Diego Garat
Towards De-identification of Legal Texts
Oct 09, 2019



Abstract:In many countries, personal information that can be published or shared between organizations is regulated and, therefore, documents must undergo a process of de-identification to eliminate or obfuscate confidential data. Our work focuses on the de-identification of legal texts, where the goal is to hide the names of the actors involved in a lawsuit without losing the sense of the story. We present a first evaluation on our corpus of NLP tools in tasks such as segmentation, tokenization and recognition of named entities, and we analyze several evaluation measures for our de-identification task. Results are meager: 84% of the documents have at least one name not covered by NER tools, something that might lead to the re-identification of involved names. We conclude that tools must be strongly adapted for processing texts of this particular domain.
A Crowd-Annotated Spanish Corpus for Humor Analysis
Jul 19, 2018
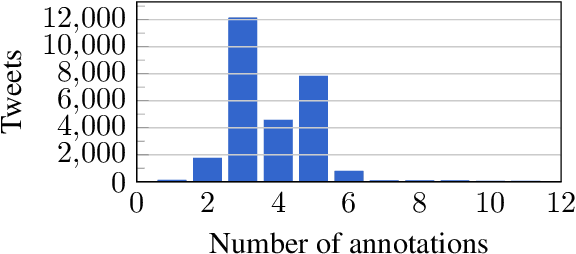
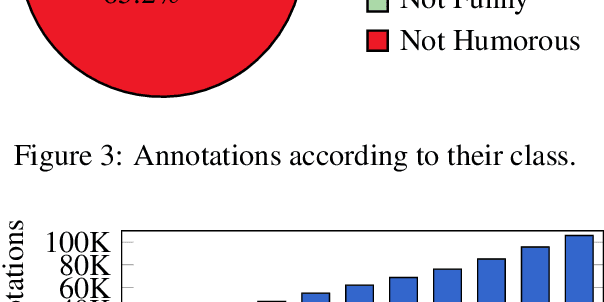
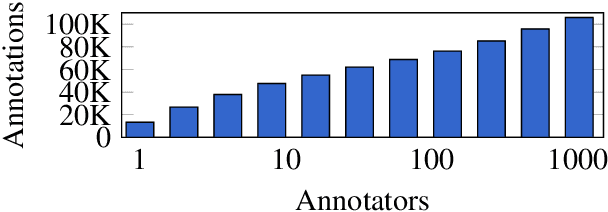
Abstract:Computational Humor involves several tasks, such as humor recognition, humor generation, and humor scoring, for which it is useful to have human-curated data. In this work we present a corpus of 27,000 tweets written in Spanish and crowd-annotated by their humor value and funniness score, with about four annotations per tweet, tagged by 1,300 people over the Internet. It is equally divided between tweets coming from humorous and non-humorous accounts. The inter-annotator agreement Krippendorff's alpha value is 0.5710. The dataset is available for general use and can serve as a basis for humor detection and as a first step to tackle subjectivity.
Is This a Joke? Detecting Humor in Spanish Tweets
Mar 28, 2017



Abstract:While humor has been historically studied from a psychological, cognitive and linguistic standpoint, its study from a computational perspective is an area yet to be explored in Computational Linguistics. There exist some previous works, but a characterization of humor that allows its automatic recognition and generation is far from being specified. In this work we build a crowdsourced corpus of labeled tweets, annotated according to its humor value, letting the annotators subjectively decide which are humorous. A humor classifier for Spanish tweets is assembled based on supervised learning, reaching a precision of 84% and a recall of 69%.
* Preprint version, without referral
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge