Deming Li
MS-GS: Multi-Appearance Sparse-View 3D Gaussian Splatting in the Wild
Sep 19, 2025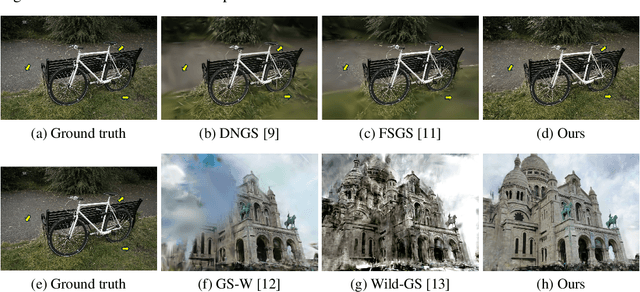
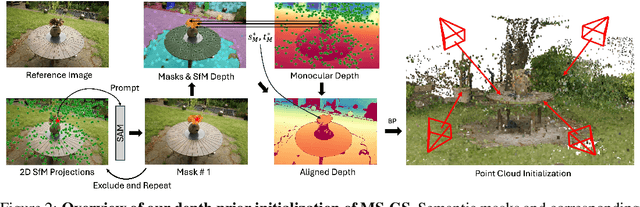
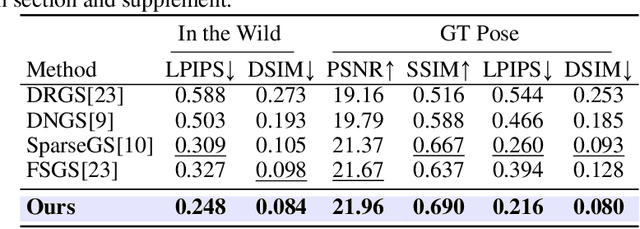
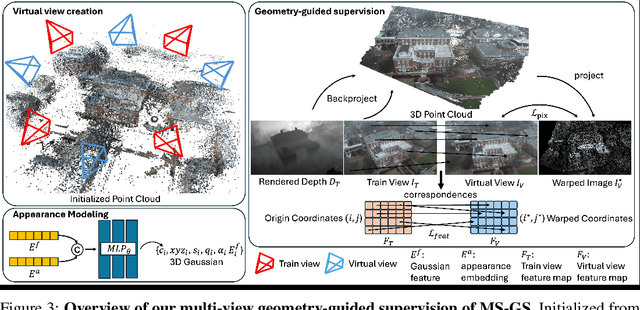
Abstract:In-the-wild photo collections often contain limited volumes of imagery and exhibit multiple appearances, e.g., taken at different times of day or seasons, posing significant challenges to scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis. Although recent adaptations of Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have improved in these areas, they tend to oversmooth and are prone to overfitting. In this paper, we present MS-GS, a novel framework designed with Multi-appearance capabilities in Sparse-view scenarios using 3DGS. To address the lack of support due to sparse initializations, our approach is built on the geometric priors elicited from monocular depth estimations. The key lies in extracting and utilizing local semantic regions with a Structure-from-Motion (SfM) points anchored algorithm for reliable alignment and geometry cues. Then, to introduce multi-view constraints, we propose a series of geometry-guided supervision at virtual views in a fine-grained and coarse scheme to encourage 3D consistency and reduce overfitting. We also introduce a dataset and an in-the-wild experiment setting to set up more realistic benchmarks. We demonstrate that MS-GS achieves photorealistic renderings under various challenging sparse-view and multi-appearance conditions and outperforms existing approaches significantly across different datasets.
SPARS3R: Semantic Prior Alignment and Regularization for Sparse 3D Reconstruction
Nov 15, 2024



Abstract:Recent efforts in Gaussian-Splat-based Novel View Synthesis can achieve photorealistic rendering; however, such capability is limited in sparse-view scenarios due to sparse initialization and over-fitting floaters. Recent progress in depth estimation and alignment can provide dense point cloud with few views; however, the resulting pose accuracy is suboptimal. In this work, we present SPARS3R, which combines the advantages of accurate pose estimation from Structure-from-Motion and dense point cloud from depth estimation. To this end, SPARS3R first performs a Global Fusion Alignment process that maps a prior dense point cloud to a sparse point cloud from Structure-from-Motion based on triangulated correspondences. RANSAC is applied during this process to distinguish inliers and outliers. SPARS3R then performs a second, Semantic Outlier Alignment step, which extracts semantically coherent regions around the outliers and performs local alignment in these regions. Along with several improvements in the evaluation process, we demonstrate that SPARS3R can achieve photorealistic rendering with sparse images and significantly outperforms existing approaches.
BAGS: Blur Agnostic Gaussian Splatting through Multi-Scale Kernel Modeling
Mar 07, 2024Abstract:Recent efforts in using 3D Gaussians for scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis can achieve impressive results on curated benchmarks; however, images captured in real life are often blurry. In this work, we analyze the robustness of Gaussian-Splatting-based methods against various image blur, such as motion blur, defocus blur, downscaling blur, \etc. Under these degradations, Gaussian-Splatting-based methods tend to overfit and produce worse results than Neural-Radiance-Field-based methods. To address this issue, we propose Blur Agnostic Gaussian Splatting (BAGS). BAGS introduces additional 2D modeling capacities such that a 3D-consistent and high quality scene can be reconstructed despite image-wise blur. Specifically, we model blur by estimating per-pixel convolution kernels from a Blur Proposal Network (BPN). BPN is designed to consider spatial, color, and depth variations of the scene to maximize modeling capacity. Additionally, BPN also proposes a quality-assessing mask, which indicates regions where blur occur. Finally, we introduce a coarse-to-fine kernel optimization scheme; this optimization scheme is fast and avoids sub-optimal solutions due to a sparse point cloud initialization, which often occurs when we apply Structure-from-Motion on blurry images. We demonstrate that BAGS achieves photorealistic renderings under various challenging blur conditions and imaging geometry, while significantly improving upon existing approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge