08, 2025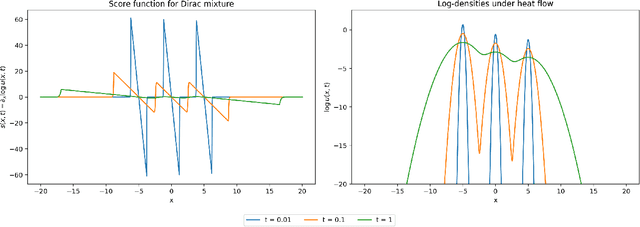
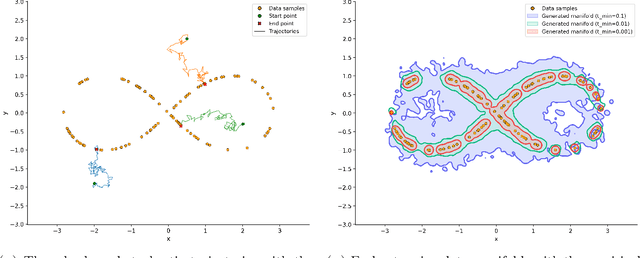
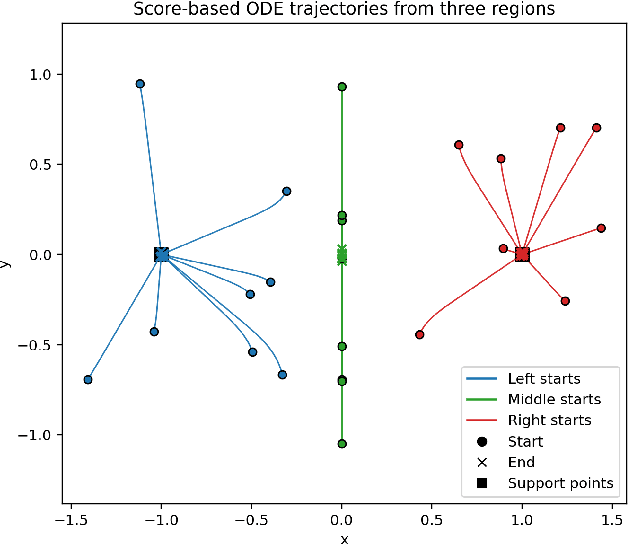
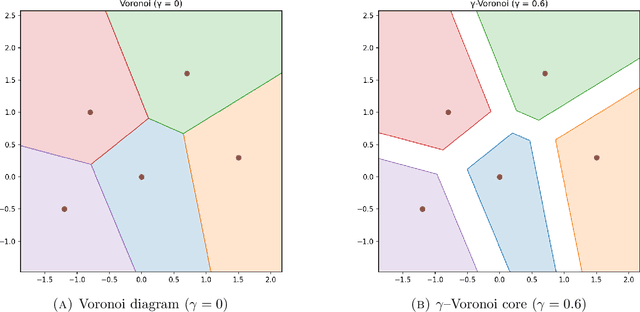
Abstract:Score-based diffusion models have emerged as a powerful class of generative methods, achieving state-of-the-art performance across diverse domains. Despite their empirical success, the mathematical foundations of those models remain only partially understood, particularly regarding the stability and consistency of the underlying stochastic and partial differential equations governing their dynamics. In this work, we develop a rigorous partial differential equation (PDE) framework for score-based diffusion processes. Building on the Li--Yau differential inequality for the heat flow, we prove well-posedness and derive sharp $L^p$-stability estimates for the associated score-based Fokker--Planck dynamics, providing a mathematically consistent description of their temporal evolution. Through entropy stability methods, we further show that the reverse-time dynamics of diffusion models concentrate on the data manifold for compactly supported data distributions and a broad class of initialization schemes, with a concentration rate of order $\sqrt{t}$ as $t \to 0$. These results yield a theoretical guarantee that, under exact score guidance, diffusion trajectories return to the data manifold while preserving imitation fidelity. Our findings also provide practical insights for designing diffusion models, including principled criteria for score-function construction, loss formulation, and stopping-time selection. Altogether, this framework provides a quantitative understanding of the trade-off between generative capacity and imitation fidelity, bridging rigorous analysis and model design within a unified mathematical perspective.
Exact Sequence Classification with Hardmax Transformers
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:We prove that hardmax attention transformers perfectly classify datasets of $N$ labeled sequences in $\mathbb{R}^d$, $d\geq 2$. Specifically, given $N$ sequences with an arbitrary but finite length in $\mathbb{R}^d$, we construct a transformer with $\mathcal{O}(N)$ blocks and $\mathcal{O}(Nd)$ parameters perfectly classifying this dataset. Our construction achieves the best complexity estimate to date, independent of the length of the sequences, by innovatively alternating feed-forward and self-attention layers and by capitalizing on the clustering effect inherent to the latter. Our novel constructive method also uses low-rank parameter matrices within the attention mechanism, a common practice in real-life transformer implementations. Consequently, our analysis holds twofold significance: it substantially advances the mathematical theory of transformers and it rigorously justifies their exceptional real-world performance in sequence classification tasks.
Representation and Regression Problems in Neural Networks: Relaxation, Generalization, and Numerics
Dec 02, 2024



Abstract:In this work, we address three non-convex optimization problems associated with the training of shallow neural networks (NNs) for exact and approximate representation, as well as for regression tasks. Through a mean-field approach, we convexify these problems and, applying a representer theorem, prove the absence of relaxation gaps. We establish generalization bounds for the resulting NN solutions, assessing their predictive performance on test datasets and, analyzing the impact of key hyperparameters on these bounds, propose optimal choices. On the computational side, we examine the discretization of the convexified problems and derive convergence rates. For low-dimensional datasets, these discretized problems are efficiently solvable using the simplex method. For high-dimensional datasets, we propose a sparsification algorithm that, combined with gradient descent for over-parameterized shallow NNs, yields effective solutions to the primal problems.
A Potential Game Perspective in Federated Learning
Nov 18, 2024Abstract:Federated learning (FL) is an emerging paradigm for training machine learning models across distributed clients. Traditionally, in FL settings, a central server assigns training efforts (or strategies) to clients. However, from a market-oriented perspective, clients may independently choose their training efforts based on rational self-interest. To explore this, we propose a potential game framework where each client's payoff is determined by their individual efforts and the rewards provided by the server. The rewards are influenced by the collective efforts of all clients and can be modulated through a reward factor. Our study begins by establishing the existence of Nash equilibria (NEs), followed by an investigation of uniqueness in homogeneous settings. We demonstrate a significant improvement in clients' training efforts at a critical reward factor, identifying it as the optimal choice for the server. Furthermore, we prove the convergence of the best-response algorithm to compute NEs for our FL game. Finally, we apply the training efforts derived from specific NEs to a real-world FL scenario, validating the effectiveness of the identified optimal reward factor.
Deep Neural Networks: Multi-Classification and Universal Approximation
Sep 10, 2024



Abstract:We demonstrate that a ReLU deep neural network with a width of $2$ and a depth of $2N+4M-1$ layers can achieve finite sample memorization for any dataset comprising $N$ elements in $\mathbb{R}^d$, where $d\ge1,$ and $M$ classes, thereby ensuring accurate classification. By modeling the neural network as a time-discrete nonlinear dynamical system, we interpret the memorization property as a problem of simultaneous or ensemble controllability. This problem is addressed by constructing the network parameters inductively and explicitly, bypassing the need for training or solving any optimization problem. Additionally, we establish that such a network can achieve universal approximation in $L^p(\Omega;\mathbb{R}_+)$, where $\Omega$ is a bounded subset of $\mathbb{R}^d$ and $p\in[1,\infty)$, using a ReLU deep neural network with a width of $d+1$. We also provide depth estimates for approximating $W^{1,p}$ functions and width estimates for approximating $L^p(\Omega;\mathbb{R}^m)$ for $m\geq1$. Our proofs are constructive, offering explicit values for the biases and weights involved.
Clustering in pure-attention hardmax transformers and its role in sentiment analysis
Jun 26, 2024Abstract:Transformers are extremely successful machine learning models whose mathematical properties remain poorly understood. Here, we rigorously characterize the behavior of transformers with hardmax self-attention and normalization sublayers as the number of layers tends to infinity. By viewing such transformers as discrete-time dynamical systems describing the evolution of points in a Euclidean space, and thanks to a geometric interpretation of the self-attention mechanism based on hyperplane separation, we show that the transformer inputs asymptotically converge to a clustered equilibrium determined by special points called leaders. We then leverage this theoretical understanding to solve sentiment analysis problems from language processing using a fully interpretable transformer model, which effectively captures `context' by clustering meaningless words around leader words carrying the most meaning. Finally, we outline remaining challenges to bridge the gap between the mathematical analysis of transformers and their real-life implementation.
FedADMM-InSa: An Inexact and Self-Adaptive ADMM for Federated Learning
Feb 21, 2024Abstract:Federated learning (FL) is a promising framework for learning from distributed data while maintaining privacy. The development of efficient FL algorithms encounters various challenges, including heterogeneous data and systems, limited communication capacities, and constrained local computational resources. Recently developed FedADMM methods show great resilience to both data and system heterogeneity. However, they still suffer from performance deterioration if the hyperparameters are not carefully tuned. To address this issue, we propose an inexact and self-adaptive FedADMM algorithm, termed FedADMM-InSa. First, we design an inexactness criterion for the clients' local updates to eliminate the need for empirically setting the local training accuracy. This inexactness criterion can be assessed by each client independently based on its unique condition, thereby reducing the local computational cost and mitigating the undesirable straggle effect. The convergence of the resulting inexact ADMM is proved under the assumption of strongly convex loss functions. Additionally, we present a self-adaptive scheme that dynamically adjusts each client's penalty parameter, enhancing algorithm robustness by mitigating the need for empirical penalty parameter choices for each client. Extensive numerical experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets are conducted. As validated by some numerical tests, our proposed algorithm can reduce the clients' local computational load significantly and also accelerate the learning process compared to the vanilla FedADMM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge