Tuan M. V. Le
Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes for Inferring Topics and Visualization
Oct 25, 2020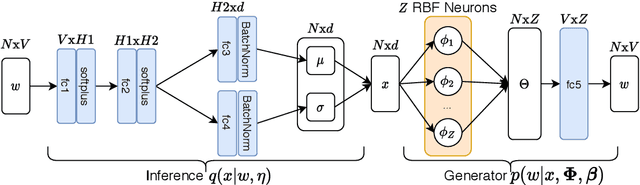
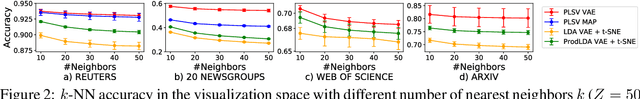
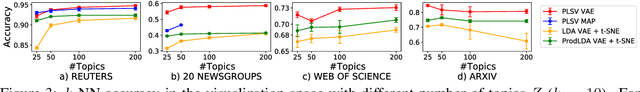
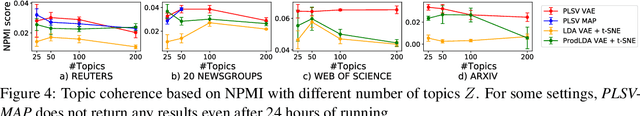
Abstract:Visualization and topic modeling are widely used approaches for text analysis. Traditional visualization methods find low-dimensional representations of documents in the visualization space (typically 2D or 3D) that can be displayed using a scatterplot. In contrast, topic modeling aims to discover topics from text, but for visualization, one needs to perform a post-hoc embedding using dimensionality reduction methods. Recent approaches propose using a generative model to jointly find topics and visualization, allowing the semantics to be infused in the visualization space for a meaningful interpretation. A major challenge that prevents these methods from being used practically is the scalability of their inference algorithms. We present, to the best of our knowledge, the first fast Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes based inference method for jointly inferring topics and visualization. Since our method is black box, it can handle model changes efficiently with little mathematical rederivation effort. We demonstrate the efficiency and effectiveness of our method on real-world large datasets and compare it with existing baselines.
WordNet-Based Information Retrieval Using Common Hypernyms and Combined Features
Jul 15, 2018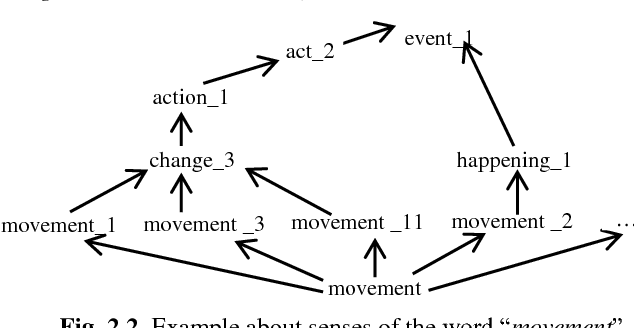
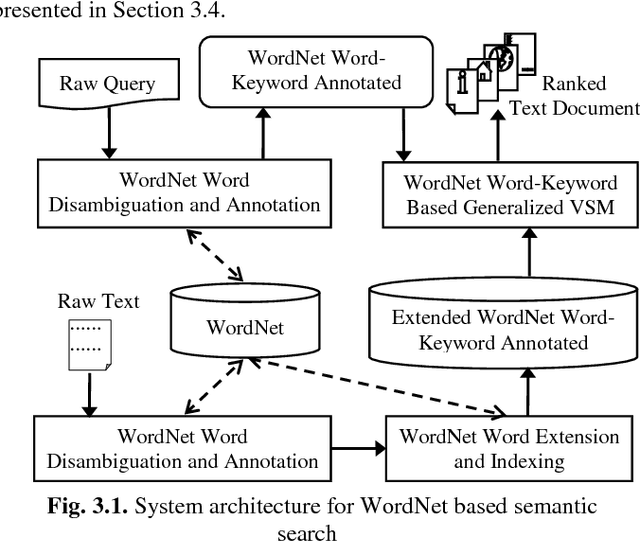
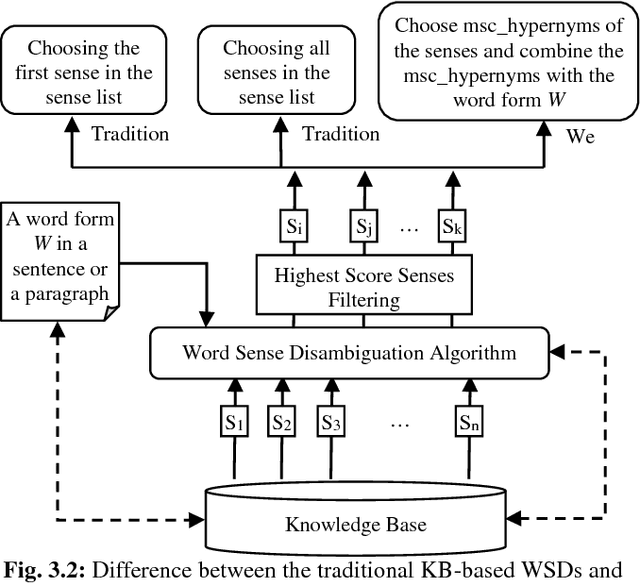
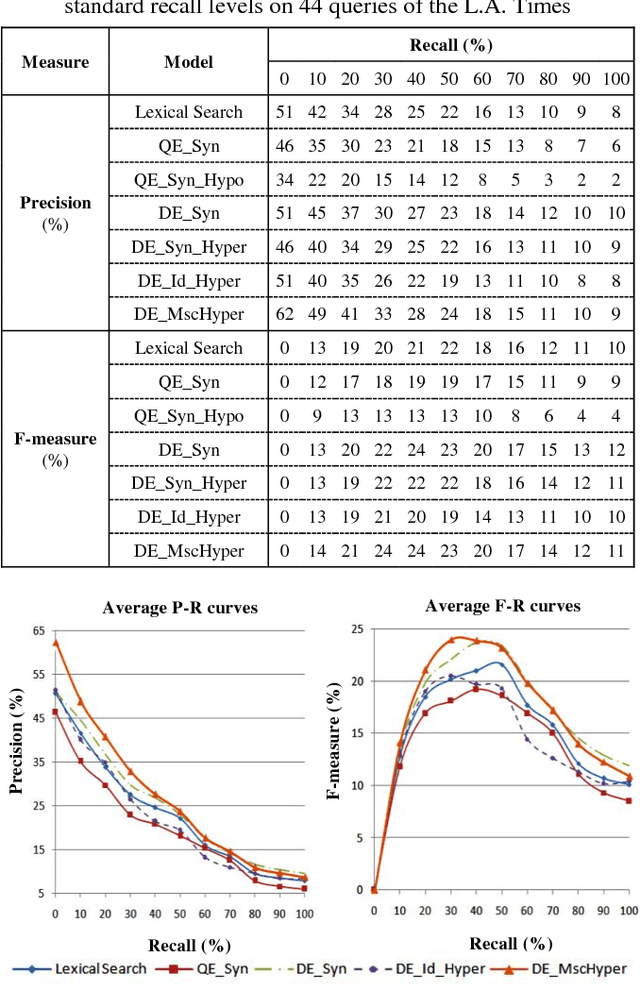
Abstract:Text search based on lexical matching of keywords is not satisfactory due to polysemous and synonymous words. Semantic search that exploits word meanings, in general, improves search performance. In this paper, we survey WordNet-based information retrieval systems, which employ a word sense disambiguation method to process queries and documents. The problem is that in many cases a word has more than one possible direct sense, and picking only one of them may give a wrong sense for the word. Moreover, the previous systems use only word forms to represent word senses and their hypernyms. We propose a novel approach that uses the most specific common hypernym of the remaining undisambiguated multi-senses of a word, as well as combined WordNet features to represent word meanings. Experiments on a benchmark dataset show that, in terms of the MAP measure, our search engine is 17.7% better than the lexical search, and at least 9.4% better than all surveyed search systems using WordNet. Keywords Ontology, word sense disambiguation, semantic annotation, semantic search.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge