Douglas Thomson
Recurrent Auto-Encoders for Enhanced Deep Reinforcement Learning in Wilderness Search and Rescue Planning
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Wilderness search and rescue operations are often carried out over vast landscapes. The search efforts, however, must be undertaken in minimum time to maximize the chance of survival of the victim. Whilst the advent of cheap multicopters in recent years has changed the way search operations are handled, it has not solved the challenges of the massive areas at hand. The problem therefore is not one of complete coverage, but one of maximizing the information gathered in the limited time available. In this work we propose that a combination of a recurrent autoencoder and deep reinforcement learning is a more efficient solution to the search problem than previous pure deep reinforcement learning or optimisation approaches. The autoencoder training paradigm efficiently maximizes the information throughput of the encoder into its latent space representation which deep reinforcement learning is primed to leverage. Without the overhead of independently solving the problem that the recurrent autoencoder is designed for, it is more efficient in learning the control task. We further implement three additional architectures for a comprehensive comparison of the main proposed architecture. Similarly, we apply both soft actor-critic and proximal policy optimisation to provide an insight into the performance of both in a highly non-linear and complex application with a large observation Results show that the proposed architecture is vastly superior to the benchmarks, with soft actor-critic achieving the best performance. This model further outperformed work from the literature whilst having below a fifth of the total learnable parameters and training in a quarter of the time.
Predictive Probability Density Mapping for Search and Rescue Using An Agent-Based Approach with Sparse Data
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:Predicting the location where a lost person could be found is crucial for search and rescue operations with limited resources. To improve the precision and efficiency of these predictions, simulated agents can be created to emulate the behavior of the lost person. Within this study, we introduce an innovative agent-based model designed to replicate diverse psychological profiles of lost persons, allowing these agents to navigate real-world landscapes while making decisions autonomously without the need for location-specific training. The probability distribution map depicting the potential location of the lost person emerges through a combination of Monte Carlo simulations and mobility-time-based sampling. Validation of the model is achieved using real-world Search and Rescue data to train a Gaussian Process model. This allows generalization of the data to sample initial starting points for the agents during validation. Comparative analysis with historical data showcases promising outcomes relative to alternative methods. This work introduces a flexible agent that can be employed in search and rescue operations, offering adaptability across various geographical locations.
Design of a Health Monitoring System for a Planetary Exploration Rover
Jul 04, 2024



Abstract:It is generally considered that a trustworthy autonomous planetary exploration rover must be able to operate safely and effectively within its environment. Central to trustworthy operation is the ability for the rover to recognise and diagnose abnormal behaviours during its operation. Failure to diagnose faulty behaviour could lead to degraded performance or an unplanned halt in operation. This work investigates a health monitoring method that can be used to improve the capabilities of a fault detection system for a planetary exploration rover. A suite of four metrics, named 'rover vitals', are evaluated as indicators of degradation in the rover's performance. These vitals are combined to give an overall estimate of the rover's 'health'. By comparing the behaviour of a faulty real system with a non-faulty observer, residuals are generated in terms of two high-level metrics: heading and velocity. Adaptive thresholds are applied to the residuals to enable the detection of faulty behaviour, where the adaptive thresholds are informed by the rover's perceived health. Simulation experiments carried out in MATLAB showed that the proposed health monitoring and fault detection methodology can detect high-risk faults in both the sensors and actuators of the rover.
Deep Reinforcement Learning for Time-Critical Wilderness Search And Rescue Using Drones
May 22, 2024Abstract:Traditional search and rescue methods in wilderness areas can be time-consuming and have limited coverage. Drones offer a faster and more flexible solution, but optimizing their search paths is crucial. This paper explores the use of deep reinforcement learning to create efficient search missions for drones in wilderness environments. Our approach leverages a priori data about the search area and the missing person in the form of a probability distribution map. This allows the deep reinforcement learning agent to learn optimal flight paths that maximize the probability of finding the missing person quickly. Experimental results show that our method achieves a significant improvement in search times compared to traditional coverage planning and search planning algorithms. In one comparison, deep reinforcement learning is found to outperform other algorithms by over $160\%$, a difference that can mean life or death in real-world search operations. Additionally, unlike previous work, our approach incorporates a continuous action space enabled by cubature, allowing for more nuanced flight patterns.
A Novel Methodology for Autonomous Planetary Exploration Using Multi-Robot Teams
May 21, 2024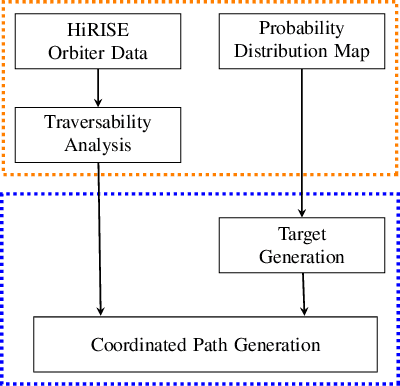



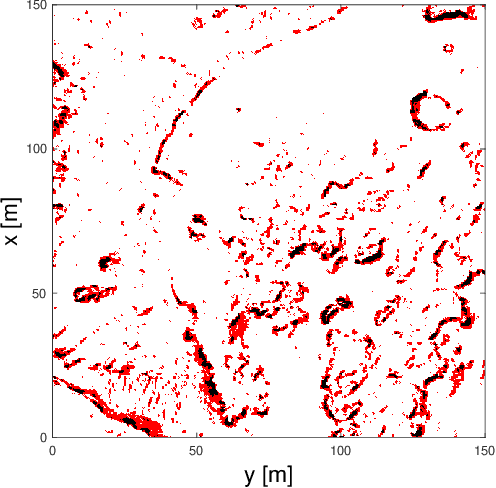
Abstract:One of the fundamental limiting factors in planetary exploration is the autonomous capabilities of planetary exploration rovers. This study proposes a novel methodology for trustworthy autonomous multi-robot teams which incorporates data from multiple sources (HiRISE orbiter imaging, probability distribution maps, and on-board rover sensors) to find efficient exploration routes in Jezero crater. A map is generated, consisting of a 3D terrain model, traversability analysis, and probability distribution map of points of scientific interest. A three-stage mission planner generates an efficient route, which maximises the accumulated probability of identifying points of interest. A 4D RRT* algorithm is used to determine smooth, flat paths, and prioritised planning is used to coordinate a safe set of paths. The above methodology is shown to coordinate safe and efficient rover paths, which ensure the rovers remain within their nominal pitch and roll limits throughout operation.
Enhancing Reinforcement Learning in Sensor Fusion: A Comparative Analysis of Cubature and Sampling-based Integration Methods for Rover Search Planning
May 15, 2024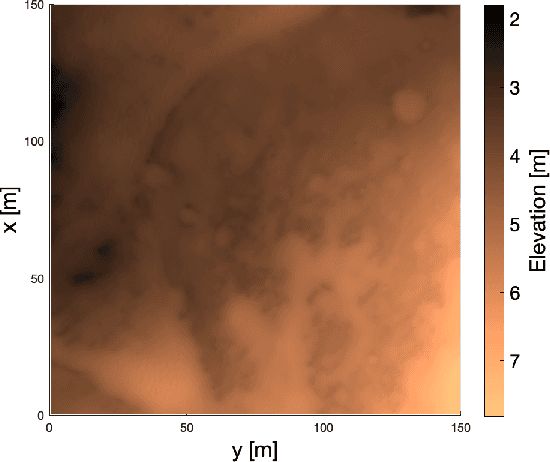
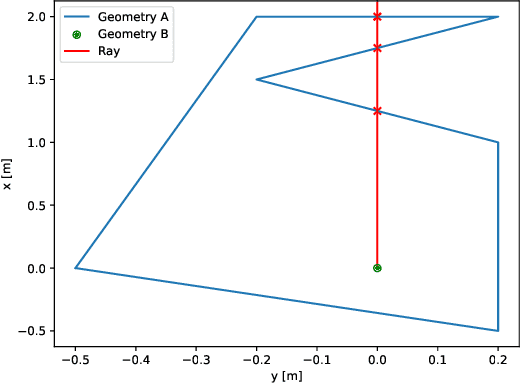
Abstract:This study investigates the computational speed and accuracy of two numerical integration methods, cubature and sampling-based, for integrating an integrand over a 2D polygon. Using a group of rovers searching the Martian surface with a limited sensor footprint as a test bed, the relative error and computational time are compared as the area was subdivided to improve accuracy in the sampling-based approach. The results show that the sampling-based approach exhibits a $14.75\%$ deviation in relative error compared to cubature when it matches the computational performance at $100\%$. Furthermore, achieving a relative error below $1\%$ necessitates a $10000\%$ increase in relative time to calculate due to the $\mathcal{O}(N^2)$ complexity of the sampling-based method. It is concluded that for enhancing reinforcement learning capabilities and other high iteration algorithms, the cubature method is preferred over the sampling-based method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge