Eleni Petraki
Machine Education: Designing semantically ordered and ontologically guided modular neural networks
Feb 07, 2020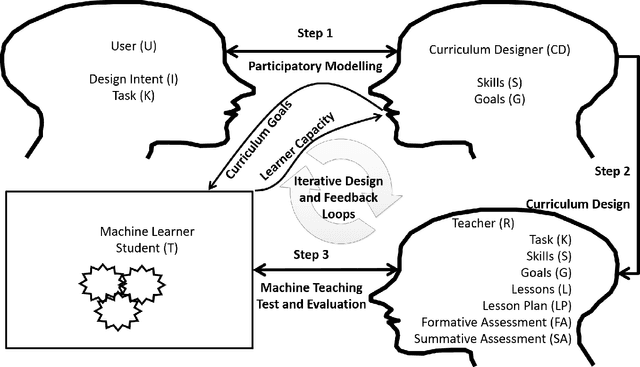
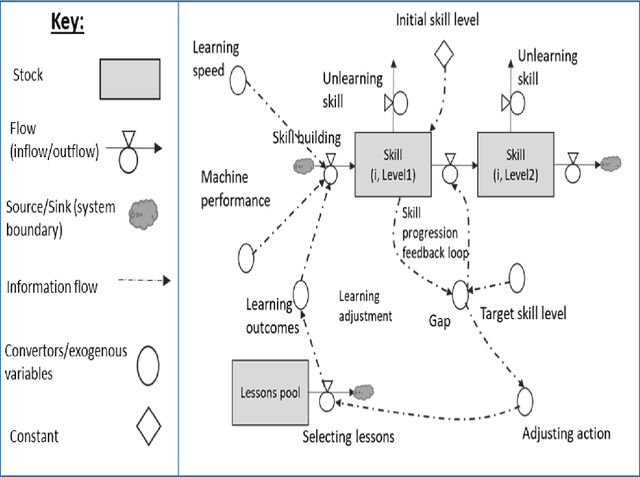
Abstract:The literature on machine teaching, machine education, and curriculum design for machines is in its infancy with sparse papers on the topic primarily focusing on data and model engineering factors to improve machine learning. In this paper, we first discuss selected attempts to date on machine teaching and education. We then bring theories and methodologies together from human education to structure and mathematically define the core problems in lesson design for machine education and the modelling approaches required to support the steps for machine education. Last, but not least, we offer an ontology-based methodology to guide the development of lesson plans to produce transparent and explainable modular learning machines, including neural networks.
Shaping Influence and Influencing Shaping: A Computational Red Teaming Trust-based Swarm Intelligence Model
Feb 26, 2018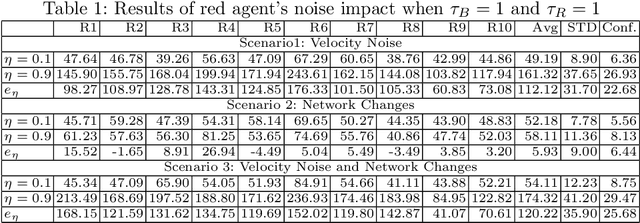
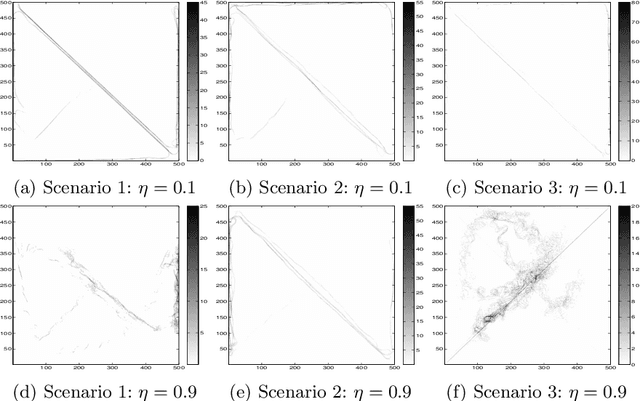
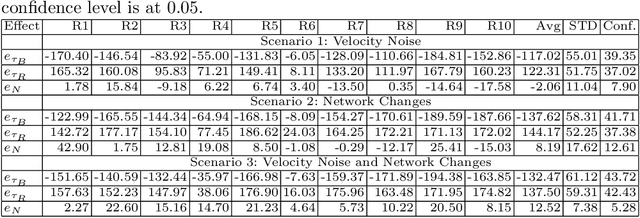
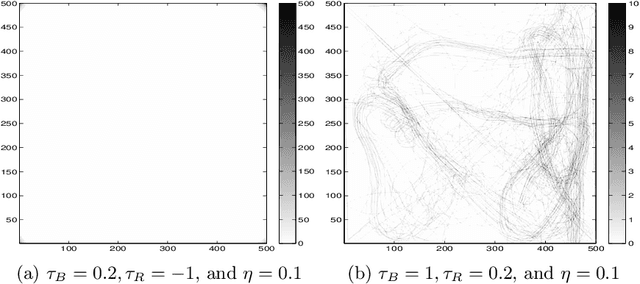
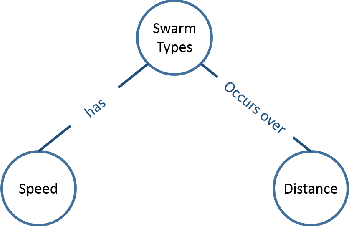
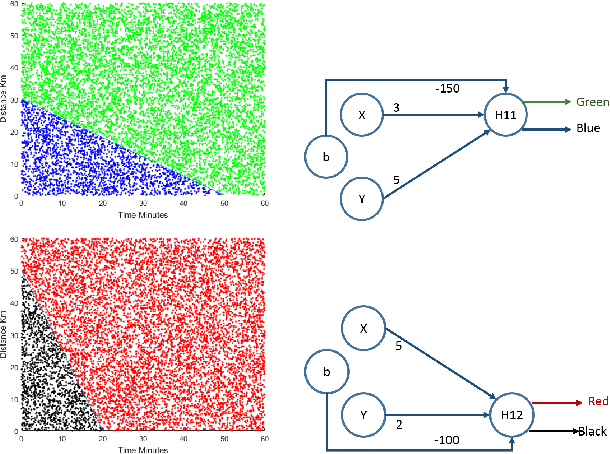
Abstract:Sociotechnical systems are complex systems, where nonlinear interaction among different players can obscure causal relationships. The absence of mechanisms to help us understand how to create a change in the system makes it hard to manage these systems. Influencing and shaping are social operators acting on sociotechnical systems to design a change. However, the two operators are usually discussed in an ad-hoc manner, without proper guiding models and metrics which assist in adopting these models successfully. Moreover, both social operators rely on accurate understanding of the concept of trust. Without such understanding, neither of these operators can create the required level to create a change in a desirable direction. In this paper, we define these concepts in a concise manner suitable for modelling the concepts and understanding their dynamics. We then introduce a model for influencing and shaping and use Computational Red Teaming principles to design and demonstrate how this model operates. We validate the results computationally through a simulation environment to show social influencing and shaping in an artificial society.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge