Elie Shammas
The benefits of synthetic data for action categorization
Jan 20, 2020

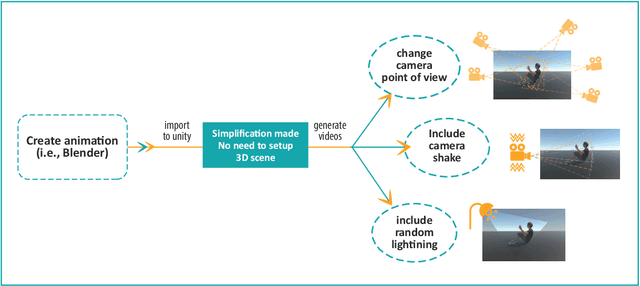
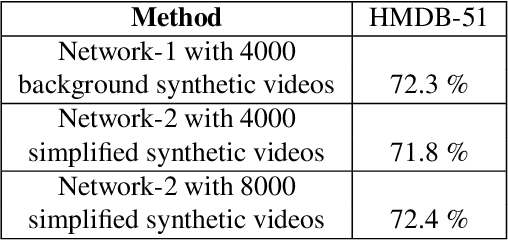
Abstract:In this paper, we study the value of using synthetically produced videos as training data for neural networks used for action categorization. Motivated by the fact that texture and background of a video play little to no significant roles in optical flow, we generated simplified texture-less and background-less videos and utilized the synthetic data to train a Temporal Segment Network (TSN). The results demonstrated that augmenting TSN with simplified synthetic data improved the original network accuracy (68.5%), achieving 71.8% on HMDB-51 when adding 4,000 videos and 72.4% when adding 8,000 videos. Also, training using simplified synthetic videos alone on 25 classes of UCF-101 achieved 30.71% when trained on 2500 videos and 52.7% when trained on 5000 videos. Finally, results showed that when reducing the number of real videos of UCF-25 to 10% and combining them with synthetic videos, the accuracy drops to only 85.41%, compared to a drop to 77.4% when no synthetic data is added.
Keyframe-based monocular SLAM: design, survey, and future directions
Jan 07, 2018
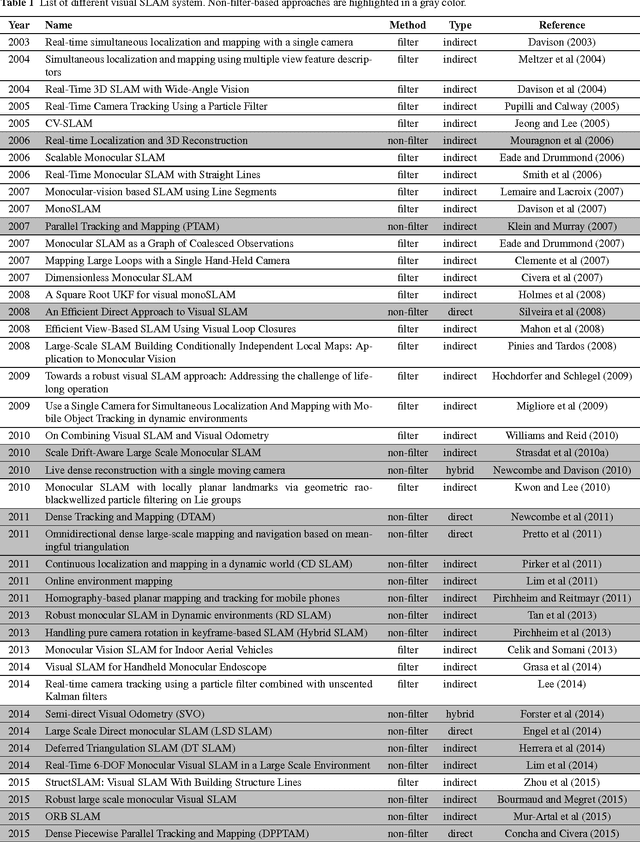

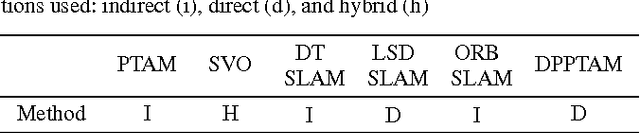
Abstract:Extensive research in the field of monocular SLAM for the past fifteen years has yielded workable systems that found their way into various applications in robotics and augmented reality. Although filter-based monocular SLAM systems were common at some time, the more efficient keyframe-based solutions are becoming the de facto methodology for building a monocular SLAM system. The objective of this paper is threefold: first, the paper serves as a guideline for people seeking to design their own monocular SLAM according to specific environmental constraints. Second, it presents a survey that covers the various keyframe-based monocular SLAM systems in the literature, detailing the components of their implementation, and critically assessing the specific strategies made in each proposed solution. Third, the paper provides insight into the direction of future research in this field, to address the major limitations still facing monocular SLAM; namely, in the issues of illumination changes, initialization, highly dynamic motion, poorly textured scenes, repetitive textures, map maintenance, and failure recovery.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge