Daniel J Perry
Improving Training Efficiency and Reducing Maintenance Costs via Language Specific Model Merging
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Fine-tuning a task-specific multilingual large language model (LLM) involves training the model on a multilingual dataset with examples in all the required languages. Updating one or more supported languages with additional data or adding support for a new language involves retraining the model, which can be computationally inefficient and creates a severe maintenance bottleneck. Recent research on merging multilingual multitask models has shown promise in terms of improved quality, but its computational and maintenance efficiency remains unstudied. In this work, we provide the first focused analysis of this merging strategy from an efficiency perspective, evaluating it across three independent tasks. We demonstrate significant efficiency gains while maintaining parity in terms of quality: this merging approach reduces the initial training time by up to 50\%. We also demonstrate that updating an individual language and re-merging as part of model maintenance reduces training costs by more than 60\%, compared to re-training the full multilingual model. We show this on both public and proprietary industry datasets confirming that the approach works well for industrial use cases in addition to academic settings already studied in previous work.
Effective Proxy for Human Labeling: Ensemble Disagreement Scores in Large Language Models for Industrial NLP
Sep 11, 2023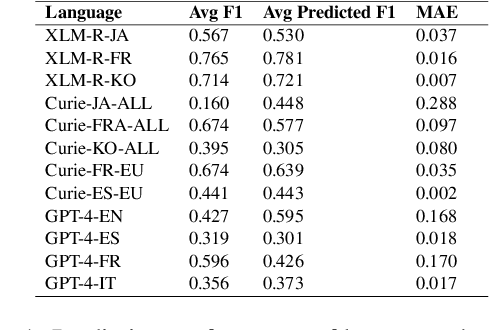
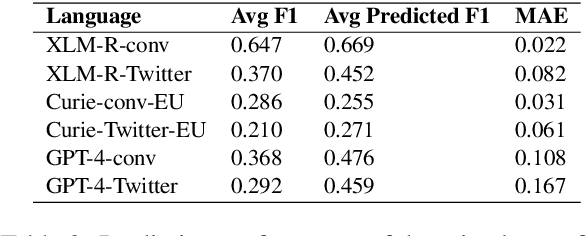
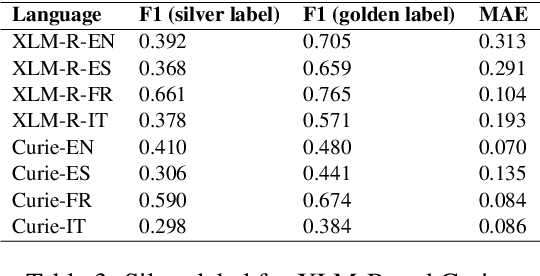
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant capability to generalize across a large number of NLP tasks. For industry applications, it is imperative to assess the performance of the LLM on unlabeled production data from time to time to validate for a real-world setting. Human labeling to assess model error requires considerable expense and time delay. Here we demonstrate that ensemble disagreement scores work well as a proxy for human labeling for language models in zero-shot, few-shot, and fine-tuned settings, per our evaluation on keyphrase extraction (KPE) task. We measure fidelity of the results by comparing to true error measured from human labeled ground truth. We contrast with the alternative of using another LLM as a source of machine labels, or silver labels. Results across various languages and domains show disagreement scores provide a better estimation of model performance with mean average error (MAE) as low as 0.4% and on average 13.8% better than using silver labels.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge