Dick Epema
SFDDM: Single-fold Distillation for Diffusion models
May 23, 2024Abstract:While diffusion models effectively generate remarkable synthetic images, a key limitation is the inference inefficiency, requiring numerous sampling steps. To accelerate inference and maintain high-quality synthesis, teacher-student distillation is applied to compress the diffusion models in a progressive and binary manner by retraining, e.g., reducing the 1024-step model to a 128-step model in 3 folds. In this paper, we propose a single-fold distillation algorithm, SFDDM, which can flexibly compress the teacher diffusion model into a student model of any desired step, based on reparameterization of the intermediate inputs from the teacher model. To train the student diffusion, we minimize not only the output distance but also the distribution of the hidden variables between the teacher and student model. Extensive experiments on four datasets demonstrate that our student model trained by the proposed SFDDM is able to sample high-quality data with steps reduced to as little as approximately 1%, thus, trading off inference time. Our remarkable performance highlights that SFDDM effectively transfers knowledge in single-fold distillation, achieving semantic consistency and meaningful image interpolation.
Active Learning for Noisy Data Streams Using Weak and Strong Labelers
Oct 27, 2020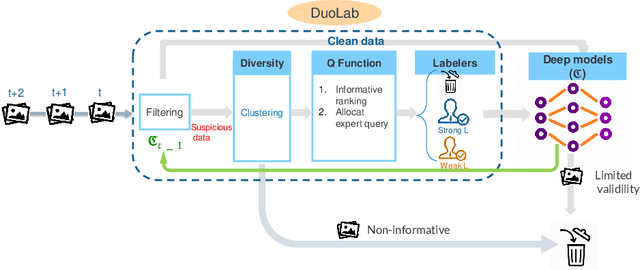
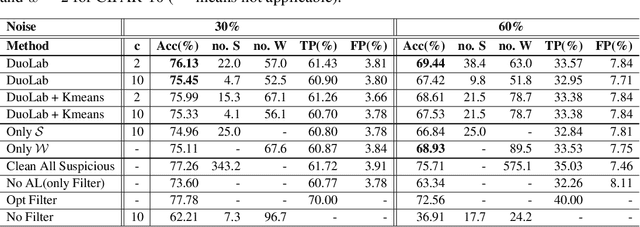
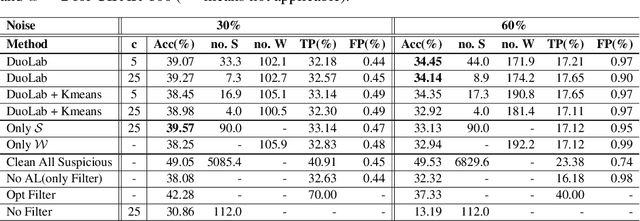
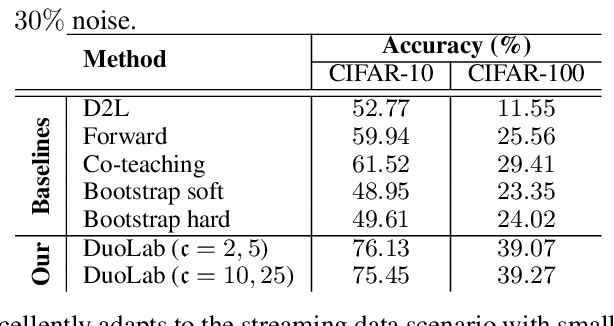
Abstract:Labeling data correctly is an expensive and challenging task in machine learning, especially for on-line data streams. Deep learning models especially require a large number of clean labeled data that is very difficult to acquire in real-world problems. Choosing useful data samples to label while minimizing the cost of labeling is crucial to maintain efficiency in the training process. When confronted with multiple labelers with different expertise and respective labeling costs, deciding which labeler to choose is nontrivial. In this paper, we consider a novel weak and strong labeler problem inspired by humans natural ability for labeling, in the presence of data streams with noisy labels and constrained by a limited budget. We propose an on-line active learning algorithm that consists of four steps: filtering, adding diversity, informative sample selection, and labeler selection. We aim to filter out the suspicious noisy samples and spend the budget on the diverse informative data using strong and weak labelers in a cost-effective manner. We derive a decision function that measures the information gain by combining the informativeness of individual samples and model confidence. We evaluate our proposed algorithm on the well-known image classification datasets CIFAR10 and CIFAR100 with up to 60% noise. Experiments show that by intelligently deciding which labeler to query, our algorithm maintains the same accuracy compared to the case of having only one of the labelers available while spending less of the budget.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge