Emily Doucette
Evolving Multi-label Classification Rules by Exploiting High-order Label Correlation
Jul 22, 2020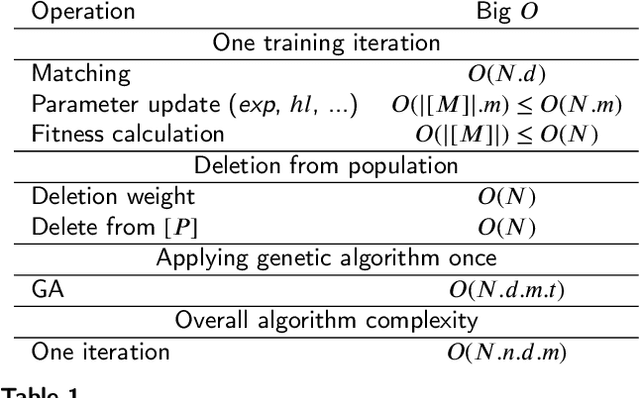
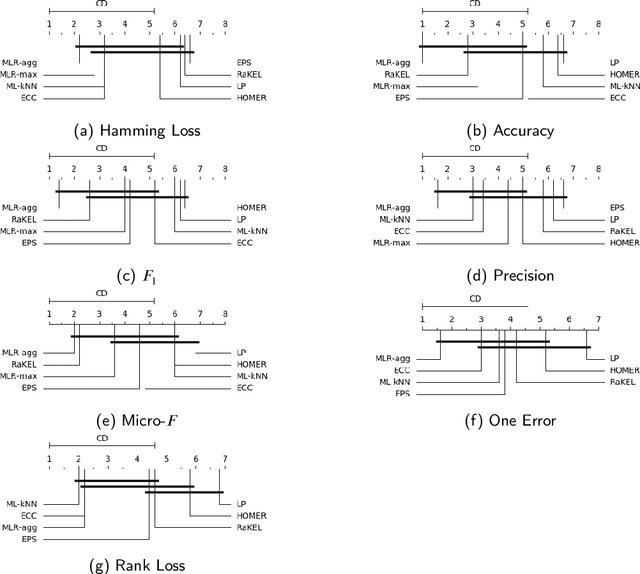
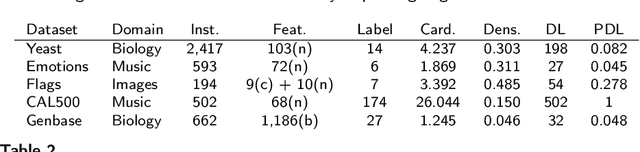
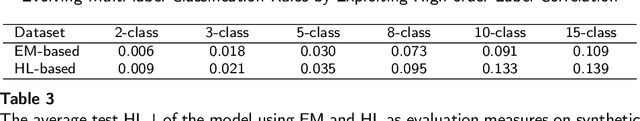
Abstract:In multi-label classification tasks, each problem instance is associated with multiple classes simultaneously. In such settings, the correlation between labels contains valuable information that can be used to obtain more accurate classification models. The correlation between labels can be exploited at different levels such as capturing the pair-wise correlation or exploiting the higher-order correlations. Even though the high-order approach is more capable of modeling the correlation, it is computationally more demanding and has scalability issues. This paper aims at exploiting the high-order label correlation within subsets of labels using a supervised learning classifier system (UCS). For this purpose, the label powerset (LP) strategy is employed and a prediction aggregation within the set of the relevant labels to an unseen instance is utilized to increase the prediction capability of the LP method in the presence of unseen labelsets. Exact match ratio and Hamming loss measures are considered to evaluate the rule performance and the expected fitness value of a classifier is investigated for both metrics. Also, a computational complexity analysis is provided for the proposed algorithm. The experimental results of the proposed method are compared with other well-known LP-based methods on multiple benchmark datasets and confirm the competitive performance of this method.
Vision-Based Distributed Formation Control of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
Sep 01, 2018


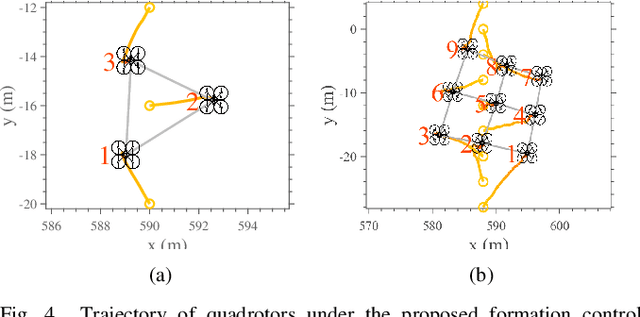
Abstract:We present a novel control strategy for a team of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to autonomously achieve a desired formation using only visual feedback provided by the UAV's onboard cameras. This effectively eliminates the need for global position measurements. The proposed pipeline is fully distributed and encompasses a collision avoidance scheme. In our approach, each UAV extracts feature points from captured images and communicates their pixel coordinates and descriptors among its neighbors. These feature points are used in our novel pose estimation algorithm, QuEst, to localize the neighboring UAVs. Compared to existing methods, QuEst has better estimation accuracy and is robust to feature point degeneracies. We demonstrate the proposed pipeline in a high-fidelity simulation environment and show that UAVs can achieve a desired formation in a natural environment without any fiducial markers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge