Diego Carrera
MuRAL-CPD: Active Learning for Multiresolution Change Point Detection
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Change Point Detection (CPD) is a critical task in time series analysis, aiming to identify moments when the underlying data-generating process shifts. Traditional CPD methods often rely on unsupervised techniques, which lack adaptability to task-specific definitions of change and cannot benefit from user knowledge. To address these limitations, we propose MuRAL-CPD, a novel semi-supervised method that integrates active learning into a multiresolution CPD algorithm. MuRAL-CPD leverages a wavelet-based multiresolution decomposition to detect changes across multiple temporal scales and incorporates user feedback to iteratively optimize key hyperparameters. This interaction enables the model to align its notion of change with that of the user, improving both accuracy and interpretability. Our experimental results on several real-world datasets show the effectiveness of MuRAL-CPD against state-of-the-art methods, particularly in scenarios where minimal supervision is available.
Composite Layers for Deep Anomaly Detection on 3D Point Clouds
Sep 23, 2022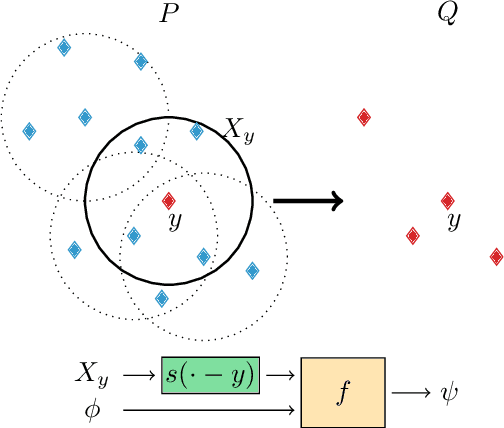
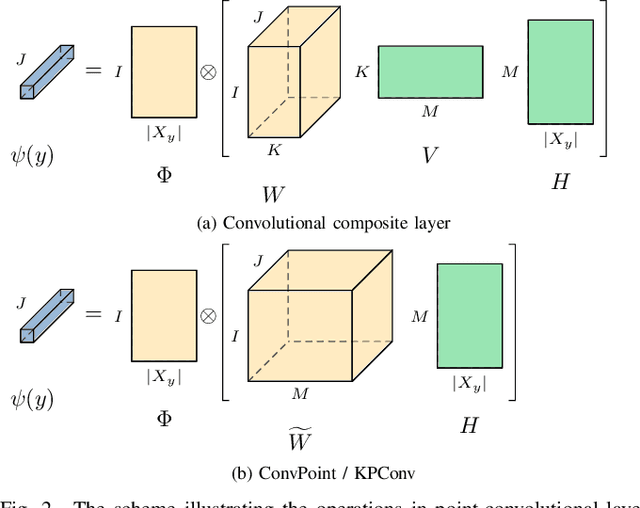
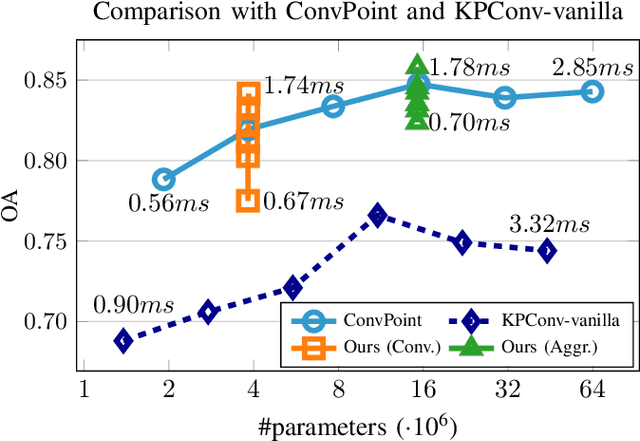
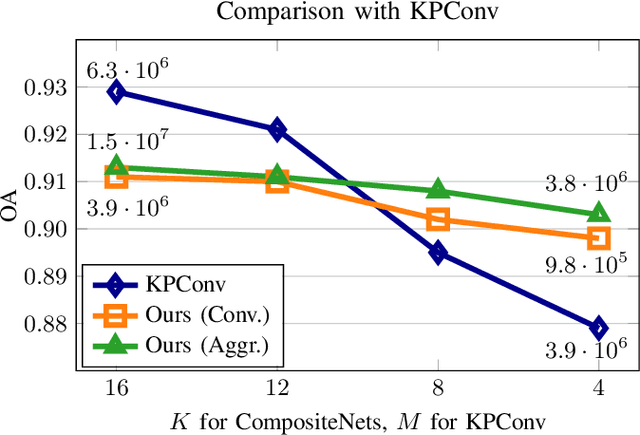
Abstract:Deep neural networks require specific layers to process point clouds, as the scattered and irregular location of points prevents us from using convolutional filters. Here we introduce the composite layer, a new convolutional operator for point clouds. The peculiarity of our composite layer is that it extracts and compresses the spatial information from the position of points before combining it with their feature vectors. Compared to well-known point-convolutional layers such as those of ConvPoint and KPConv, our composite layer provides additional regularization and guarantees greater flexibility in terms of design and number of parameters. To demonstrate the design flexibility, we also define an aggregate composite layer that combines spatial information and features in a nonlinear manner, and we use these layers to implement a convolutional and an aggregate CompositeNet. We train our CompositeNets to perform classification and, most remarkably, unsupervised anomaly detection. Our experiments on synthetic and real-world datasets show that, in both tasks, our CompositeNets outperform ConvPoint and achieve similar results as KPConv despite having a much simpler architecture. Moreover, our CompositeNets substantially outperform existing solutions for anomaly detection on point clouds.
Deep Open-Set Recognition for Silicon Wafer Production Monitoring
Aug 30, 2022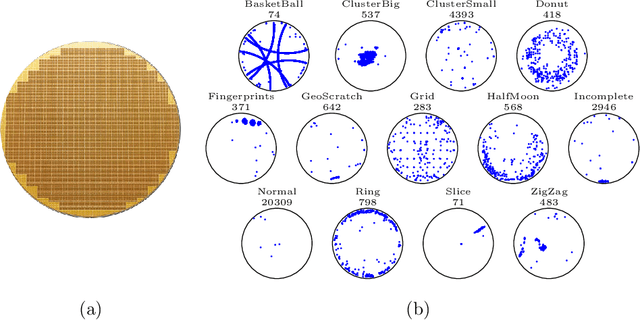
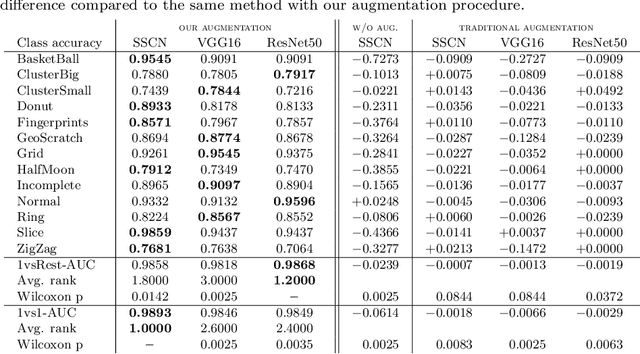
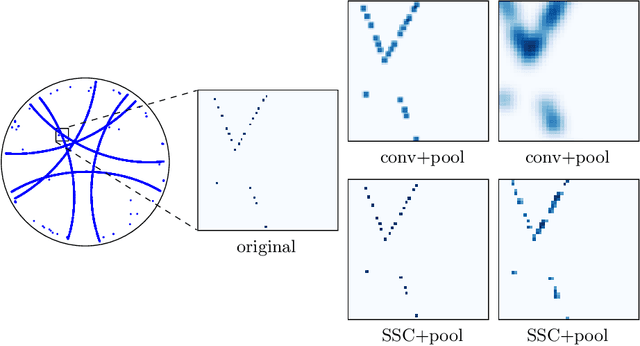
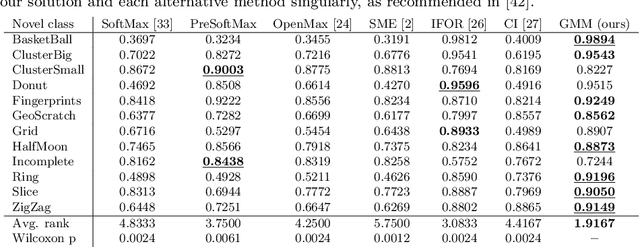
Abstract:The chips contained in any electronic device are manufactured over circular silicon wafers, which are monitored by inspection machines at different production stages. Inspection machines detect and locate any defect within the wafer and return a Wafer Defect Map (WDM), i.e., a list of the coordinates where defects lie, which can be considered a huge, sparse, and binary image. In normal conditions, wafers exhibit a small number of randomly distributed defects, while defects grouped in specific patterns might indicate known or novel categories of failures in the production line. Needless to say, a primary concern of semiconductor industries is to identify these patterns and intervene as soon as possible to restore normal production conditions. Here we address WDM monitoring as an open-set recognition problem to accurately classify WDM in known categories and promptly detect novel patterns. In particular, we propose a comprehensive pipeline for wafer monitoring based on a Submanifold Sparse Convolutional Network, a deep architecture designed to process sparse data at an arbitrary resolution, which is trained on the known classes. To detect novelties, we define an outlier detector based on a Gaussian Mixture Model fitted on the latent representation of the classifier. Our experiments on a real dataset of WDMs show that directly processing full-resolution WDMs by Submanifold Sparse Convolutions yields superior classification performance on known classes than traditional Convolutional Neural Networks, which require a preliminary binning to reduce the size of the binary images representing WDMs. Moreover, our solution outperforms state-of-the-art open-set recognition solutions in detecting novelties.
Nonparametric and Online Change Detection in Multivariate Datastreams using QuantTree
Aug 30, 2022
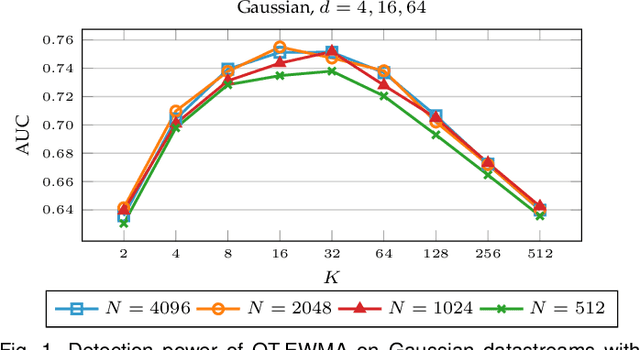

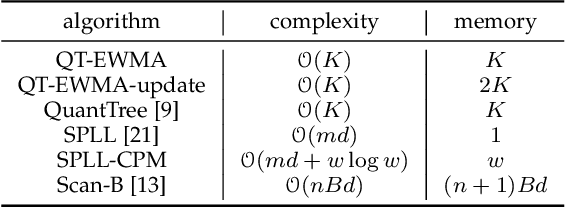
Abstract:We address the problem of online change detection in multivariate datastreams, and we introduce QuantTree Exponentially Weighted Moving Average (QT-EWMA), a nonparametric change-detection algorithm that can control the expected time before a false alarm, yielding a desired Average Run Length (ARL$_0$). Controlling false alarms is crucial in many applications and is rarely guaranteed by online change-detection algorithms that can monitor multivariate datastreams without knowing the data distribution. Like many change-detection algorithms, QT-EWMA builds a model of the data distribution, in our case a QuantTree histogram, from a stationary training set. To monitor datastreams even when the training set is extremely small, we propose QT-EWMA-update, which incrementally updates the QuantTree histogram during monitoring, always keeping the ARL$_0$ under control. Our experiments, performed on synthetic and real-world datastreams, demonstrate that QT-EWMA and QT-EWMA-update control the ARL$_0$ and the false alarm rate better than state-of-the-art methods operating in similar conditions, achieving lower or comparable detection delays.
Change Detection in Multivariate Datastreams: Likelihood and Detectability Loss
Apr 27, 2016

Abstract:We address the problem of detecting changes in multivariate datastreams, and we investigate the intrinsic difficulty that change-detection methods have to face when the data dimension scales. In particular, we consider a general approach where changes are detected by comparing the distribution of the log-likelihood of the datastream over different time windows. Despite the fact that this approach constitutes the frame of several change-detection methods, its effectiveness when data dimension scales has never been investigated, which is indeed the goal of our paper. We show that the magnitude of the change can be naturally measured by the symmetric Kullback-Leibler divergence between the pre- and post-change distributions, and that the detectability of a change of a given magnitude worsens when the data dimension increases. This problem, which we refer to as \emph{detectability loss}, is due to the linear relationship between the variance of the log-likelihood and the data dimension. We analytically derive the detectability loss on Gaussian-distributed datastreams, and empirically demonstrate that this problem holds also on real-world datasets and that can be harmful even at low data-dimensions (say, 10).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge