Deqiang Kong
To See in the Dark: N2DGAN for Background Modeling in Nighttime Scene
Dec 12, 2019



Abstract:Due to the deteriorated conditions of \mbox{illumination} lack and uneven lighting, nighttime images have lower contrast and higher noise than their daytime counterparts of the same scene, which limits seriously the performances of conventional background modeling methods. For such a challenging problem of background modeling under nighttime scene, an innovative and reasonable solution is proposed in this paper, which paves a new way completely different from the existing ones. To make background modeling under nighttime scene performs as well as in daytime condition, we put forward a promising generation-based background modeling framework for foreground surveillance. With a pre-specified daytime reference image as background frame, the {\bfseries GAN} based generation model, called {\bfseries N2DGAN}, is trained to transfer each frame of {\bfseries n}ighttime video {\bfseries to} a virtual {\bfseries d}aytime image with the same scene to the reference image except for the foreground region. Specifically, to balance the preservation of background scene and the foreground object(s) in generating the virtual daytime image, we present a two-pathway generation model, in which the global and local sub-networks are well combined with spatial and temporal consistency constraints. For the sequence of generated virtual daytime images, a multi-scale Bayes model is further proposed to characterize pertinently the temporal variation of background. We evaluate on collected datasets with manually labeled ground truth, which provides a valuable resource for related research community. The impressive results illustrated in both the main paper and supplementary show efficacy of our proposed approach.
EA-LSTM: Evolutionary Attention-based LSTM for Time Series Prediction
Nov 09, 2018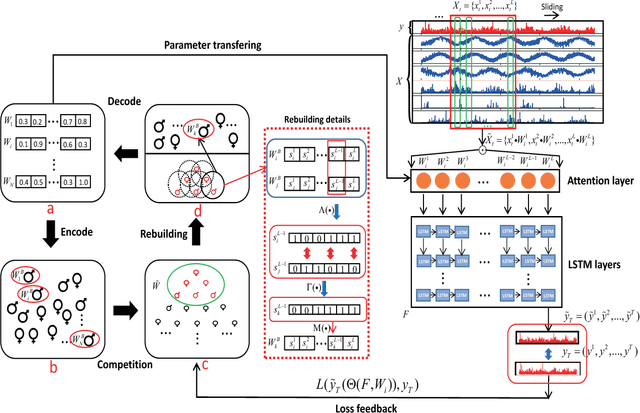

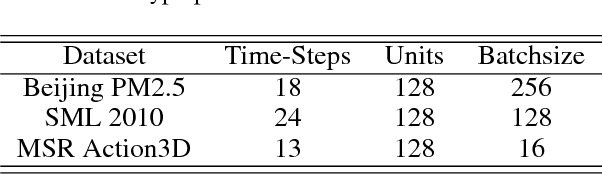
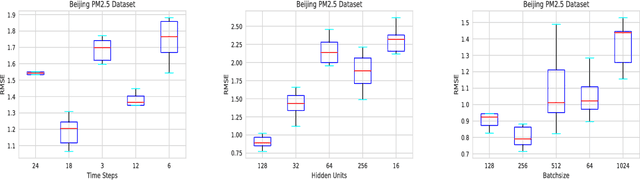
Abstract:Time series prediction with deep learning methods, especially long short-term memory neural networks (LSTMs), have scored significant achievements in recent years. Despite the fact that the LSTMs can help to capture long-term dependencies, its ability to pay different degree of attention on sub-window feature within multiple time-steps is insufficient. To address this issue, an evolutionary attention-based LSTM training with competitive random search is proposed for multivariate time series prediction. By transferring shared parameters, an evolutionary attention learning approach is introduced to the LSTMs model. Thus, like that for biological evolution, the pattern for importance-based attention sampling can be confirmed during temporal relationship mining. To refrain from being trapped into partial optimization like traditional gradient-based methods, an evolutionary computation inspired competitive random search method is proposed, which can well configure the parameters in the attention layer. Experimental results have illustrated that the proposed model can achieve competetive prediction performance compared with other baseline methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge