Elisa Gugliotta
Université Grenoble Alpes, Laboratoires: LIG - Getalp Group, LIDILEM, Sapienza University of Rome
TArC: Tunisian Arabish Corpus First complete release
Jul 11, 2022
Abstract:In this paper we present the final result of a project on Tunisian Arabic encoded in Arabizi, the Latin-based writing system for digital conversations. The project led to the creation of two integrated and independent resources: a corpus and a NLP tool created to annotate the former with various levels of linguistic information: word classification, transliteration, tokenization, POS-tagging, lemmatization. We discuss our choices in terms of computational and linguistic methodology and the strategies adopted to improve our results. We report on the experiments performed in order to outline our research path. Finally, we explain why we believe in the potential of these resources for both computational and linguistic researches. Keywords: Tunisian Arabizi, Annotated Corpus, Neural Network Architecture
Multi-Task Sequence Prediction For Tunisian Arabizi Multi-Level Annotation
Nov 10, 2020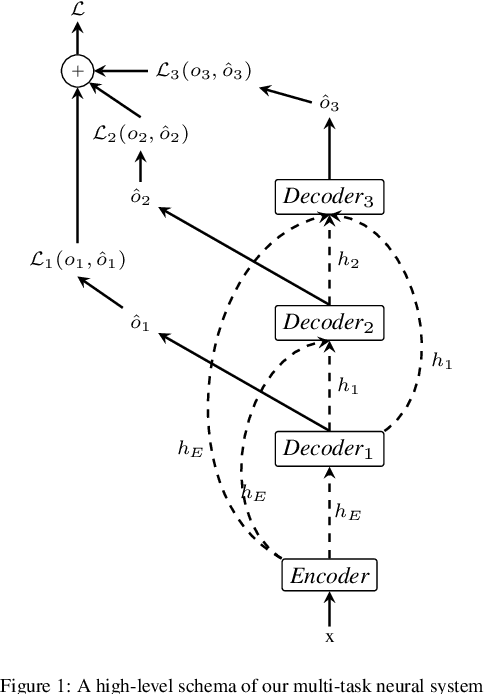
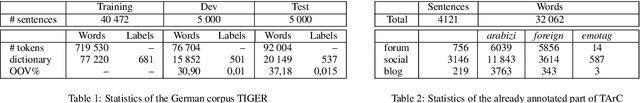
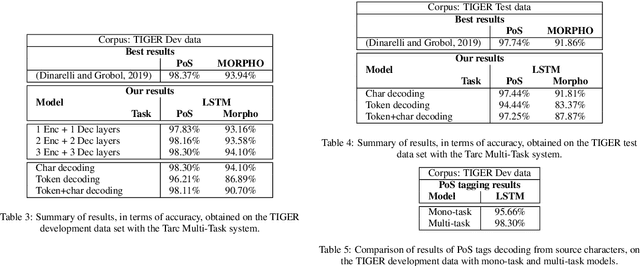
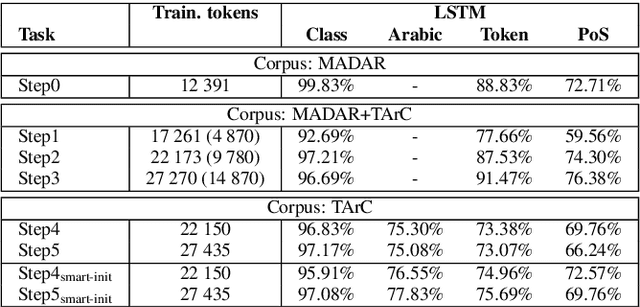
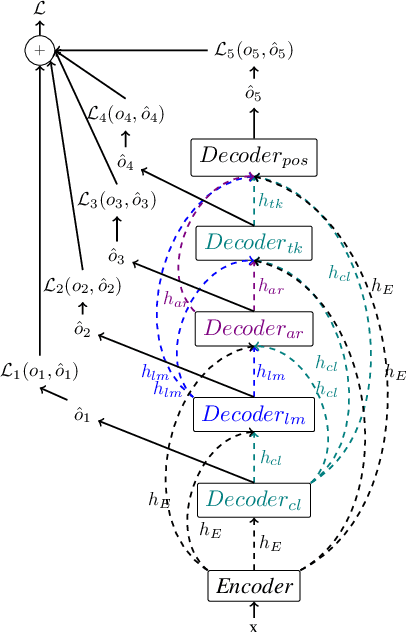
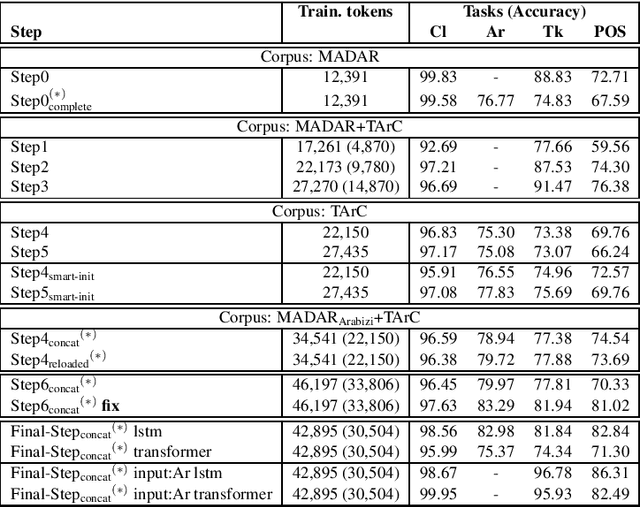
Abstract:In this paper we propose a multi-task sequence prediction system, based on recurrent neural networks and used to annotate on multiple levels an Arabizi Tunisian corpus. The annotation performed are text classification, tokenization, PoS tagging and encoding of Tunisian Arabizi into CODA* Arabic orthography. The system is learned to predict all the annotation levels in cascade, starting from Arabizi input. We evaluate the system on the TIGER German corpus, suitably converting data to have a multi-task problem, in order to show the effectiveness of our neural architecture. We show also how we used the system in order to annotate a Tunisian Arabizi corpus, which has been afterwards manually corrected and used to further evaluate sequence models on Tunisian data. Our system is developed for the Fairseq framework, which allows for a fast and easy use for any other sequence prediction problem.
TArC: Incrementally and Semi-Automatically Collecting a Tunisian Arabish Corpus
Mar 24, 2020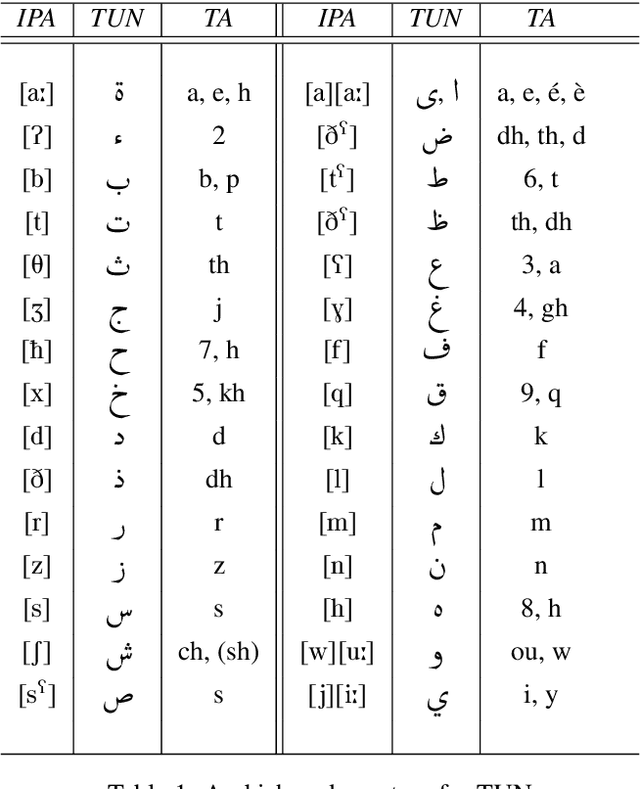
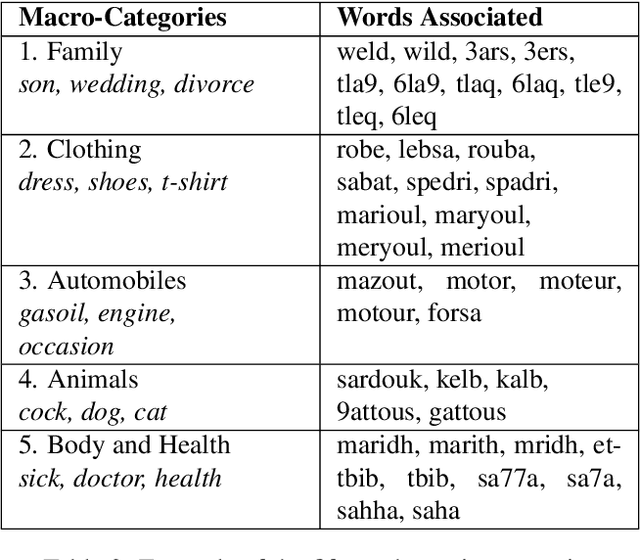
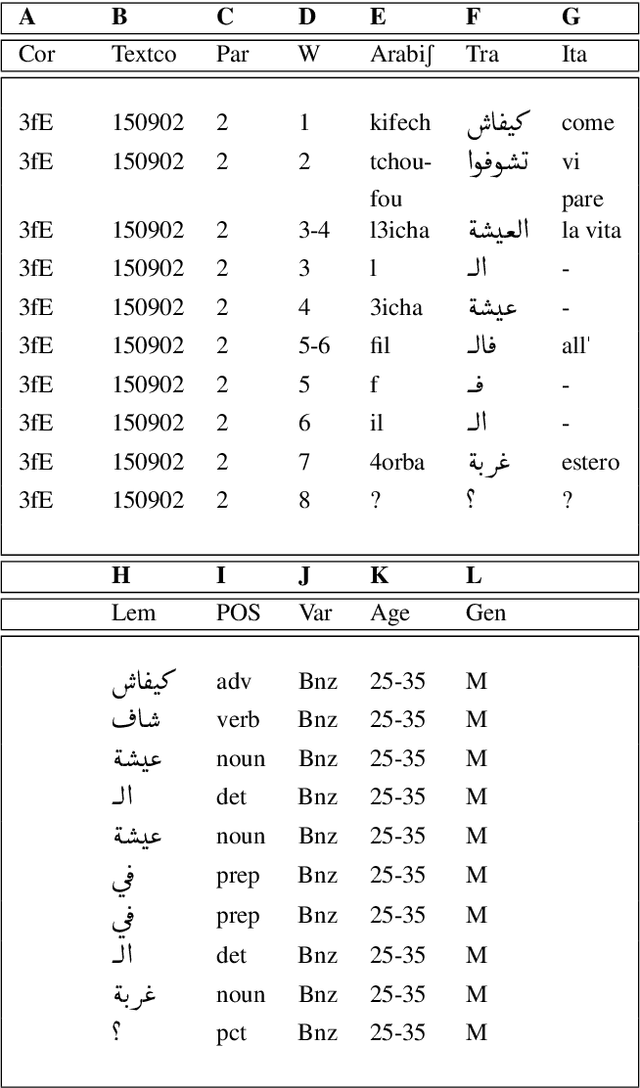
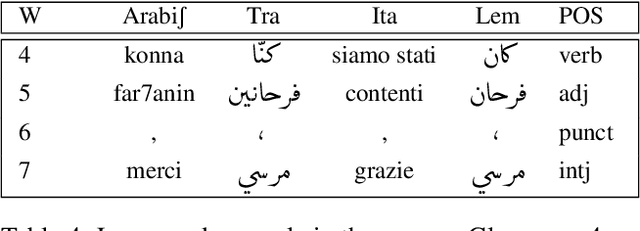
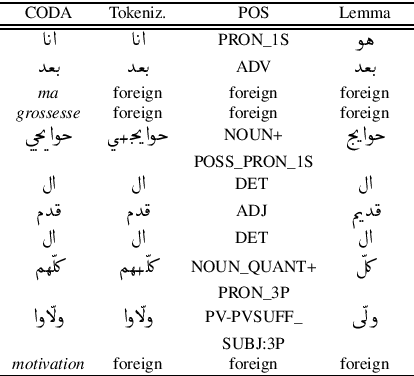
Abstract:This article describes the constitution process of the first morpho-syntactically annotated Tunisian Arabish Corpus (TArC). Arabish, also known as Arabizi, is a spontaneous coding of Arabic dialects in Latin characters and arithmographs (numbers used as letters). This code-system was developed by Arabic-speaking users of social media in order to facilitate the writing in the Computer-Mediated Communication (CMC) and text messaging informal frameworks. There is variety in the realization of Arabish amongst dialects, and each Arabish code-system is under-resourced, in the same way as most of the Arabic dialects. In the last few years, the focus on Arabic dialects in the NLP field has considerably increased. Taking this into consideration, TArC will be a useful support for different types of analyses, computational and linguistic, as well as for NLP tools training. In this article we will describe preliminary work on the TArC semi-automatic construction process and some of the first analyses we developed on TArC. In addition, in order to provide a complete overview of the challenges faced during the building process, we will present the main Tunisian dialect characteristics and their encoding in Tunisian Arabish.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge