Dingxi Yang
Radio Map-Based Spectrum Sharing for Joint Communication and Sensing
Jan 04, 2024



Abstract:The sixth-generation (6G) network is expected to provide both communication and sensing (C&S) services. However, spectrum scarcity poses a major challenge to the harmonious coexistence of C&S systems. Without effective cooperation, the interference resulting from spectrum sharing impairs the performance of both systems. This paper addresses C&S interference within a distributed network. Different from traditional schemes that require pilot-based high-frequency interactions between C&S systems, we introduce a third party named the radio map to provide the large-scale channel state information (CSI). With large-scale CSI, we optimize the transmit power of C&S systems to maximize the signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) for the radar detection, while meeting the ergodic rate requirement of the interfered user. Given the non-convexity of both the objective and constraint, we employ the techniques of auxiliary-function-based scaling and fraction programming for simplification. Subsequently, we propose an iterative algorithm to solve this problem. Simulation results collaborate our idea that the extrinsic information, i.e., positions and surroundings, is effective to decouple C&S interference.
An End-Cloud Computing Enabled Surveillance Video Transmission System
Nov 08, 2023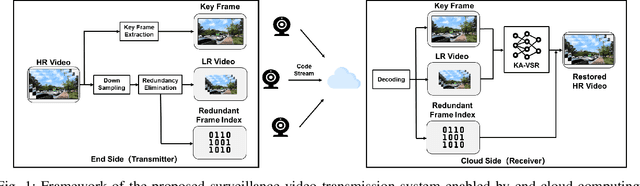
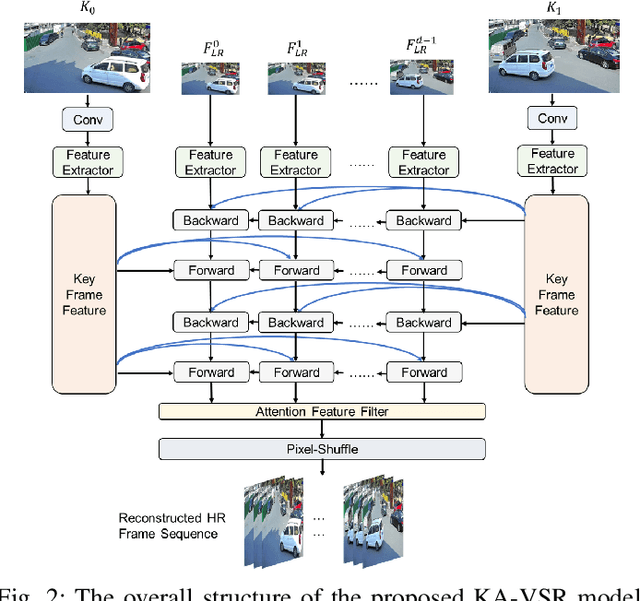
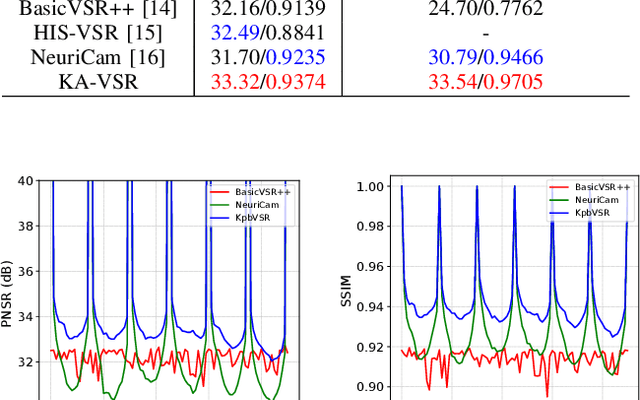
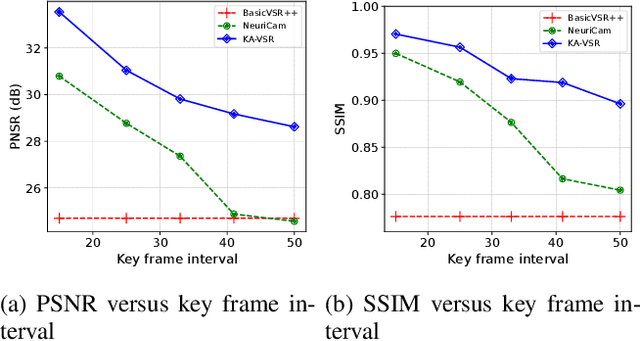
Abstract:The enormous data volume of video poses a significant burden on the network. Particularly, transferring high-definition surveillance videos to the cloud consumes a significant amount of spectrum resources. To address these issues, we propose a surveillance video transmission system enabled by end-cloud computing. Specifically, the cameras actively down-sample the original video and then a redundant frame elimination module is employed to further reduce the data volume of surveillance videos. Then we develop a key-frame assisted video super-resolution model to reconstruct the high-quality video at the cloud side. Moreover, we propose a strategy of extracting key frames from source videos for better reconstruction performance by utilizing the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) of adjacent frames to measure the propagation distance of key frame information. Simulation results show that the developed system can effectively reduce the data volume by the end-cloud collaboration and outperforms existing video super-resolution models significantly in terms of PSNR and structural similarity index (SSIM).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge