Dongwook Chung
SoccerCPD: Formation and Role Change-Point Detection in Soccer Matches Using Spatiotemporal Tracking Data
Jun 22, 2022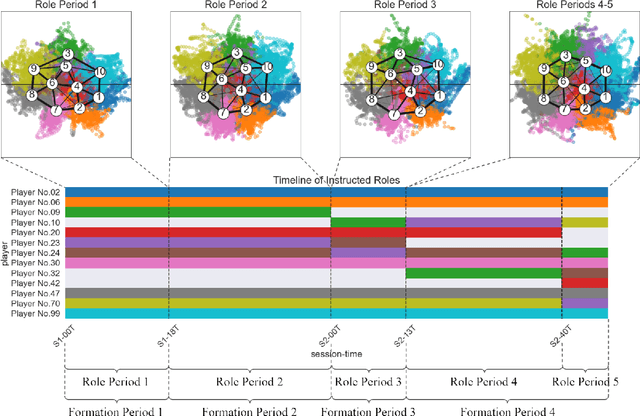
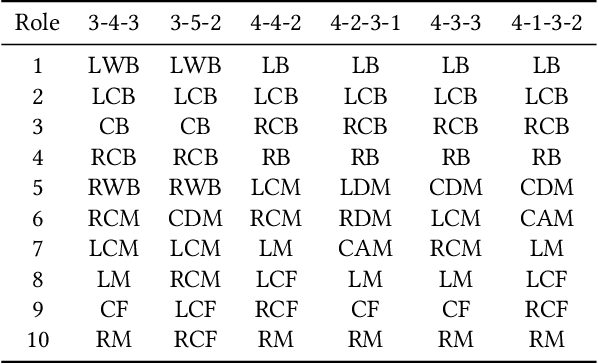
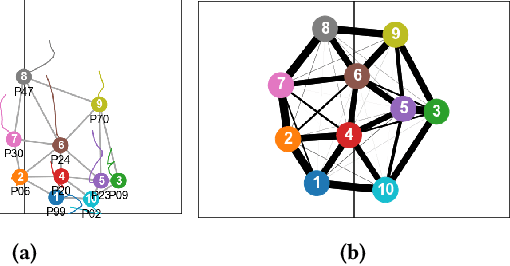
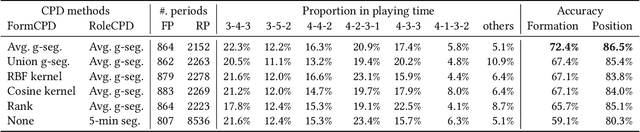
Abstract:In fluid team sports such as soccer and basketball, analyzing team formation is one of the most intuitive ways to understand tactics from domain participants' point of view. However, existing approaches either assume that team formation is consistent throughout a match or assign formations frame-by-frame, which disagree with real situations. To tackle this issue, we propose a change-point detection framework named SoccerCPD that distinguishes tactically intended formation and role changes from temporary changes in soccer matches. We first assign roles to players frame-by-frame and perform two-step change-point detections: (1) formation change-point detection based on the sequence of role-adjacency matrices and (2) role change-point detection based on the sequence of role permutations. The evaluation of SoccerCPD using the ground truth annotated by domain experts shows that our method accurately detects the points of tactical changes and estimates the formation and role assignment per segment. Lastly, we introduce practical use-cases that domain participants can easily interpret and utilize.
6MapNet: Representing soccer players from tracking data by a triplet network
Sep 10, 2021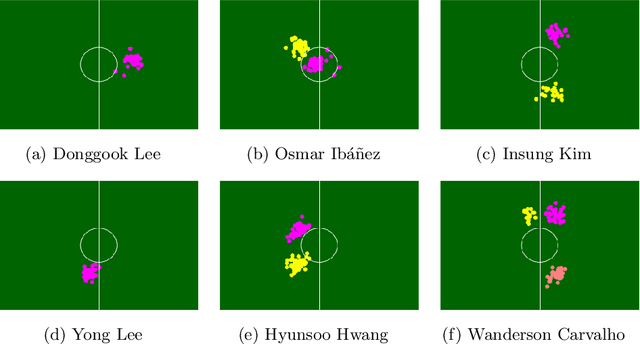
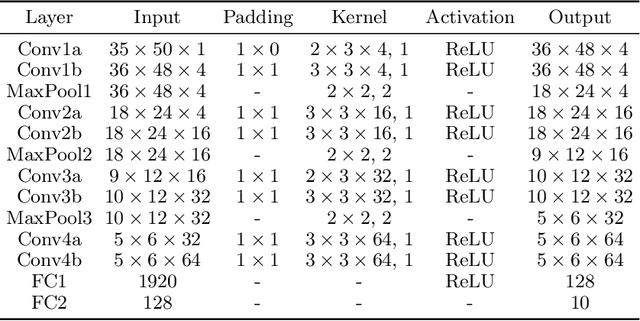
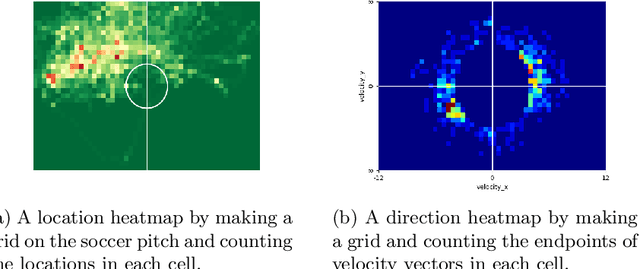
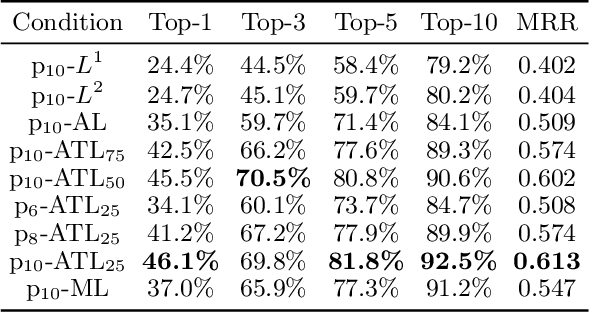
Abstract:Although the values of individual soccer players have become astronomical, subjective judgments still play a big part in the player analysis. Recently, there have been new attempts to quantitatively grasp players' styles using video-based event stream data. However, they have some limitations in scalability due to high annotation costs and sparsity of event stream data. In this paper, we build a triplet network named 6MapNet that can effectively capture the movement styles of players using in-game GPS data. Without any annotation of soccer-specific actions, we use players' locations and velocities to generate two types of heatmaps. Our subnetworks then map these heatmap pairs into feature vectors whose similarity corresponds to the actual similarity of playing styles. The experimental results show that players can be accurately identified with only a small number of matches by our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge