Cecilia Panigutti
AI Cards: Towards an Applied Framework for Machine-Readable AI and Risk Documentation Inspired by the EU AI Act
Jun 26, 2024



Abstract:With the upcoming enforcement of the EU AI Act, documentation of high-risk AI systems and their risk management information will become a legal requirement playing a pivotal role in demonstration of compliance. Despite its importance, there is a lack of standards and guidelines to assist with drawing up AI and risk documentation aligned with the AI Act. This paper aims to address this gap by providing an in-depth analysis of the AI Act's provisions regarding technical documentation, wherein we particularly focus on AI risk management. On the basis of this analysis, we propose AI Cards as a novel holistic framework for representing a given intended use of an AI system by encompassing information regarding technical specifications, context of use, and risk management, both in human- and machine-readable formats. While the human-readable representation of AI Cards provides AI stakeholders with a transparent and comprehensible overview of the AI use case, its machine-readable specification leverages on state of the art Semantic Web technologies to embody the interoperability needed for exchanging documentation within the AI value chain. This brings the flexibility required for reflecting changes applied to the AI system and its context, provides the scalability needed to accommodate potential amendments to legal requirements, and enables development of automated tools to assist with legal compliance and conformity assessment tasks. To solidify the benefits, we provide an exemplar AI Card for an AI-based student proctoring system and further discuss its potential applications within and beyond the context of the AI Act.
FairLens: Auditing Black-box Clinical Decision Support Systems
Nov 08, 2020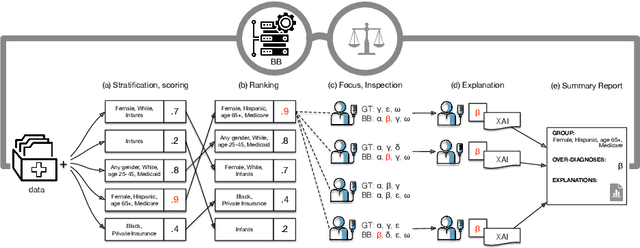
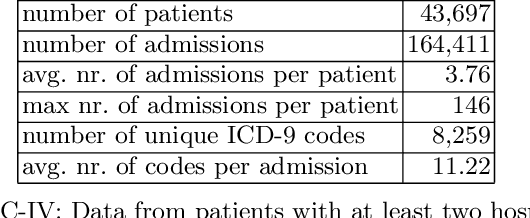
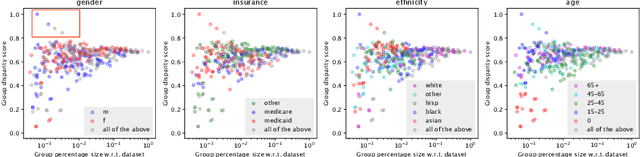

Abstract:The pervasive application of algorithmic decision-making is raising concerns on the risk of unintended bias in AI systems deployed in critical settings such as healthcare. The detection and mitigation of biased models is a very delicate task which should be tackled with care and involving domain experts in the loop. In this paper we introduce FairLens, a methodology for discovering and explaining biases. We show how our tool can be used to audit a fictional commercial black-box model acting as a clinical decision support system. In this scenario, the healthcare facility experts can use FairLens on their own historical data to discover the model's biases before incorporating it into the clinical decision flow. FairLens first stratifies the available patient data according to attributes such as age, ethnicity, gender and insurance; it then assesses the model performance on such subgroups of patients identifying those in need of expert evaluation. Finally, building on recent state-of-the-art XAI (eXplainable Artificial Intelligence) techniques, FairLens explains which elements in patients' clinical history drive the model error in the selected subgroup. Therefore, FairLens allows experts to investigate whether to trust the model and to spotlight group-specific biases that might constitute potential fairness issues.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge