Domenico G. Sorrenti
A Termination Criterion for Probabilistic PointClouds Registration
Oct 10, 2020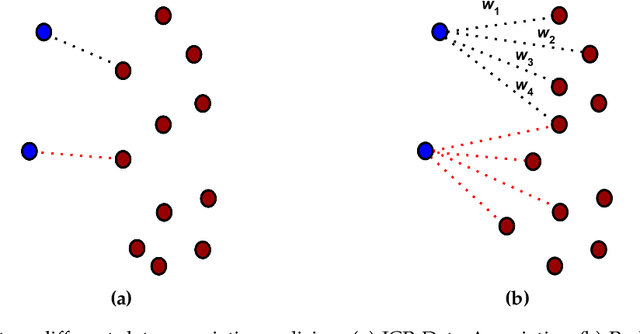
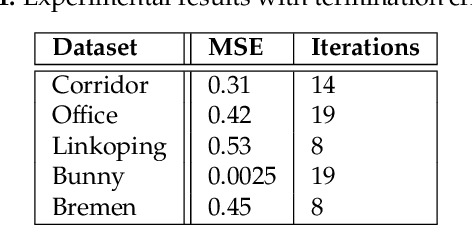

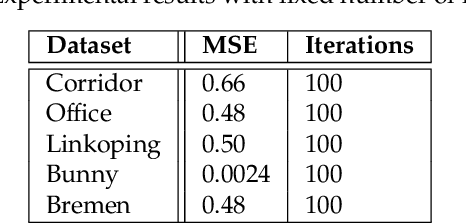
Abstract:Probabilistic Point Clouds Registration (PPCR) is an algorithm that, in its multi-iteration version, outperformed state of the art algorithms for local point clouds registration. However, its performances have been tested using a fixed high number of iterations. To be of practical usefulness, we think that the algorithm should decide by itself when to stop, to avoid an excessive number of iterations and, therefore, wasting computational time. With this work, we compare different termination criterion on several datasets and prove that the chosen one produce very good results that are comparable to those obtained using a very high number of iterations while saving computational time.
A dataset for benchmarking vision-based localization at intersections
Nov 04, 2018



Abstract:In this report we present the work performed in order to build a dataset for benchmarking vision-based localization at intersections, i.e., a set of stereo video sequences taken from a road vehicle that is approaching an intersection, altogether with a reliable measure of the observer position. This report is meant to complement our paper "Vision-Based Localization at Intersections using Digital Maps" submitted to ICRA2019. It complements the paper because the paper uses the dataset, but it had no space for describing the work done to obtain it. Moreover, the dataset is of interest for all those tackling the task of online localization at intersections for road vehicles, e.g., for a quantitative comparison with the proposal in our submitted paper, and it is therefore appropriate to put the dataset description in a separate report. We considered all datasets from road vehicles that we could find as for the end of August 2018. After our evaluation, we kept only sub-sequences from the KITTI dataset. In the future we will increase the collection of sequences with data from our vehicle.
ira_laser_tools: a ROS LaserScan manipulation toolbox
Nov 04, 2014
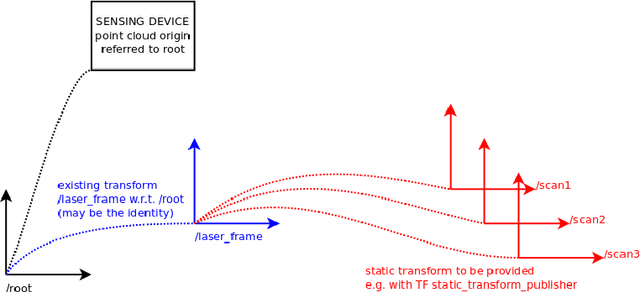

Abstract:Laser scanners are sensors of widespread use in robotic applications. Under the Robot Operating System (ROS) the information generated by laser scanners can be conveyed by either LaserScan messages or in the form of PointClouds. Many publicly available algorithms (mapping, localization, navigation, etc.) rely on LaserScan messages, yet a tool for handling multiple lasers, merging their measurements, or to generate generic LaserScan messages from PointClouds, is not available. This report describes two tools, in the form of ROS nodes, which we release as open source under the BSD license, which allow to either merge multiple single-plane laser scans or to generate virtual laser scans from a point cloud. A short tutorial, along with the main advantages and limitations of these tools are presented.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge