Elaine Wang
eRevise+RF: A Writing Evaluation System for Assessing Student Essay Revisions and Providing Formative Feedback
Jan 01, 2025Abstract:The ability to revise essays in response to feedback is important for students' writing success. An automated writing evaluation (AWE) system that supports students in revising their essays is thus essential. We present eRevise+RF, an enhanced AWE system for assessing student essay revisions (e.g., changes made to an essay to improve its quality in response to essay feedback) and providing revision feedback. We deployed the system with 6 teachers and 406 students across 3 schools in Pennsylvania and Louisiana. The results confirmed its effectiveness in (1) assessing student essays in terms of evidence usage, (2) extracting evidence and reasoning revisions across essays, and (3) determining revision success in responding to feedback. The evaluation also suggested eRevise+RF is a helpful system for young students to improve their argumentative writing skills through revision and formative feedback.
Predicting the Quality of Revisions in Argumentative Writing
Jun 01, 2023Abstract:The ability to revise in response to feedback is critical to students' writing success. In the case of argument writing in specific, identifying whether an argument revision (AR) is successful or not is a complex problem because AR quality is dependent on the overall content of an argument. For example, adding the same evidence sentence could strengthen or weaken existing claims in different argument contexts (ACs). To address this issue we developed Chain-of-Thought prompts to facilitate ChatGPT-generated ACs for AR quality predictions. The experiments on two corpora, our annotated elementary essays and existing college essays benchmark, demonstrate the superiority of the proposed ACs over baselines.
Annotation and Classification of Evidence and Reasoning Revisions in Argumentative Writing
Jul 14, 2021



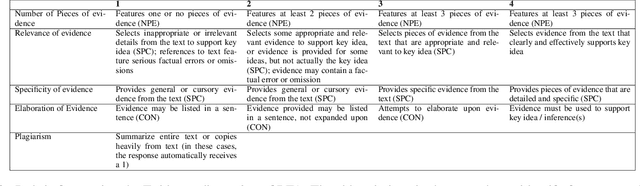
Abstract:Automated writing evaluation systems can improve students' writing insofar as students attend to the feedback provided and revise their essay drafts in ways aligned with such feedback. Existing research on revision of argumentative writing in such systems, however, has focused on the types of revisions students make (e.g., surface vs. content) rather than the extent to which revisions actually respond to the feedback provided and improve the essay. We introduce an annotation scheme to capture the nature of sentence-level revisions of evidence use and reasoning (the `RER' scheme) and apply it to 5th- and 6th-grade students' argumentative essays. We show that reliable manual annotation can be achieved and that revision annotations correlate with a holistic assessment of essay improvement in line with the feedback provided. Furthermore, we explore the feasibility of automatically classifying revisions according to our scheme.
eRevise: Using Natural Language Processing to Provide Formative Feedback on Text Evidence Usage in Student Writing
Aug 06, 2019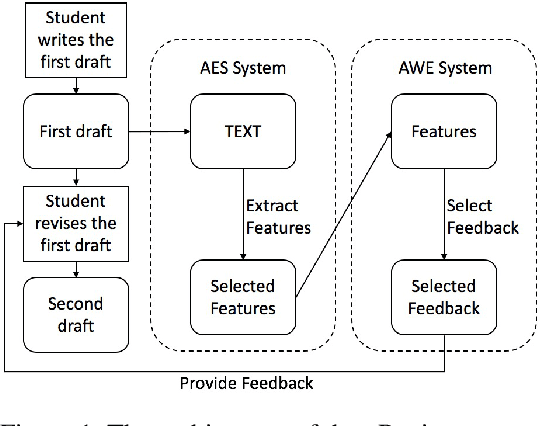

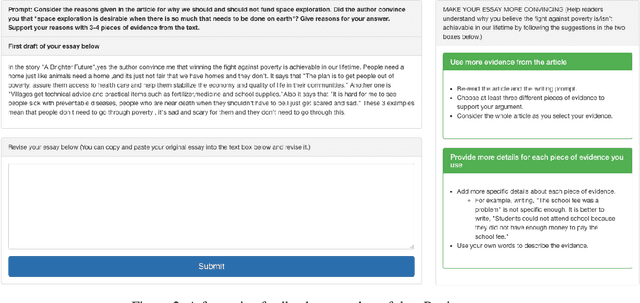
Abstract:Writing a good essay typically involves students revising an initial paper draft after receiving feedback. We present eRevise, a web-based writing and revising environment that uses natural language processing features generated for rubric-based essay scoring to trigger formative feedback messages regarding students' use of evidence in response-to-text writing. By helping students understand the criteria for using text evidence during writing, eRevise empowers students to better revise their paper drafts. In a pilot deployment of eRevise in 7 classrooms spanning grades 5 and 6, the quality of text evidence usage in writing improved after students received formative feedback then engaged in paper revision.
* Published in IAAI 19
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge