Daniele Cono D'Elia
On the Lack of Robustness of Binary Function Similarity Systems
Dec 05, 2024Abstract:Binary function similarity, which often relies on learning-based algorithms to identify what functions in a pool are most similar to a given query function, is a sought-after topic in different communities, including machine learning, software engineering, and security. Its importance stems from the impact it has in facilitating several crucial tasks, from reverse engineering and malware analysis to automated vulnerability detection. Whereas recent work cast light around performance on this long-studied problem, the research landscape remains largely lackluster in understanding the resiliency of the state-of-the-art machine learning models against adversarial attacks. As security requires to reason about adversaries, in this work we assess the robustness of such models through a simple yet effective black-box greedy attack, which modifies the topology and the content of the control flow of the attacked functions. We demonstrate that this attack is successful in compromising all the models, achieving average attack success rates of 57.06% and 95.81% depending on the problem settings (targeted and untargeted attacks). Our findings are insightful: top performance on clean data does not necessarily relate to top robustness properties, which explicitly highlights performance-robustness trade-offs one should consider when deploying such models, calling for further research.
Adversarial Attacks against Binary Similarity Systems
Mar 20, 2023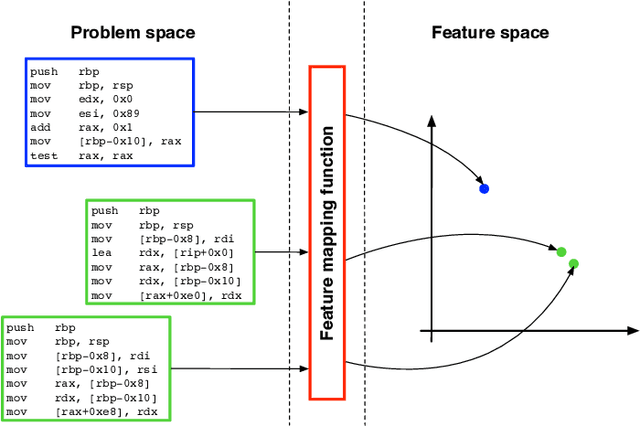
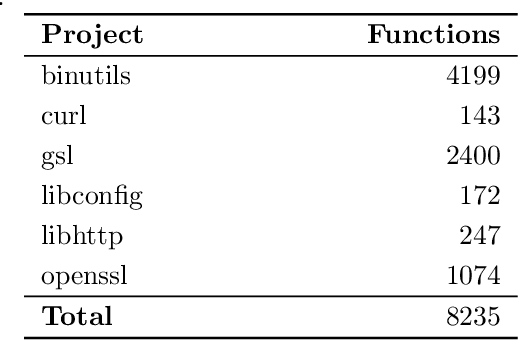
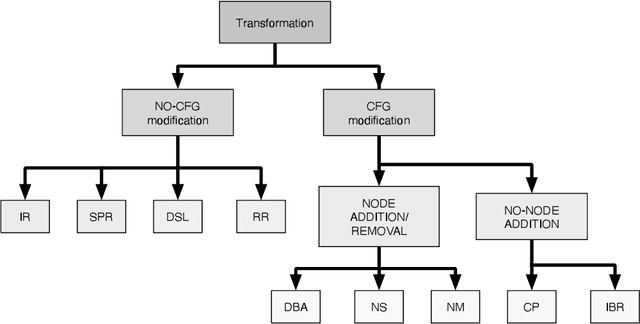
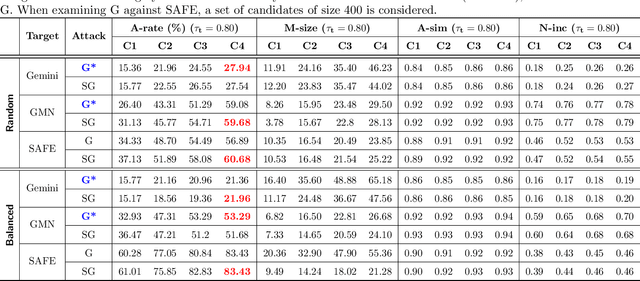
Abstract:In recent years, binary analysis gained traction as a fundamental approach to inspect software and guarantee its security. Due to the exponential increase of devices running software, much research is now moving towards new autonomous solutions based on deep learning models, as they have been showing state-of-the-art performances in solving binary analysis problems. One of the hot topics in this context is binary similarity, which consists in determining if two functions in assembly code are compiled from the same source code. However, it is unclear how deep learning models for binary similarity behave in an adversarial context. In this paper, we study the resilience of binary similarity models against adversarial examples, showing that they are susceptible to both targeted and untargeted attacks (w.r.t. similarity goals) performed by black-box and white-box attackers. In more detail, we extensively test three current state-of-the-art solutions for binary similarity against two black-box greedy attacks, including a new technique that we call Spatial Greedy, and one white-box attack in which we repurpose a gradient-guided strategy used in attacks to image classifiers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge