David Bojanić
Pose-independent 3D Anthropometry from Sparse Data
Jan 10, 2025
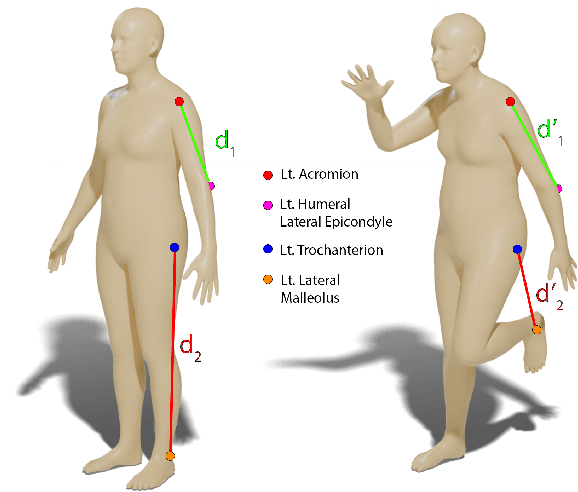


Abstract:3D digital anthropometry is the study of estimating human body measurements from 3D scans. Precise body measurements are important health indicators in the medical industry, and guiding factors in the fashion, ergonomic and entertainment industries. The measuring protocol consists of scanning the whole subject in the static A-pose, which is maintained without breathing or movement during the scanning process. However, the A-pose is not easy to maintain during the whole scanning process, which can last even up to a couple of minutes. This constraint affects the final quality of the scan, which in turn affects the accuracy of the estimated body measurements obtained from methods that rely on dense geometric data. Additionally, this constraint makes it impossible to develop a digital anthropometry method for subjects unable to assume the A-pose, such as those with injuries or disabilities. We propose a method that can obtain body measurements from sparse landmarks acquired in any pose. We make use of the sparse landmarks of the posed subject to create pose-independent features, and train a network to predict the body measurements as taken from the standard A-pose. We show that our method achieves comparable results to competing methods that use dense geometry in the standard A-pose, but has the capability of estimating the body measurements from any pose using sparse landmarks only. Finally, we address the lack of open-source 3D anthropometry methods by making our method available to the research community at https://github.com/DavidBoja/pose-independent-anthropometry.
Challenging the Universal Representation of Deep Models for 3D Point Cloud Registration
Nov 29, 2022



Abstract:Learning universal representations across different applications domain is an open research problem. In fact, finding universal architecture within the same application but across different types of datasets is still unsolved problem too, especially in applications involving processing 3D point clouds. In this work we experimentally test several state-of-the-art learning-based methods for 3D point cloud registration against the proposed non-learning baseline registration method. The proposed method either outperforms or achieves comparable results w.r.t. learning based methods. In addition, we propose a dataset on which learning based methods have a hard time to generalize. Our proposed method and dataset, along with the provided experiments, can be used in further research in studying effective solutions for universal representations. Our source code is available at: github.com/DavidBoja/greedy-grid-search.
Stochastic Modeling for Learnable Human Pose Triangulation
Oct 01, 2021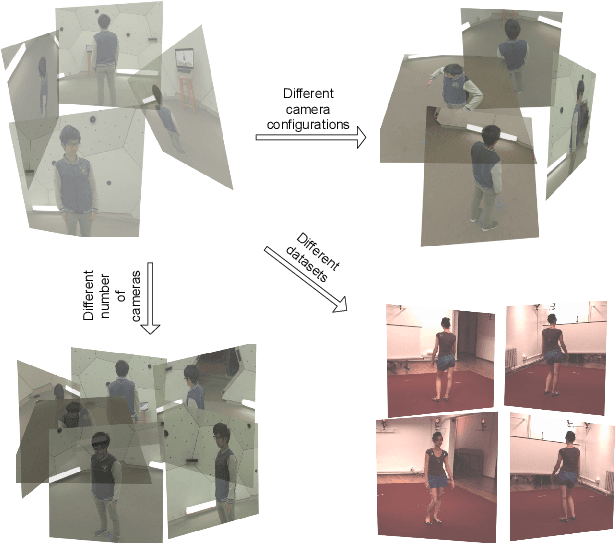
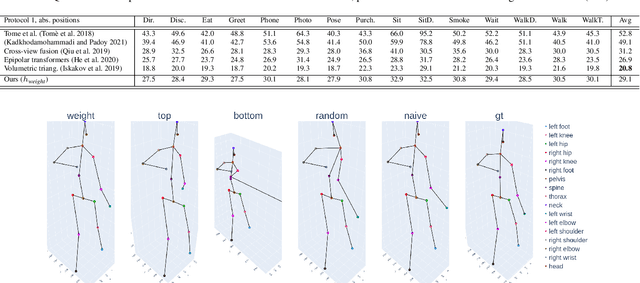
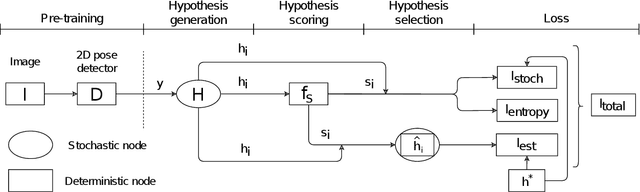
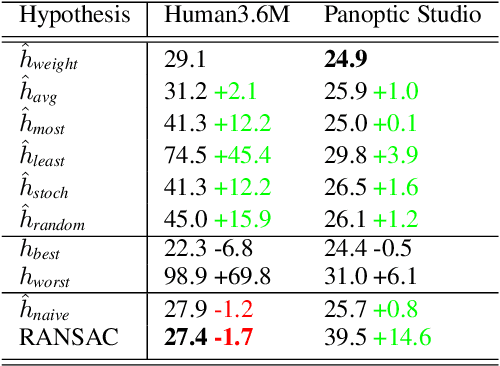
Abstract:We propose a stochastic modeling framework for 3D human pose triangulation and evaluate its performance across different datasets and spatial camera arrangements. The common approach to 3D pose estimation is to first detect 2D keypoints in images and then apply the triangulation from multiple views. However, the majority of existing triangulation models are limited to a single dataset, i.e. camera arrangement and their number. Moreover, they require known camera parameters. The proposed stochastic pose triangulation model successfully generalizes to different camera arrangements and between two public datasets. In each step, we generate a set of 3D pose hypotheses obtained by triangulation from a random subset of views. The hypotheses are evaluated by a neural network and the expectation of the triangulation error is minimized. The key novelty is that the network learns to evaluate the poses without taking into account the spatial camera arrangement, thus improving generalization. Additionally, we demonstrate that the proposed stochastic framework can also be used for fundamental matrix estimation, showing promising results towards relative camera pose estimation from noisy keypoint correspondences.
Catadioptric Stereo on a Smartphone
Sep 24, 2021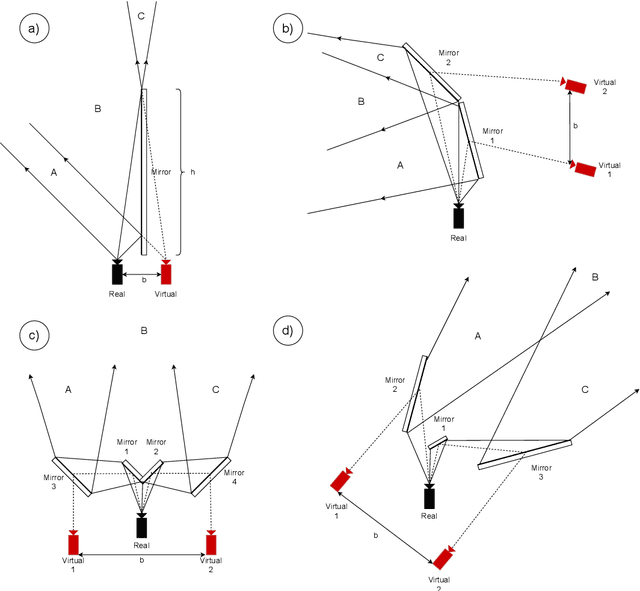
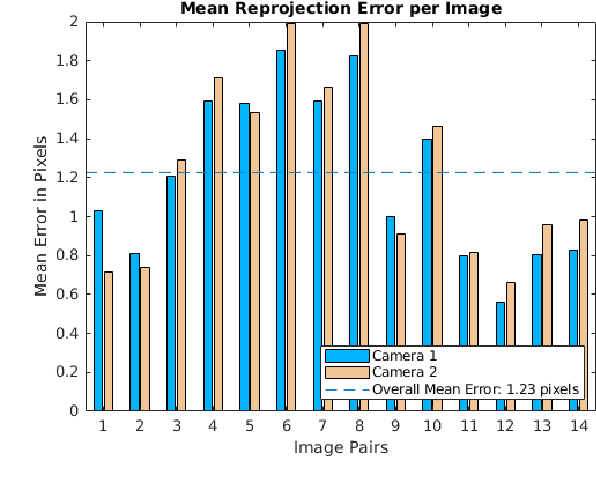
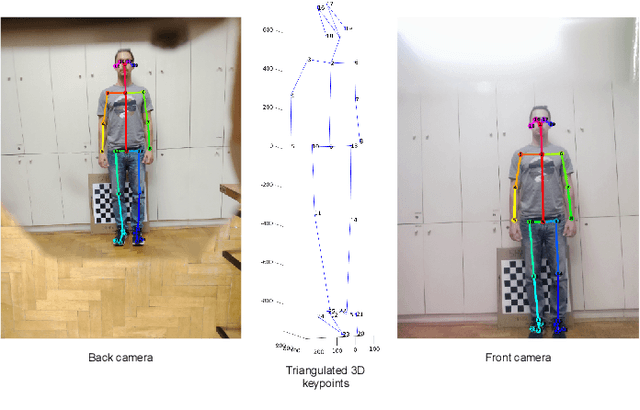
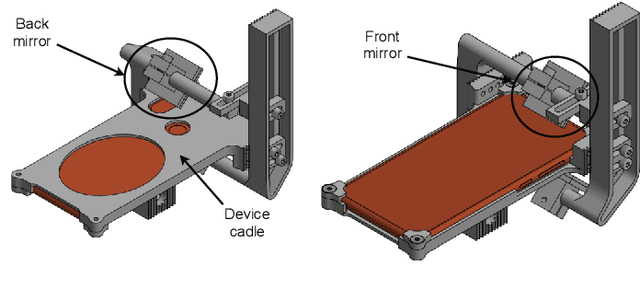
Abstract:We present a 3D printed adapter with planar mirrors for stereo reconstruction using front and back smartphone camera. The adapter presents a practical and low-cost solution for enabling any smartphone to be used as a stereo camera, which is currently only possible using high-end phones with expensive 3D sensors. Using the prototype version of the adapter, we experiment with parameters like the angles between cameras and mirrors and the distance to each camera (the stereo baseline). We find the most convenient configuration and calibrate the stereo pair. Based on the presented preliminary analysis, we identify possible improvements in the current design. To demonstrate the working prototype, we reconstruct a 3D human pose using 2D keypoint detections from the stereo pair and evaluate extracted body lengths. The result shows that the adapter can be used for anthropometric measurement of several body segments.
On the Comparison of Classic and Deep Keypoint Detector and Descriptor Methods
Jul 29, 2020
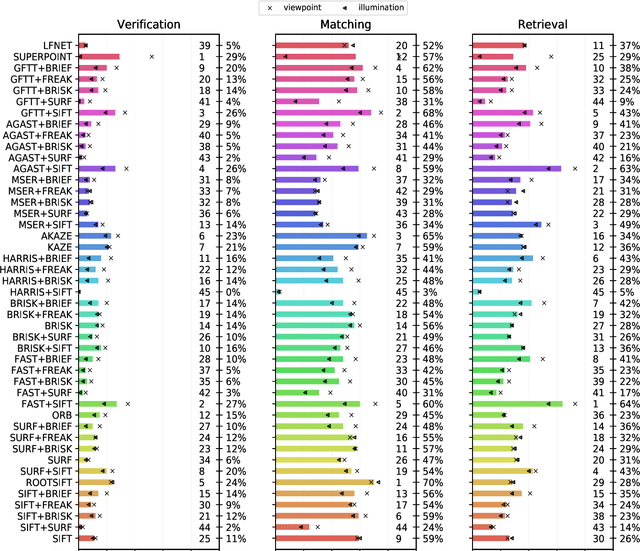
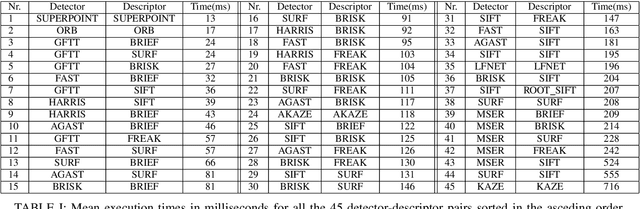
Abstract:The purpose of this study is to give a performance comparison between several classic hand-crafted and deep key-point detector and descriptor methods. In particular, we consider the following classical algorithms: SIFT, SURF, ORB, FAST, BRISK, MSER, HARRIS, KAZE, AKAZE, AGAST, GFTT, FREAK, BRIEF and RootSIFT, where a subset of all combinations is paired into detector-descriptor pipelines. Additionally, we analyze the performance of two recent and perspective deep detector-descriptor models, LF-Net and SuperPoint. Our benchmark relies on the HPSequences dataset that provides real and diverse images under various geometric and illumination changes. We analyze the performance on three evaluation tasks: keypoint verification, image matching and keypoint retrieval. The results show that certain classic and deep approaches are still comparable, with some classic detector-descriptor combinations overperforming pretrained deep models. In terms of the execution times of tested implementations, SuperPoint model is the fastest, followed by ORB. The source code is published on \url{https://github.com/kristijanbartol/keypoint-algorithms-benchmark}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge