Dayu Zhang
Multi-task Federated Learning with Encoder-Decoder Structure: Enabling Collaborative Learning Across Different Tasks
Apr 14, 2025



Abstract:Federated learning has been extensively studied and applied due to its ability to ensure data security in distributed environments while building better models. However, clients participating in federated learning still face limitations, as clients with different structures or tasks cannot participate in learning together. In view of this, constructing a federated learning framework that allows collaboration between clients with different model structures and performing different tasks, enabling them to share valuable knowledge to enhance model efficiency, holds significant practical implications for the widespread application of federated learning. To achieve this goal, we propose a multi-task federated learning with encoder-decoder structure (M-Fed). Specifically, given the widespread adoption of the encoder-decoder architecture in current models, we leverage this structure to share intra-task knowledge through traditional federated learning methods and extract general knowledge from the encoder to achieve cross-task knowledge sharing. The training process is similar to traditional federated learning, and we incorporate local decoder and global decoder information into the loss function. The local decoder iteratively updates and gradually approaches the global decoder until sufficient cross-task knowledge sharing is achieved. Our method is lightweight and modular, demonstrating innovation compared to previous research. It enables clients performing different tasks to share general knowledge while maintaining the efficiency of traditional federated learning systems. We conducted experiments on two widely used benchmark datasets to verify the feasibility of M-Fed and compared it with traditional methods. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of M-Fed in multi-task federated learning.
Efficient Multi-Task Modeling through Automated Fusion of Trained Models
Apr 14, 2025


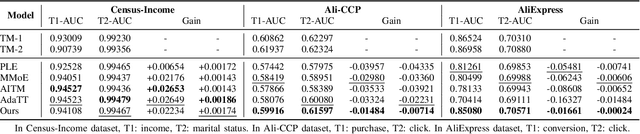
Abstract:Although multi-task learning is widely applied in intelligent services, traditional multi-task modeling methods often require customized designs based on specific task combinations, resulting in a cumbersome modeling process. Inspired by the rapid development and excellent performance of single-task models, this paper proposes an efficient multi-task modeling method that can automatically fuse trained single-task models with different structures and tasks to form a multi-task model. As a general framework, this method allows modelers to simply prepare trained models for the required tasks, simplifying the modeling process while fully utilizing the knowledge contained in the trained models. This eliminates the need for excessive focus on task relationships and model structure design. To achieve this goal, we consider the structural differences among various trained models and employ model decomposition techniques to hierarchically decompose them into multiple operable model components. Furthermore, we have designed an Adaptive Knowledge Fusion (AKF) module based on Transformer, which adaptively integrates intra-task and inter-task knowledge based on model components. Through the proposed method, we achieve efficient and automated construction of multi-task models, and its effectiveness is verified through extensive experiments on three datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge