Delaram Golpayegani
An Open Knowledge Graph-Based Approach for Mapping Concepts and Requirements between the EU AI Act and International Standards
Aug 21, 2024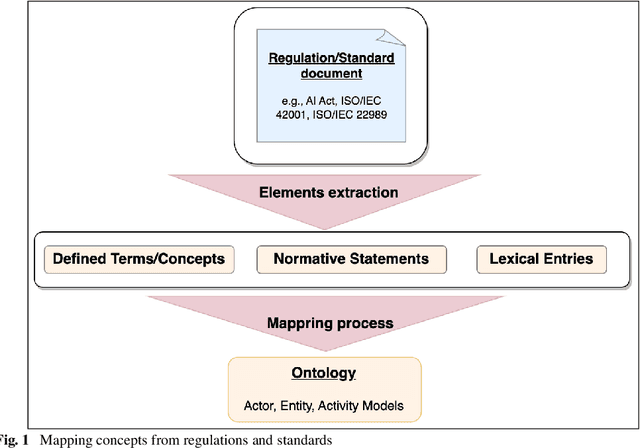
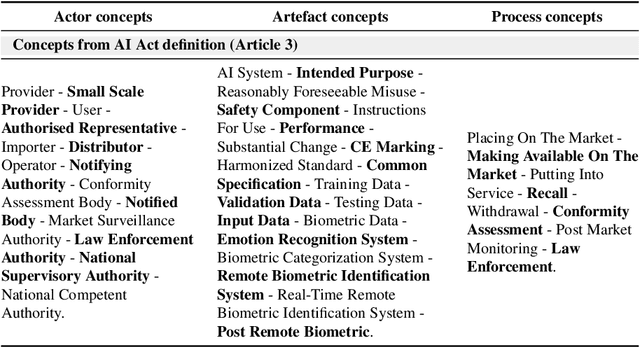
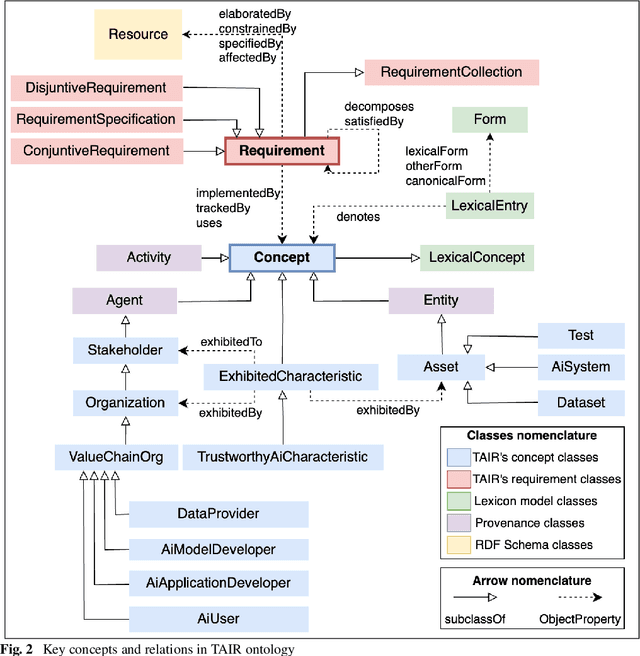
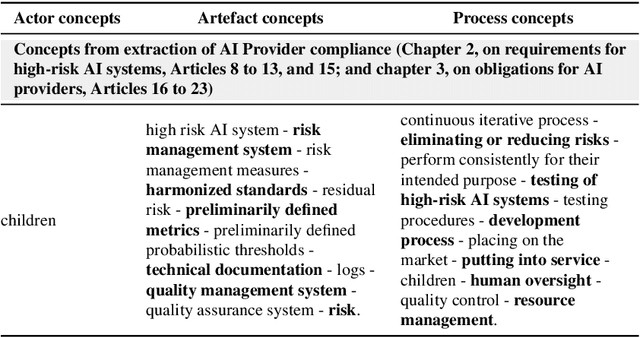
Abstract:The many initiatives on trustworthy AI result in a confusing and multipolar landscape that organizations operating within the fluid and complex international value chains must navigate in pursuing trustworthy AI. The EU's AI Act will now shift the focus of such organizations toward conformance with the technical requirements for regulatory compliance, for which the Act relies on Harmonized Standards. Though a high-level mapping to the Act's requirements will be part of such harmonization, determining the degree to which standards conformity delivers regulatory compliance with the AI Act remains a complex challenge. Variance and gaps in the definitions of concepts and how they are used in requirements between the Act and harmonized standards may impact the consistency of compliance claims across organizations, sectors, and applications. This may present regulatory uncertainty, especially for SMEs and public sector bodies relying on standards conformance rather than proprietary equivalents for developing and deploying compliant high-risk AI systems. To address this challenge, this paper offers a simple and repeatable mechanism for mapping the terms and requirements relevant to normative statements in regulations and standards, e.g., AI Act and ISO management system standards, texts into open knowledge graphs. This representation is used to assess the adequacy of standards conformance to regulatory compliance and thereby provide a basis for identifying areas where further technical consensus development in trustworthy AI value chains is required to achieve regulatory compliance.
A Collaborative, Human-Centred Taxonomy of AI, Algorithmic, and Automation Harms
Jul 01, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces a collaborative, human-centered taxonomy of AI, algorithmic and automation harms. We argue that existing taxonomies, while valuable, can be narrow, unclear, typically cater to practitioners and government, and often overlook the needs of the wider public. Drawing on existing taxonomies and a large repository of documented incidents, we propose a taxonomy that is clear and understandable to a broad set of audiences, as well as being flexible, extensible, and interoperable. Through iterative refinement with topic experts and crowdsourced annotation testing, we propose a taxonomy that can serve as a powerful tool for civil society organisations, educators, policymakers, product teams and the general public. By fostering a greater understanding of the real-world harms of AI and related technologies, we aim to increase understanding, empower NGOs and individuals to identify and report violations, inform policy discussions, and encourage responsible technology development and deployment.
AI Cards: Towards an Applied Framework for Machine-Readable AI and Risk Documentation Inspired by the EU AI Act
Jun 26, 2024



Abstract:With the upcoming enforcement of the EU AI Act, documentation of high-risk AI systems and their risk management information will become a legal requirement playing a pivotal role in demonstration of compliance. Despite its importance, there is a lack of standards and guidelines to assist with drawing up AI and risk documentation aligned with the AI Act. This paper aims to address this gap by providing an in-depth analysis of the AI Act's provisions regarding technical documentation, wherein we particularly focus on AI risk management. On the basis of this analysis, we propose AI Cards as a novel holistic framework for representing a given intended use of an AI system by encompassing information regarding technical specifications, context of use, and risk management, both in human- and machine-readable formats. While the human-readable representation of AI Cards provides AI stakeholders with a transparent and comprehensible overview of the AI use case, its machine-readable specification leverages on state of the art Semantic Web technologies to embody the interoperability needed for exchanging documentation within the AI value chain. This brings the flexibility required for reflecting changes applied to the AI system and its context, provides the scalability needed to accommodate potential amendments to legal requirements, and enables development of automated tools to assist with legal compliance and conformity assessment tasks. To solidify the benefits, we provide an exemplar AI Card for an AI-based student proctoring system and further discuss its potential applications within and beyond the context of the AI Act.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge