Damir Vrabac
MedSelect: Selective Labeling for Medical Image Classification Combining Meta-Learning with Deep Reinforcement Learning
Mar 26, 2021


Abstract:We propose a selective learning method using meta-learning and deep reinforcement learning for medical image interpretation in the setting of limited labeling resources. Our method, MedSelect, consists of a trainable deep learning selector that uses image embeddings obtained from contrastive pretraining for determining which images to label, and a non-parametric selector that uses cosine similarity to classify unseen images. We demonstrate that MedSelect learns an effective selection strategy outperforming baseline selection strategies across seen and unseen medical conditions for chest X-ray interpretation. We also perform an analysis of the selections performed by MedSelect comparing the distribution of latent embeddings and clinical features, and find significant differences compared to the strongest performing baseline. We believe that our method may be broadly applicable across medical imaging settings where labels are expensive to acquire.
DLBCL-Morph: Morphological features computed using deep learning for an annotated digital DLBCL image set
Sep 24, 2020


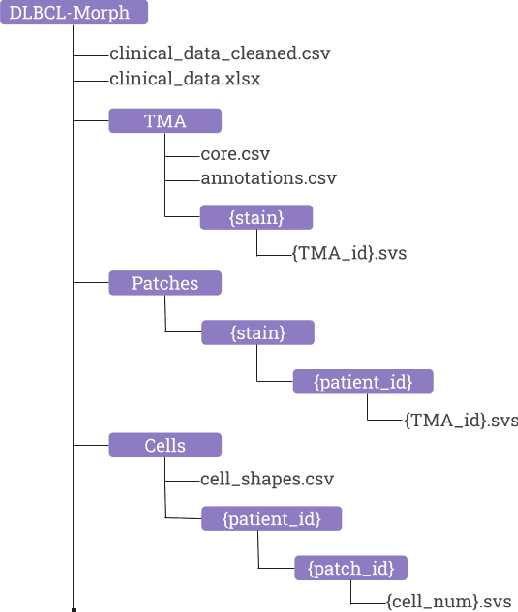
Abstract:Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Though histologically DLBCL shows varying morphologies, no morphologic features have been consistently demonstrated to correlate with prognosis. We present a morphologic analysis of histology sections from 209 DLBCL cases with associated clinical and cytogenetic data. Duplicate tissue core sections were arranged in tissue microarrays (TMAs), and replicate sections were stained with H&E and immunohistochemical stains for CD10, BCL6, MUM1, BCL2, and MYC. The TMAs are accompanied by pathologist-annotated regions-of-interest (ROIs) that identify areas of tissue representative of DLBCL. We used a deep learning model to segment all tumor nuclei in the ROIs, and computed several geometric features for each segmented nucleus. We fit a Cox proportional hazards model to demonstrate the utility of these geometric features in predicting survival outcome, and found that it achieved a C-index (95% CI) of 0.635 (0.574,0.691). Our finding suggests that geometric features computed from tumor nuclei are of prognostic importance, and should be validated in prospective studies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge