Dharmendra Modha
Structured Convolution Matrices for Energy-efficient Deep learning
Jun 08, 2016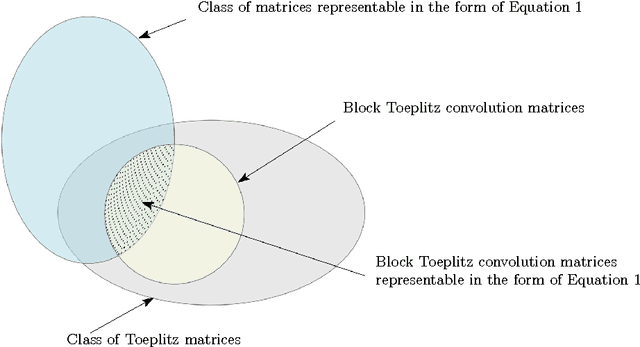
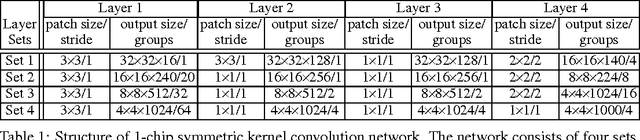
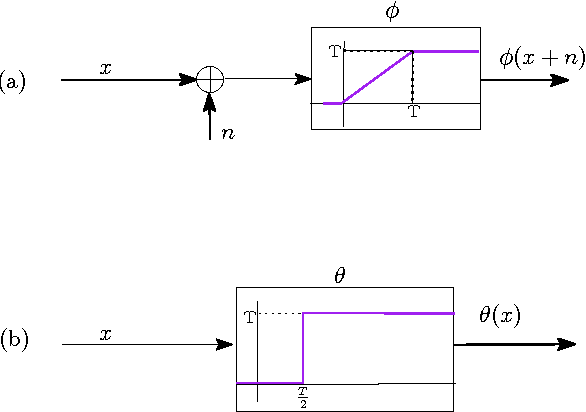
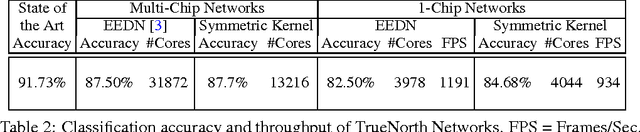
Abstract:We derive a relationship between network representation in energy-efficient neuromorphic architectures and block Toplitz convolutional matrices. Inspired by this connection, we develop deep convolutional networks using a family of structured convolutional matrices and achieve state-of-the-art trade-off between energy efficiency and classification accuracy for well-known image recognition tasks. We also put forward a novel method to train binary convolutional networks by utilising an existing connection between noisy-rectified linear units and binary activations.
Deep neural networks are robust to weight binarization and other non-linear distortions
Jun 07, 2016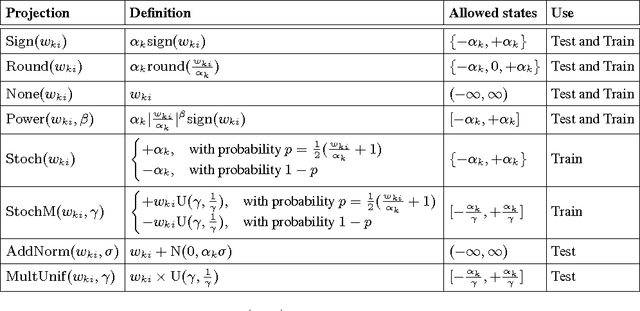
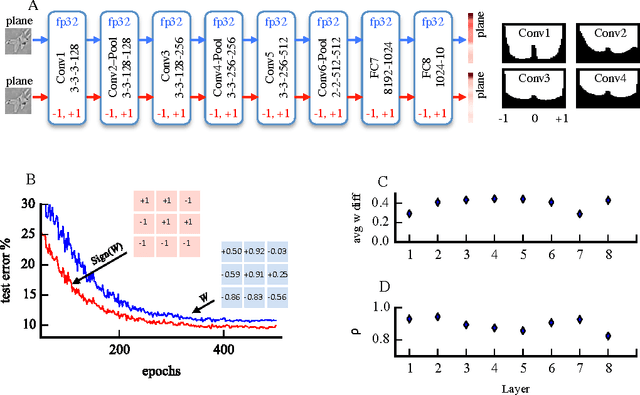
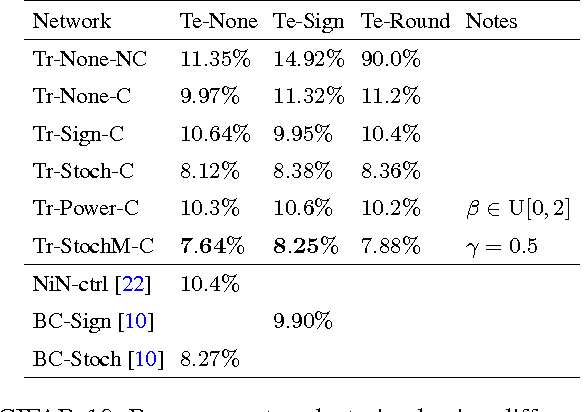
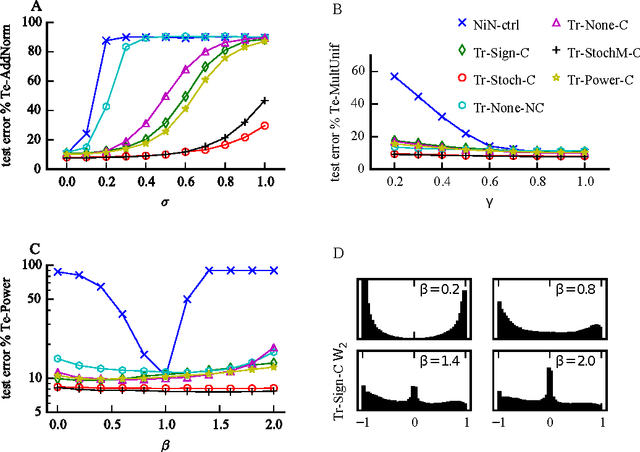
Abstract:Recent results show that deep neural networks achieve excellent performance even when, during training, weights are quantized and projected to a binary representation. Here, we show that this is just the tip of the iceberg: these same networks, during testing, also exhibit a remarkable robustness to distortions beyond quantization, including additive and multiplicative noise, and a class of non-linear projections where binarization is just a special case. To quantify this robustness, we show that one such network achieves 11% test error on CIFAR-10 even with 0.68 effective bits per weight. Furthermore, we find that a common training heuristic--namely, projecting quantized weights during backpropagation--can be altered (or even removed) and networks still achieve a base level of robustness during testing. Specifically, training with weight projections other than quantization also works, as does simply clipping the weights, both of which have never been reported before. We confirm our results for CIFAR-10 and ImageNet datasets. Finally, drawing from these ideas, we propose a stochastic projection rule that leads to a new state of the art network with 7.64% test error on CIFAR-10 using no data augmentation.
Gibbs Sampling with Low-Power Spiking Digital Neurons
Mar 27, 2015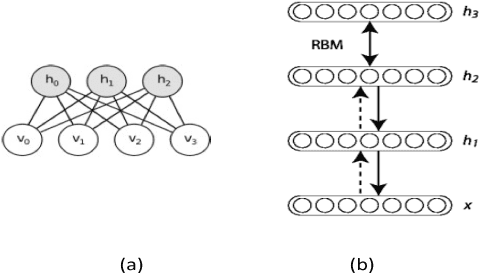
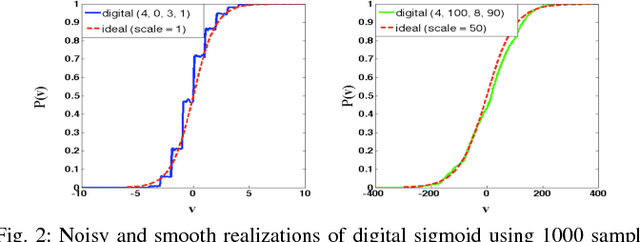
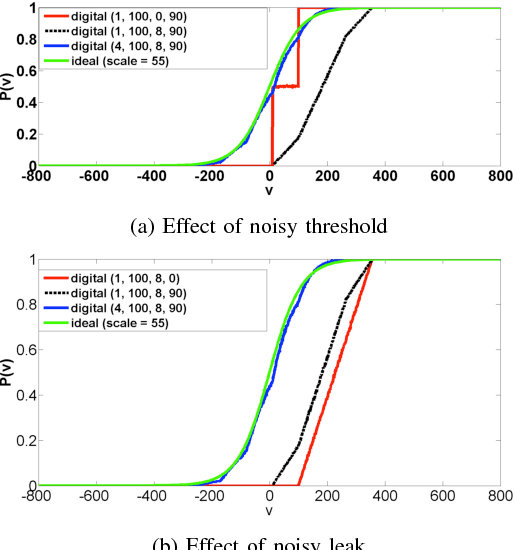

Abstract:Restricted Boltzmann Machines and Deep Belief Networks have been successfully used in a wide variety of applications including image classification and speech recognition. Inference and learning in these algorithms uses a Markov Chain Monte Carlo procedure called Gibbs sampling. A sigmoidal function forms the kernel of this sampler which can be realized from the firing statistics of noisy integrate-and-fire neurons on a neuromorphic VLSI substrate. This paper demonstrates such an implementation on an array of digital spiking neurons with stochastic leak and threshold properties for inference tasks and presents some key performance metrics for such a hardware-based sampler in both the generative and discriminative contexts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge