David R. Dewhurst
Storywrangler: A massive exploratorium for sociolinguistic, cultural, socioeconomic, and political timelines using Twitter
Jul 25, 2020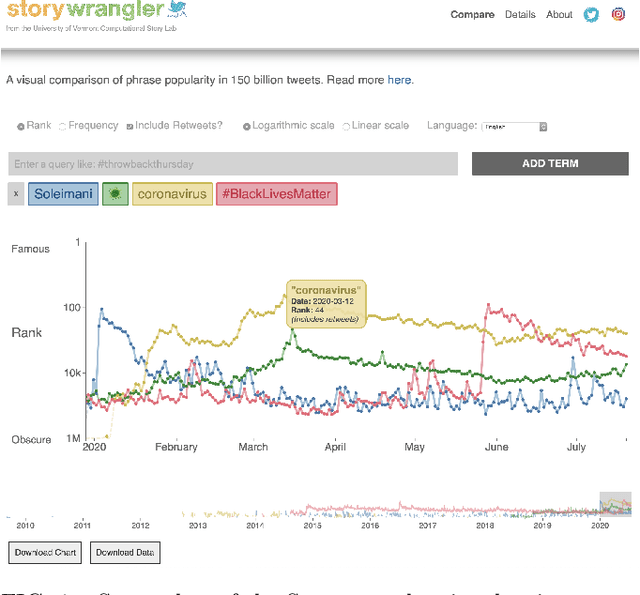
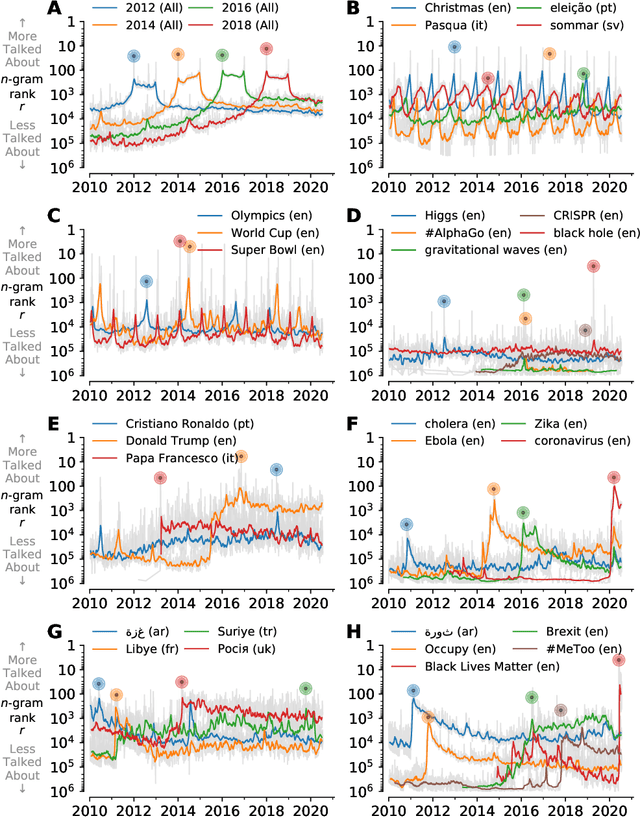
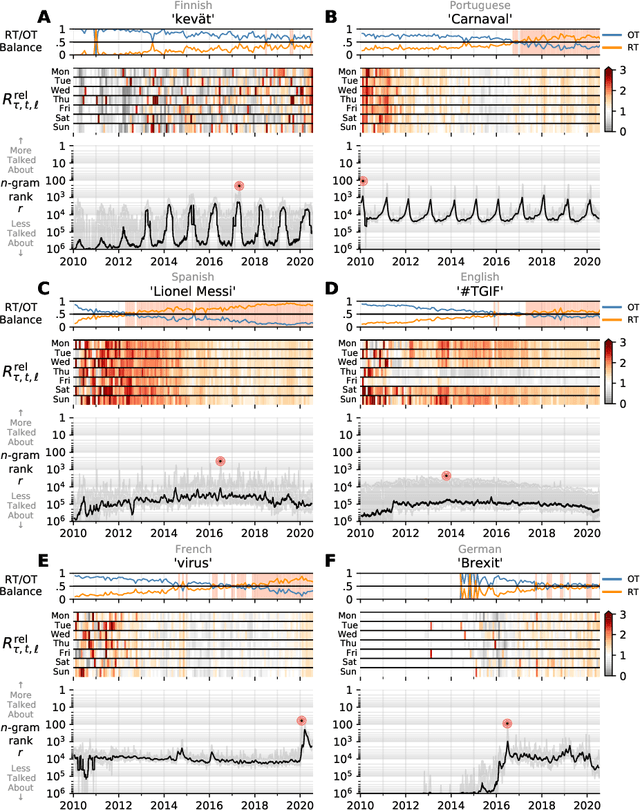
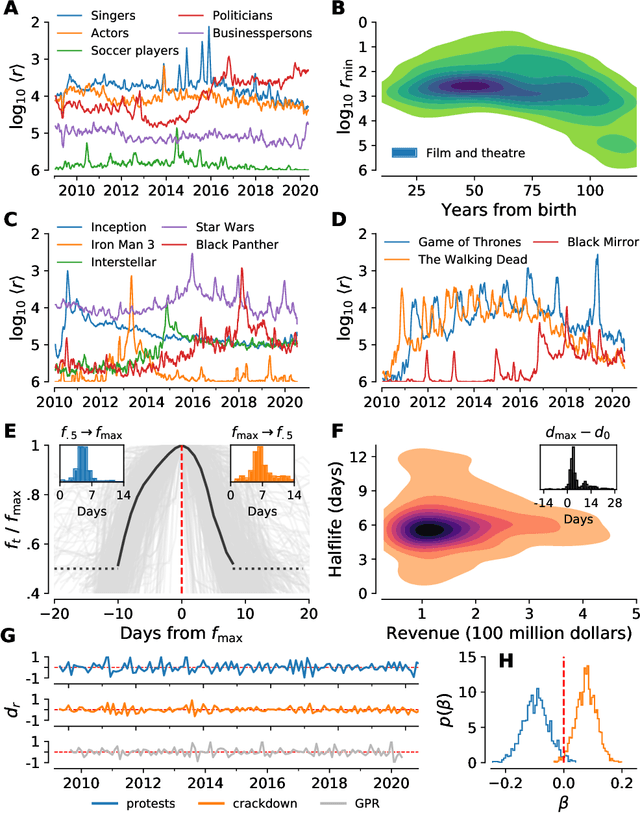
Abstract:In real-time, Twitter strongly imprints world events, popular culture, and the day-to-day; Twitter records an ever growing compendium of language use and change; and Twitter has been shown to enable certain kinds of prediction. Vitally, and absent from many standard corpora such as books and news archives, Twitter also encodes popularity and spreading through retweets. Here, we describe Storywrangler, an ongoing, day-scale curation of over 100 billion tweets containing around 1 trillion 1-grams from 2008 to 2020. For each day, we break tweets into 1-, 2-, and 3-grams across 150+ languages, record usage frequencies, and generate Zipf distributions. We make the data set available through an interactive time series viewer, and as downloadable time series and daily distributions. We showcase a few examples of the many possible avenues of study we aim to enable including how social amplification can be visualized through 'contagiograms'.
The growing echo chamber of social media: Measuring temporal and social contagion dynamics for over 150 languages on Twitter for 2009--2020
Mar 15, 2020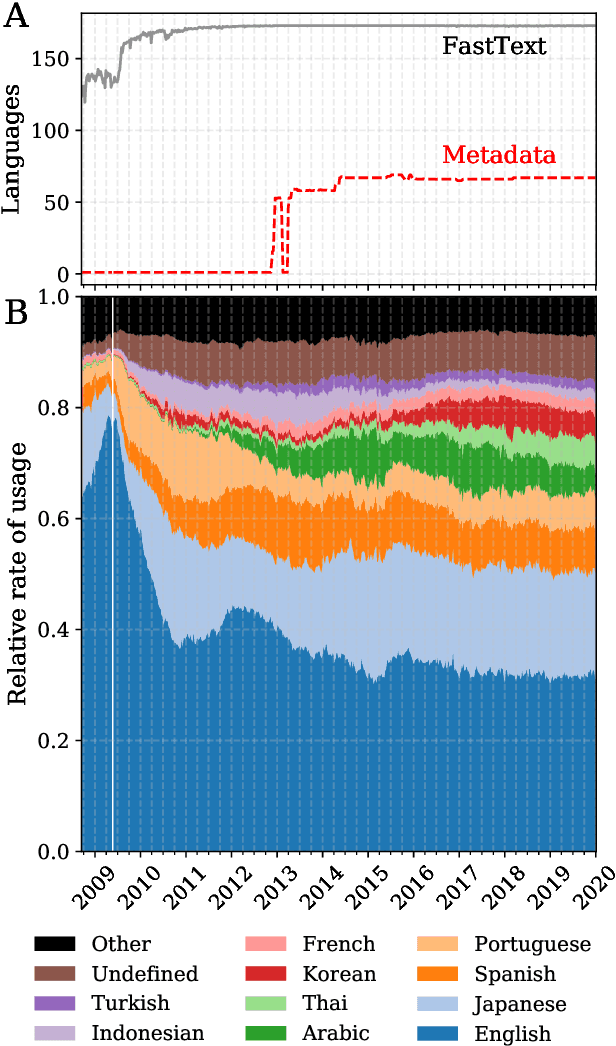
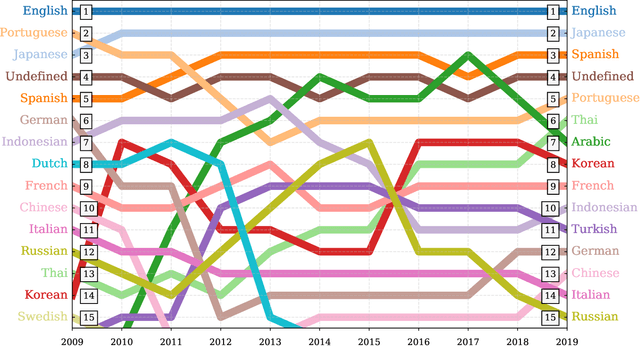
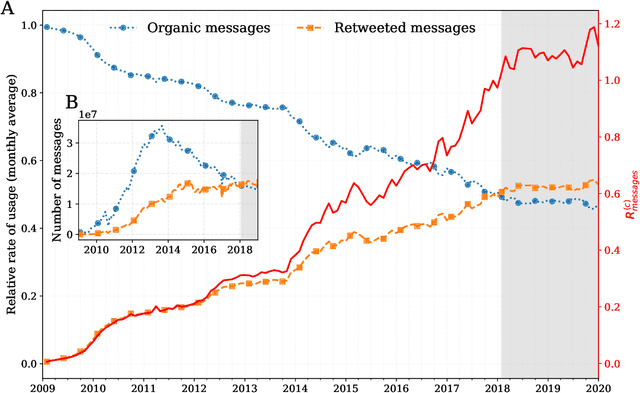
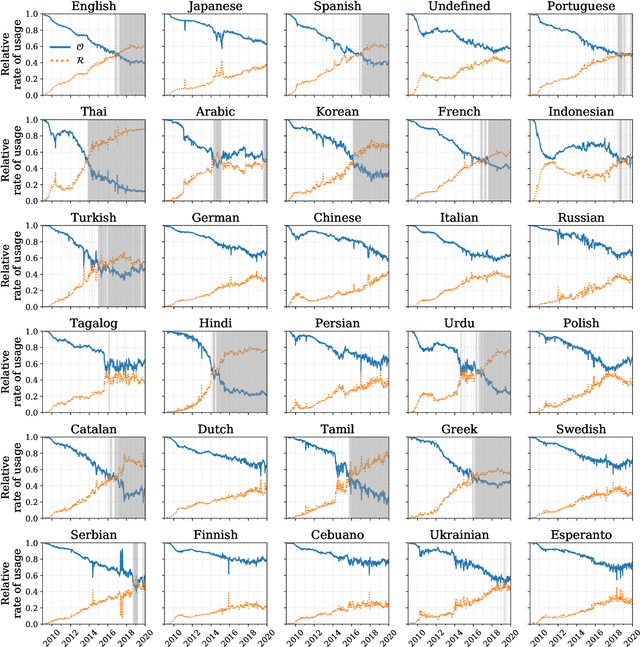
Abstract:Working from a dataset of 118 billion messages running from the start of 2009 to the end of 2019, we identify and explore the relative daily use of over 150 languages on Twitter. We find that eight languages comprise 80% of all tweets, with English, Japanese, Spanish, and Portuguese being the most dominant. To quantify each language's level of being a Twitter `echo chamber' over time, we compute the `contagion ratio': the balance of retweets to organic messages. We find that for the most common languages on Twitter there is a growing tendency, though not universal, to retweet rather than share new content. By the end of 2019, the contagion ratios for half of the top 30 languages, including English and Spanish, had reached above 1---the naive contagion threshold. In 2019, the top 5 languages with the highest average daily ratios were, in order, Thai (7.3), Hindi, Tamil, Urdu, and Catalan, while the bottom 5 were Russian, Swedish, Esperanto, Cebuano, and Finnish (0.26). Further, we show that over time, the contagion ratios for most common languages are growing more strongly than those of rare languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge