Diego Olaya
To do or not to do: cost-sensitive causal decision-making
Jan 05, 2021
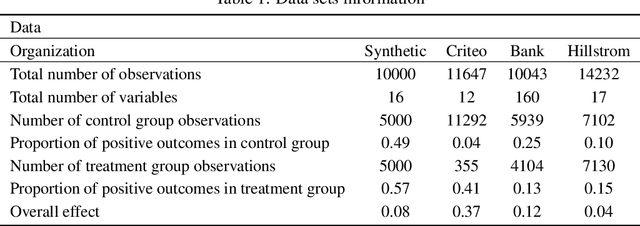

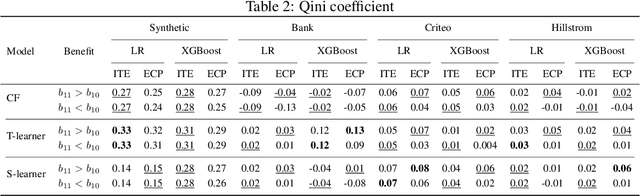
Abstract:Causal classification models are adopted across a variety of operational business processes to predict the effect of a treatment on a categorical business outcome of interest depending on the process instance characteristics. This allows optimizing operational decision-making and selecting the optimal treatment to apply in each specific instance, with the aim of maximizing the positive outcome rate. While various powerful approaches have been presented in the literature for learning causal classification models, no formal framework has been elaborated for optimal decision-making based on the estimated individual treatment effects, given the cost of the various treatments and the benefit of the potential outcomes. In this article, we therefore extend upon the expected value framework and formally introduce a cost-sensitive decision boundary for double binary causal classification, which is a linear function of the estimated individual treatment effect, the positive outcome probability and the cost and benefit parameters of the problem setting. The boundary allows causally classifying instances in the positive and negative treatment class to maximize the expected causal profit, which is introduced as the objective at hand in cost-sensitive causal classification. We introduce the expected causal profit ranker which ranks instances for maximizing the expected causal profit at each possible threshold for causally classifying instances and differs from the conventional ranking approach based on the individual treatment effect. The proposed ranking approach is experimentally evaluated on synthetic and marketing campaign data sets. The results indicate that the presented ranking method effectively outperforms the cost-insensitive ranking approach and allows boosting profitability.
The foundations of cost-sensitive causal classification
Aug 19, 2020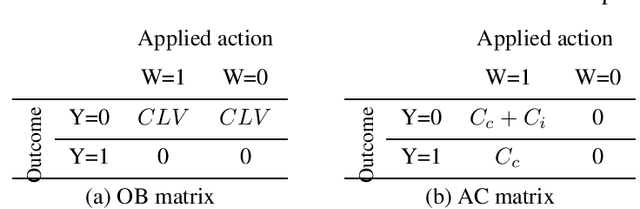
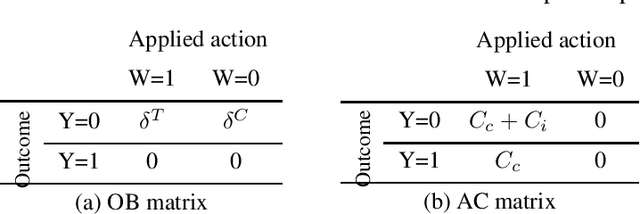
Abstract:Classification is a well-studied machine learning task which concerns the assignment of instances to a set of outcomes. Classification models support the optimization of managerial decision-making across a variety of operational business processes. For instance, customer churn prediction models are adopted to increase the efficiency of retention campaigns by optimizing the selection of customers that are to be targeted. Cost-sensitive and causal classification methods have independently been proposed to improve the performance of classification models. The former considers the benefits and costs of correct and incorrect classifications, such as the benefit of a retained customer, whereas the latter estimates the causal effect of an action, such as a retention campaign, on the outcome of interest. This study integrates cost-sensitive and causal classification by elaborating a unifying evaluation framework. The framework encompasses a range of existing and novel performance measures for evaluating both causal and conventional classification models in a cost-sensitive as well as a cost-insensitive manner. We proof that conventional classification is a specific case of causal classification in terms of a range of performance measures when the number of actions is equal to one. The framework is shown to instantiate to application-specific cost-sensitive performance measures that have been recently proposed for evaluating customer retention and response uplift models, and allows to maximize profitability when adopting a causal classification model for optimizing decision-making. The proposed framework paves the way toward the development of cost-sensitive causal learning methods and opens a range of opportunities for improving data-driven business decision-making.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge