E. R. MacQuarrie
BATIS: Bootstrapping, Autonomous Testing, and Initialization System for Quantum Dot Devices
Dec 10, 2024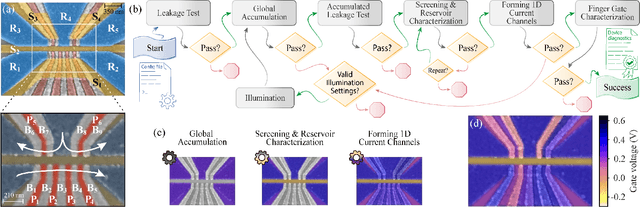
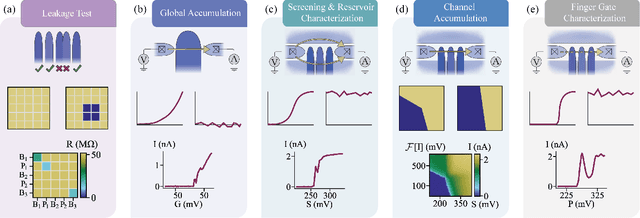
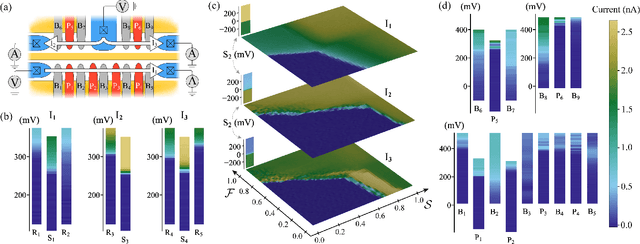
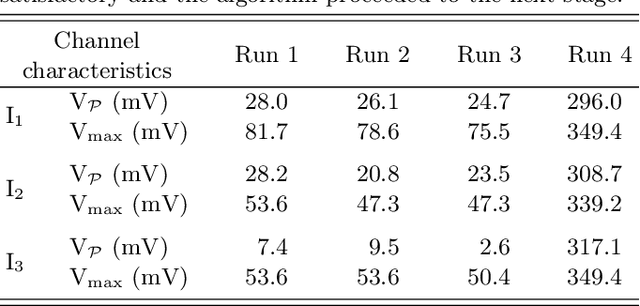
Abstract:Semiconductor quantum dot (QD) devices have become central to advancements in spin-based quantum computing. As the complexity of QD devices grows, manual tuning becomes increasingly infeasible, necessitating robust and scalable autotuning solutions. Tuning large arrays of QD qubits depends on efficient choices of automated protocols. Here, we introduce a bootstrapping, autonomous testing, and initialization system (BATIS), an automated framework designed to streamline QD device testing and initialization. BATIS navigates high-dimensional gate voltage spaces, automating essential steps such as leakage testing and gate characterization. The current channel formation protocol follows a novel and scalable approach that requires a single measurement regardless of the number of channels. Demonstrated at 1.3 K on a quad-QD Si/Si$_x$Ge$_{1-x}$ device, BATIS eliminates the need for deep cryogenic environments during initial device diagnostics, significantly enhancing scalability and reducing setup times. By requiring minimal prior knowledge of the device architecture, BATIS represents a platform-agnostic solution, adaptable to various QD systems, which bridges a critical gap in QD autotuning.
Ray-based framework for state identification in quantum dot devices
Feb 23, 2021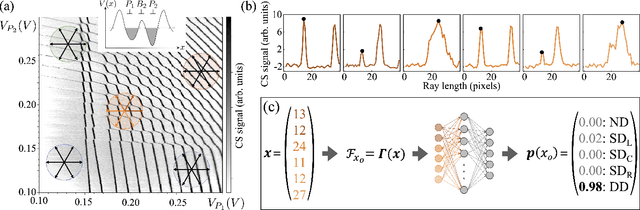
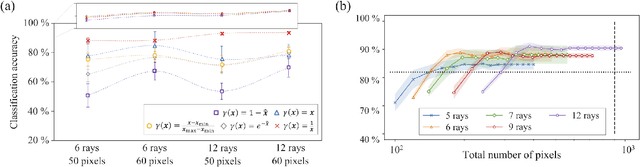
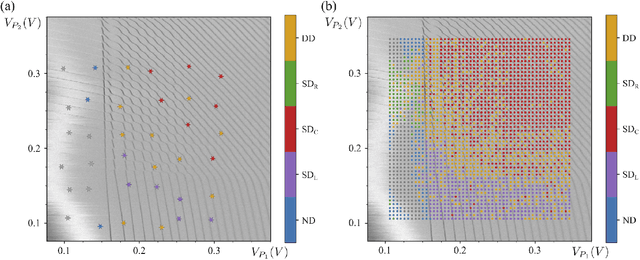
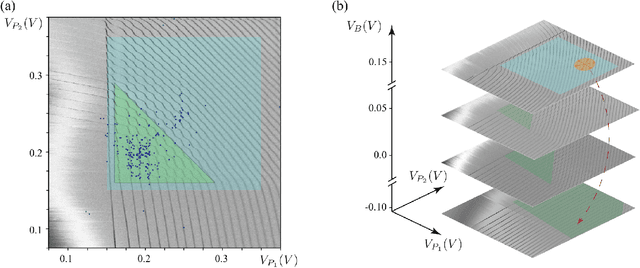
Abstract:Quantum dots (QDs) defined with electrostatic gates are a leading platform for a scalable quantum computing implementation. However, with increasing numbers of qubits, the complexity of the control parameter space also grows. Traditional measurement techniques, relying on complete or near-complete exploration via two-parameter scans (images) of the device response, quickly become impractical with increasing numbers of gates. Here, we propose to circumvent this challenge by introducing a measurement technique relying on one-dimensional projections of the device response in the multi-dimensional parameter space. Dubbed as the ray-based classification (RBC) framework, we use this machine learning (ML) approach to implement a classifier for QD states, enabling automated recognition of qubit-relevant parameter regimes. We show that RBC surpasses the 82 % accuracy benchmark from the experimental implementation of image-based classification techniques from prior work while cutting down the number of measurement points needed by up to 70 %. The reduction in measurement cost is a significant gain for time-intensive QD measurements and is a step forward towards the scalability of these devices. We also discuss how the RBC-based optimizer, which tunes the device to a multi-qubit regime, performs when tuning in the two- and three-dimensional parameter spaces defined by plunger and barrier gates that control the dots. This work provides experimental validation of both efficient state identification and optimization with ML techniques for non-traditional measurements in quantum systems with high-dimensional parameter spaces and time-intensive measurements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge