Dang Pham
Follow the Water: Finding Water, Snow and Clouds on Terrestrial Exoplanets with Photometry and Machine Learning
Mar 08, 2022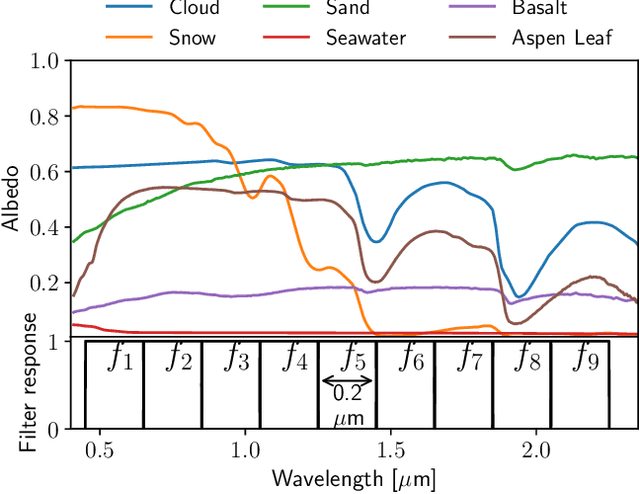
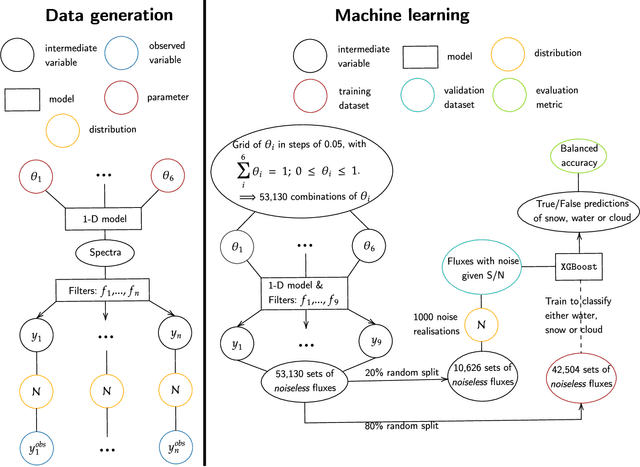
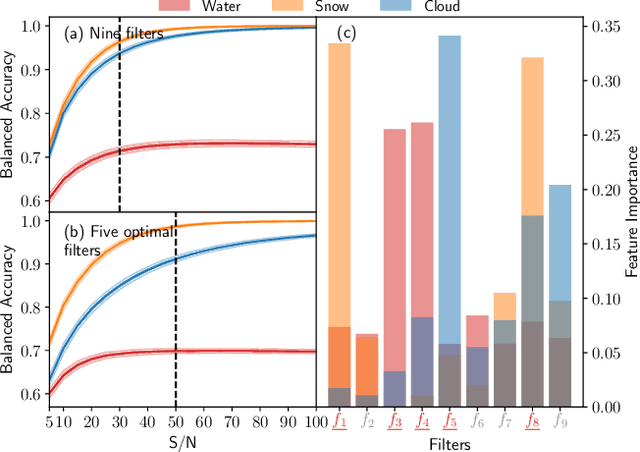
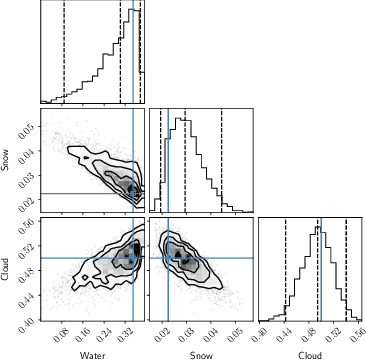
Abstract:All life on Earth needs water. NASA's quest to follow the water links water to the search for life in the cosmos. Telescopes like JWST and mission concepts like HabEx, LUVOIR and Origins are designed to characterise rocky exoplanets spectroscopically. However, spectroscopy remains time-intensive and therefore, initial characterisation is critical to prioritisation of targets. Here, we study machine learning as a tool to assess water's existence through broadband-filter reflected photometric flux on Earth-like exoplanets in three forms: seawater, water-clouds and snow; based on 53,130 spectra of cold, Earth-like planets with 6 major surfaces. XGBoost, a well-known machine learning algorithm, achieves over 90\% balanced accuracy in detecting the existence of snow or clouds for S/N$\gtrsim 20$, and 70\% for liquid seawater for S/N $\gtrsim 30$. Finally, we perform mock Bayesian analysis with Markov-chain Monte Carlo with five filters identified to derive exact surface compositions to test for retrieval feasibility. The results show that the use of machine learning to identify water on the surface of exoplanets from broadband-filter photometry provides a promising initial characterisation tool of water in different forms. Planned small and large telescope missions could use this to aid their prioritisation of targets for time-intense follow-up observations.
Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes for Inferring Topics and Visualization
Oct 25, 2020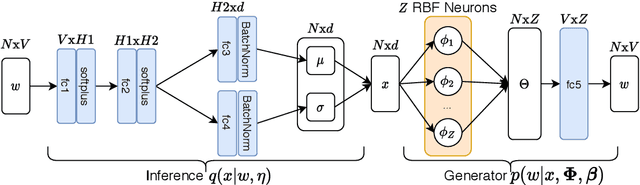
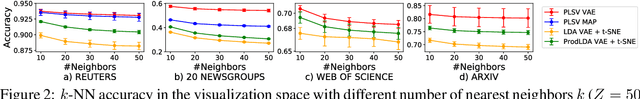
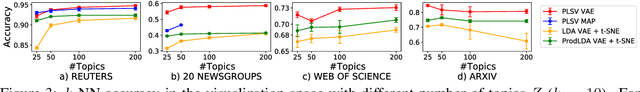
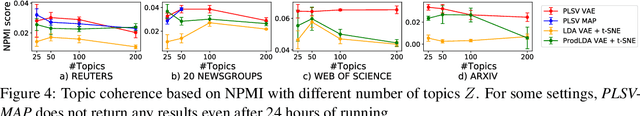
Abstract:Visualization and topic modeling are widely used approaches for text analysis. Traditional visualization methods find low-dimensional representations of documents in the visualization space (typically 2D or 3D) that can be displayed using a scatterplot. In contrast, topic modeling aims to discover topics from text, but for visualization, one needs to perform a post-hoc embedding using dimensionality reduction methods. Recent approaches propose using a generative model to jointly find topics and visualization, allowing the semantics to be infused in the visualization space for a meaningful interpretation. A major challenge that prevents these methods from being used practically is the scalability of their inference algorithms. We present, to the best of our knowledge, the first fast Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes based inference method for jointly inferring topics and visualization. Since our method is black box, it can handle model changes efficiently with little mathematical rederivation effort. We demonstrate the efficiency and effectiveness of our method on real-world large datasets and compare it with existing baselines.
Combination of Domain Knowledge and Deep Learning for Sentiment Analysis of Short and Informal Messages on Social Media
Feb 16, 2019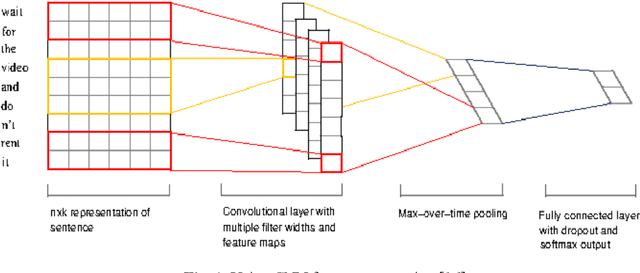
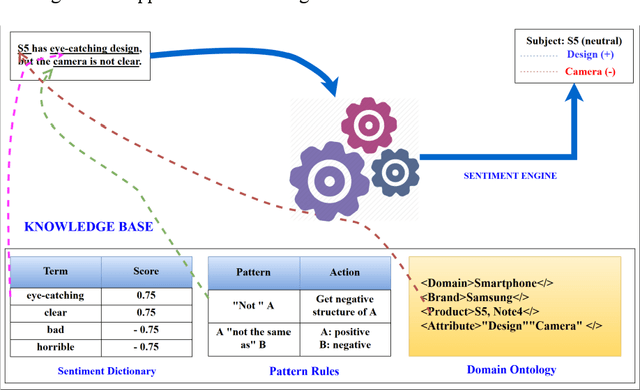
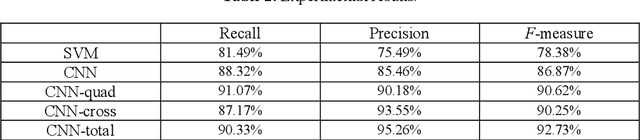
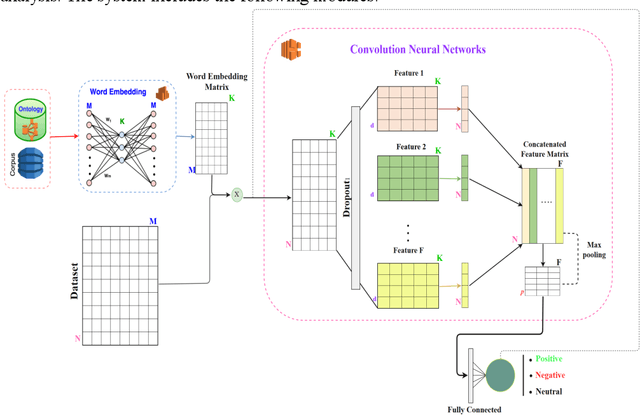
Abstract:Sentiment analysis has been emerging recently as one of the major natural language processing (NLP) tasks in many applications. Especially, as social media channels (e.g. social networks or forums) have become significant sources for brands to observe user opinions about their products, this task is thus increasingly crucial. However, when applied with real data obtained from social media, we notice that there is a high volume of short and informal messages posted by users on those channels. This kind of data makes the existing works suffer from many difficulties to handle, especially ones using deep learning approaches. In this paper, we propose an approach to handle this problem. This work is extended from our previous work, in which we proposed to combine the typical deep learning technique of Convolutional Neural Networks with domain knowledge. The combination is used for acquiring additional training data augmentation and a more reasonable loss function. In this work, we further improve our architecture by various substantial enhancements, including negation-based data augmentation, transfer learning for word embeddings, the combination of word-level embeddings and character-level embeddings, and using multitask learning technique for attaching domain knowledge rules in the learning process. Those enhancements, specifically aiming to handle short and informal messages, help us to enjoy significant improvement in performance once experimenting on real datasets.
Combination of Domain Knowledge and Deep Learning for Sentiment Analysis
Jun 26, 2018



Abstract:The emerging technique of deep learning has been widely applied in many different areas. However, when adopted in a certain specific domain, this technique should be combined with domain knowledge to improve efficiency and accuracy. In particular, when analyzing the applications of deep learning in sentiment analysis, we found that the current approaches are suffering from the following drawbacks: (i) the existing works have not paid much attention to the importance of different types of sentiment terms, which is an important concept in this area; and (ii) the loss function currently employed does not well reflect the degree of error of sentiment misclassification. To overcome such problem, we propose to combine domain knowledge with deep learning. Our proposal includes using sentiment scores, learnt by regression, to augment training data; and introducing penalty matrix for enhancing the loss function of cross entropy. When experimented, we achieved a significant improvement in classification results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge