Denis Turdakov
Model Mimic Attack: Knowledge Distillation for Provably Transferable Adversarial Examples
Oct 21, 2024



Abstract:The vulnerability of artificial neural networks to adversarial perturbations in the black-box setting is widely studied in the literature. The majority of attack methods to construct these perturbations suffer from an impractically large number of queries required to find an adversarial example. In this work, we focus on knowledge distillation as an approach to conduct transfer-based black-box adversarial attacks and propose an iterative training of the surrogate model on an expanding dataset. This work is the first, to our knowledge, to provide provable guarantees on the success of knowledge distillation-based attack on classification neural networks: we prove that if the student model has enough learning capabilities, the attack on the teacher model is guaranteed to be found within the finite number of distillation iterations.
Graph Neural Network for Crawling Target Nodes in Social Networks
Mar 20, 2024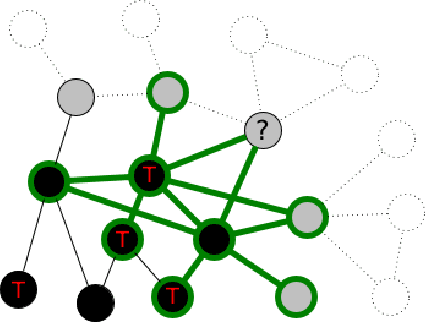
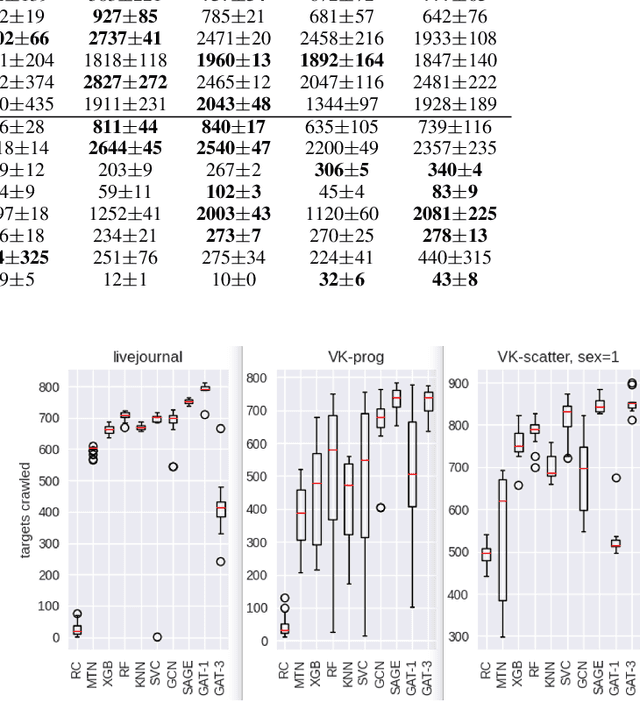
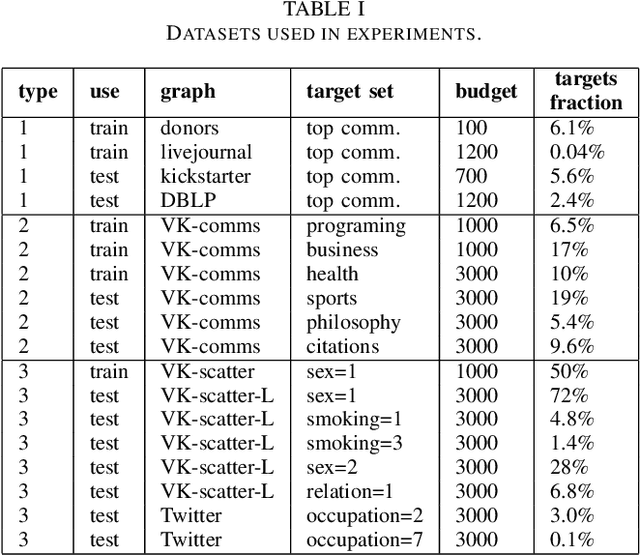
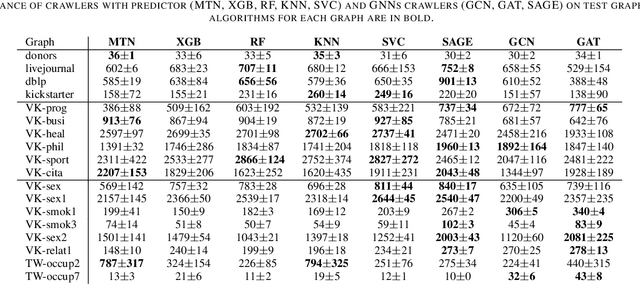
Abstract:Social networks crawling is in the focus of active research the last years. One of the challenging task is to collect target nodes in an initially unknown graph given a budget of crawling steps. Predicting a node property based on its partially known neighbourhood is at the heart of a successful crawler. In this paper we adopt graph neural networks for this purpose and show they are competitive to traditional classifiers and are better for individual cases. Additionally we suggest a training sample boosting technique, which helps to diversify the training set at early stages of crawling and thus improves the predictor quality. The experimental study on three types of target set topology indicates GNN based approach has a potential in crawling task, especially in the case of distributed target nodes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge