Dongjian Huo
WMFormer++: Nested Transformer for Visible Watermark Removal via Implict Joint Learning
Aug 22, 2023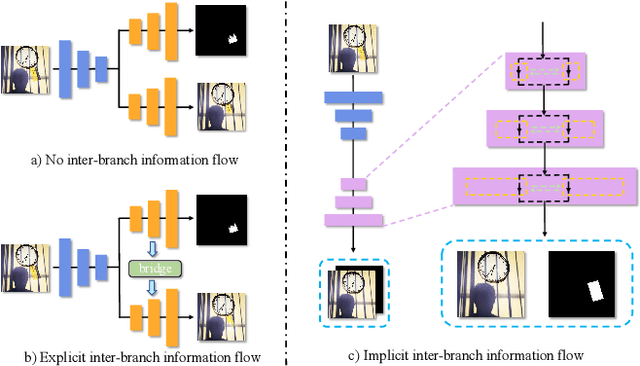
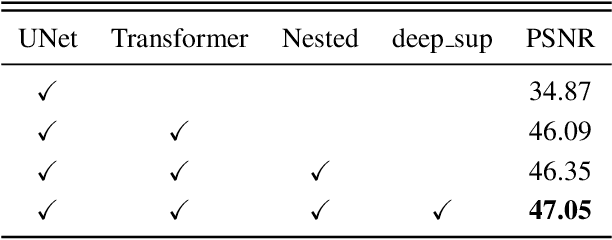
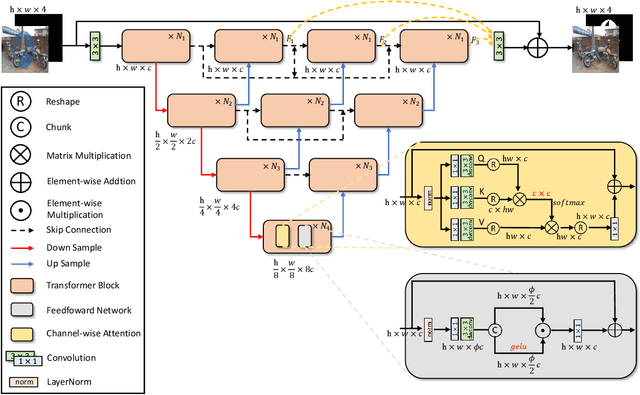
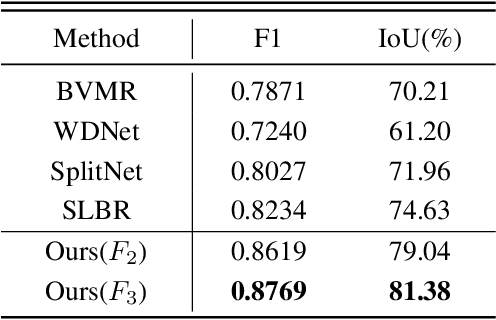
Abstract:Watermarking serves as a widely adopted approach to safeguard media copyright. In parallel, the research focus has extended to watermark removal techniques, offering an adversarial means to enhance watermark robustness and foster advancements in the watermarking field. Existing watermark removal methods mainly rely on UNet with task-specific decoder branches--one for watermark localization and the other for background image restoration. However, watermark localization and background restoration are not isolated tasks; precise watermark localization inherently implies regions necessitating restoration, and the background restoration process contributes to more accurate watermark localization. To holistically integrate information from both branches, we introduce an implicit joint learning paradigm. This empowers the network to autonomously navigate the flow of information between implicit branches through a gate mechanism. Furthermore, we employ cross-channel attention to facilitate local detail restoration and holistic structural comprehension, while harnessing nested structures to integrate multi-scale information. Extensive experiments are conducted on various challenging benchmarks to validate the effectiveness of our proposed method. The results demonstrate our approach's remarkable superiority, surpassing existing state-of-the-art methods by a large margin.
Dual Progressive Transformations for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Sep 30, 2022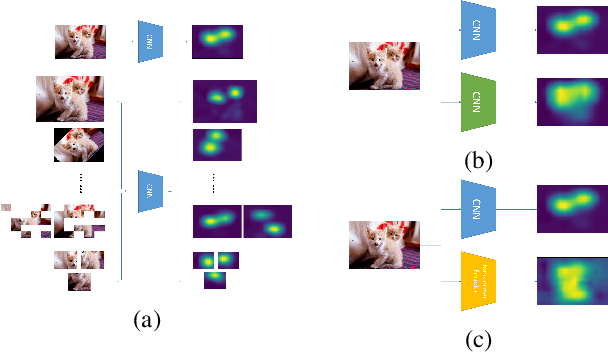
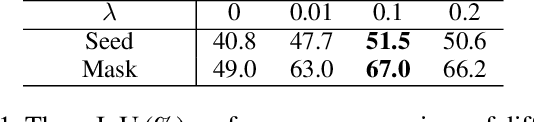

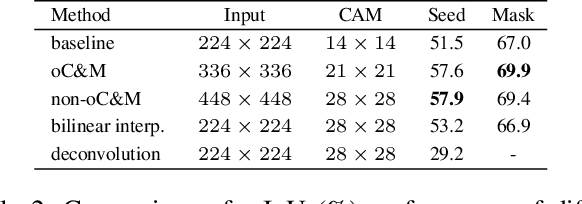
Abstract:Weakly supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS), which aims to mine the object regions by merely using class-level labels, is a challenging task in computer vision. The current state-of-the-art CNN-based methods usually adopt Class-Activation-Maps (CAMs) to highlight the potential areas of the object, however, they may suffer from the part-activated issues. To this end, we try an early attempt to explore the global feature attention mechanism of vision transformer in WSSS task. However, since the transformer lacks the inductive bias as in CNN models, it can not boost the performance directly and may yield the over-activated problems. To tackle these drawbacks, we propose a Convolutional Neural Networks Refined Transformer (CRT) to mine a globally complete and locally accurate class activation maps in this paper. To validate the effectiveness of our proposed method, extensive experiments are conducted on PASCAL VOC 2012 and CUB-200-2011 datasets. Experimental evaluations show that our proposed CRT achieves the new state-of-the-art performance on both the weakly supervised semantic segmentation task the weakly supervised object localization task, which outperform others by a large margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge