Emilian-Claudiu Mănescu
End-to-End Lip Reading in Romanian with Cross-Lingual Domain Adaptation and Lateral Inhibition
Oct 07, 2023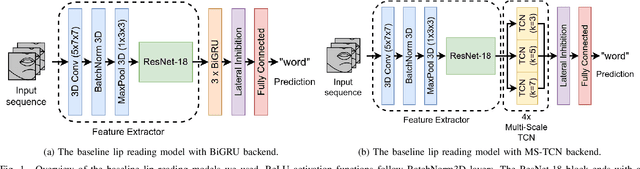
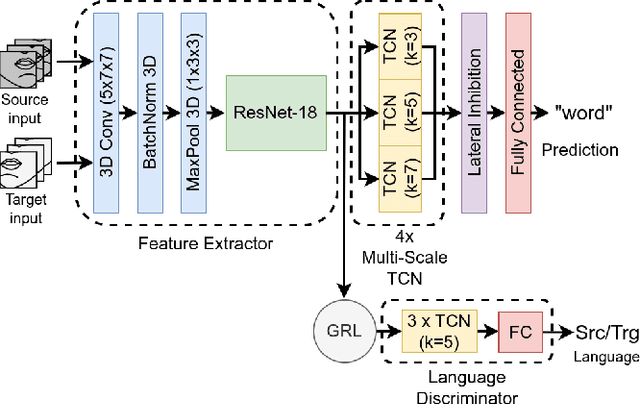
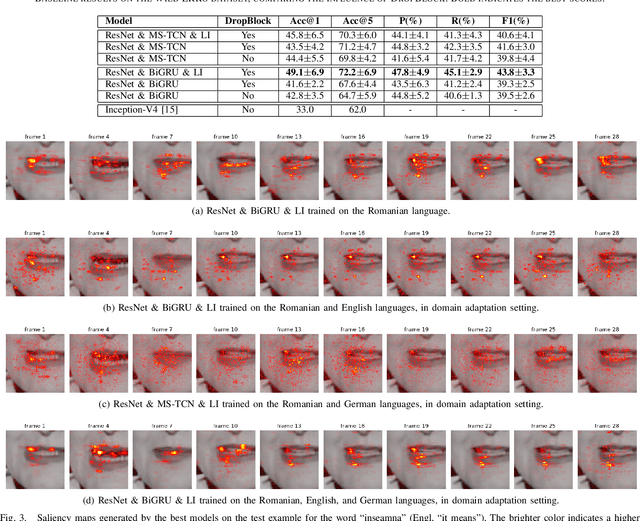
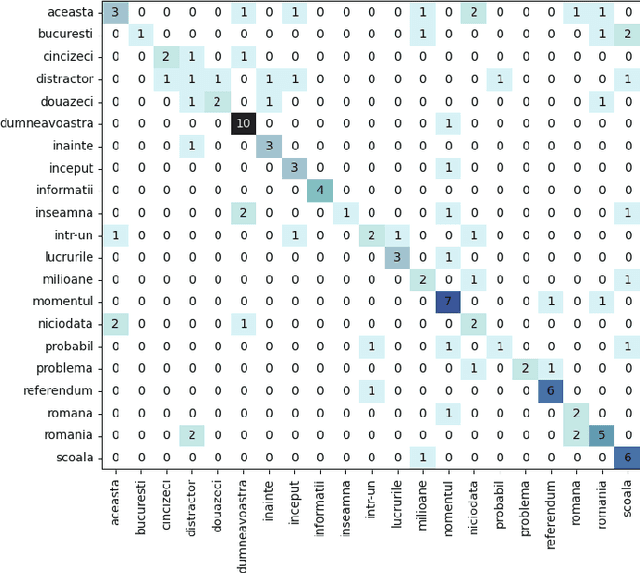
Abstract:Lip reading or visual speech recognition has gained significant attention in recent years, particularly because of hardware development and innovations in computer vision. While considerable progress has been obtained, most models have only been tested on a few large-scale datasets. This work addresses this shortcoming by analyzing several architectures and optimizations on the underrepresented, short-scale Romanian language dataset called Wild LRRo. Most notably, we compare different backend modules, demonstrating the effectiveness of adding ample regularization methods. We obtain state-of-the-art results using our proposed method, namely cross-lingual domain adaptation and unlabeled videos from English and German datasets to help the model learn language-invariant features. Lastly, we assess the performance of adding a layer inspired by the neural inhibition mechanism.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge