Damir Korenčić
Rudjer Bošković Institute, Croatia
What distinguishes conspiracy from critical narratives? A computational analysis of oppositional discourse
Jul 15, 2024Abstract:The current prevalence of conspiracy theories on the internet is a significant issue, tackled by many computational approaches. However, these approaches fail to recognize the relevance of distinguishing between texts which contain a conspiracy theory and texts which are simply critical and oppose mainstream narratives. Furthermore, little attention is usually paid to the role of inter-group conflict in oppositional narratives. We contribute by proposing a novel topic-agnostic annotation scheme that differentiates between conspiracies and critical texts, and that defines span-level categories of inter-group conflict. We also contribute with the multilingual XAI-DisInfodemics corpus (English and Spanish), which contains a high-quality annotation of Telegram messages related to COVID-19 (5,000 messages per language). We also demonstrate the feasibility of an NLP-based automatization by performing a range of experiments that yield strong baseline solutions. Finally, we perform an analysis which demonstrates that the promotion of intergroup conflict and the presence of violence and anger are key aspects to distinguish between the two types of oppositional narratives, i.e., conspiracy vs. critical.
IRB-NLP at SemEval-2022 Task 1: Exploring the Relationship Between Words and Their Semantic Representations
May 13, 2022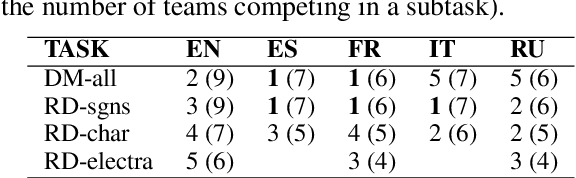
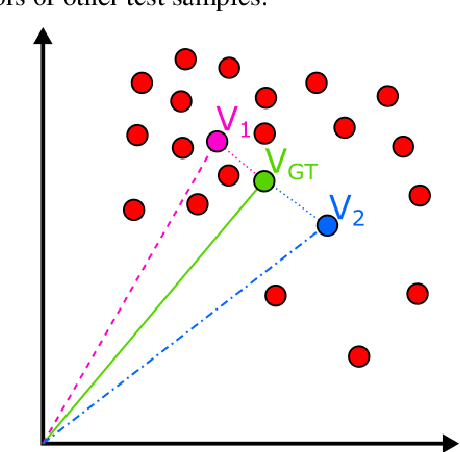
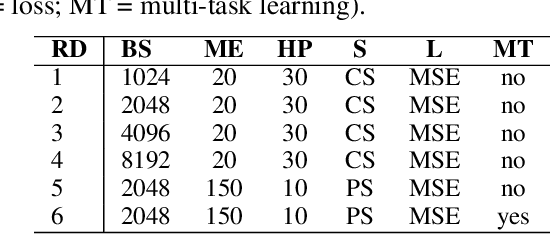
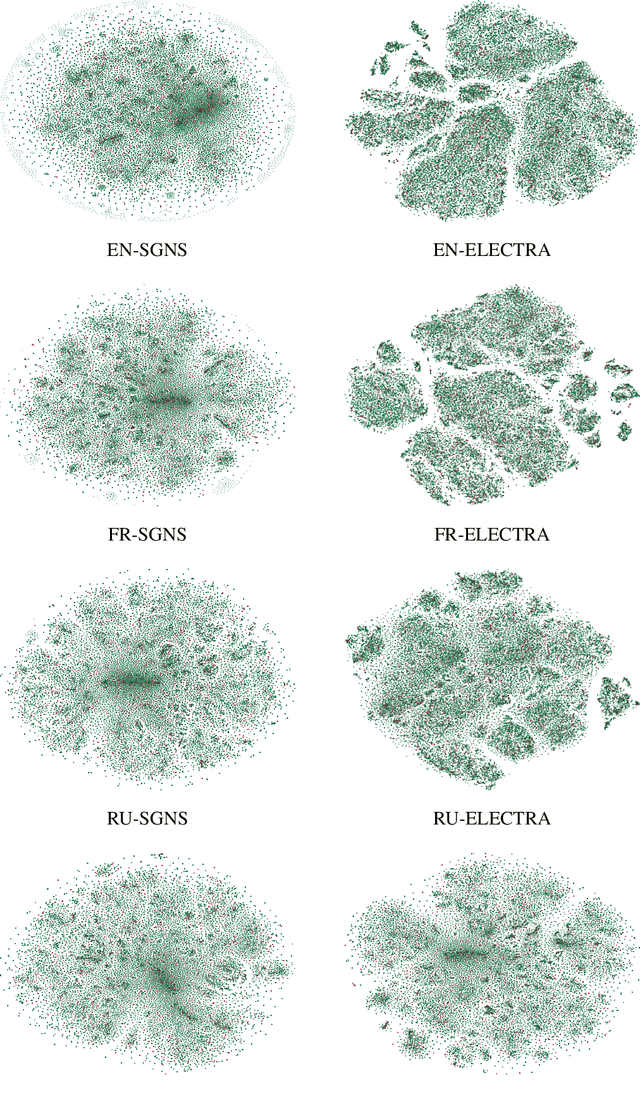
Abstract:What is the relation between a word and its description, or a word and its embedding? Both descriptions and embeddings are semantic representations of words. But, what information from the original word remains in these representations? Or more importantly, which information about a word do these two representations share? Definition Modeling and Reverse Dictionary are two opposite learning tasks that address these questions. The goal of the Definition Modeling task is to investigate the power of information laying inside a word embedding to express the meaning of the word in a humanly understandable way -- as a dictionary definition. Conversely, the Reverse Dictionary task explores the ability to predict word embeddings directly from its definition. In this paper, by tackling these two tasks, we are exploring the relationship between words and their semantic representations. We present our findings based on the descriptive, exploratory, and predictive data analysis conducted on the CODWOE dataset. We give a detailed overview of the systems that we designed for Definition Modeling and Reverse Dictionary tasks, and that achieved top scores on SemEval-2022 CODWOE challenge in several subtasks. We hope that our experimental results concerning the predictive models and the data analyses we provide will prove useful in future explorations of word representations and their relationships.
A Topic Coverage Approach to Evaluation of Topic Models
Dec 11, 2020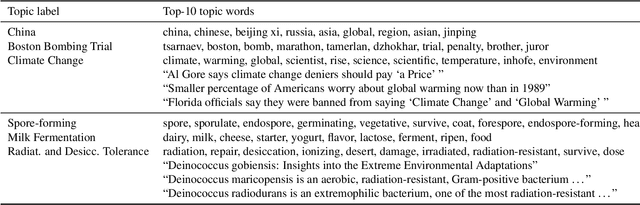
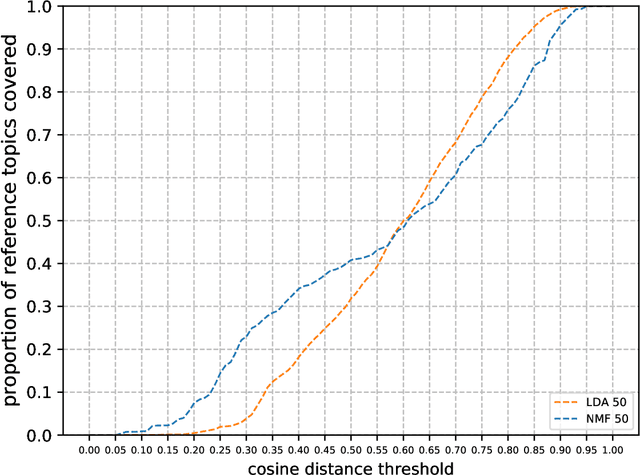
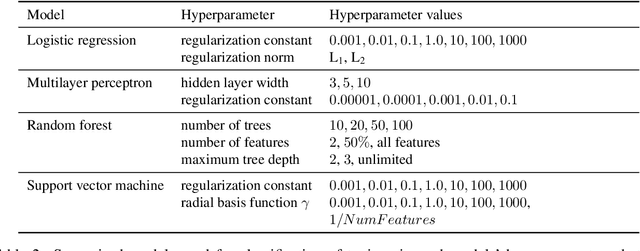
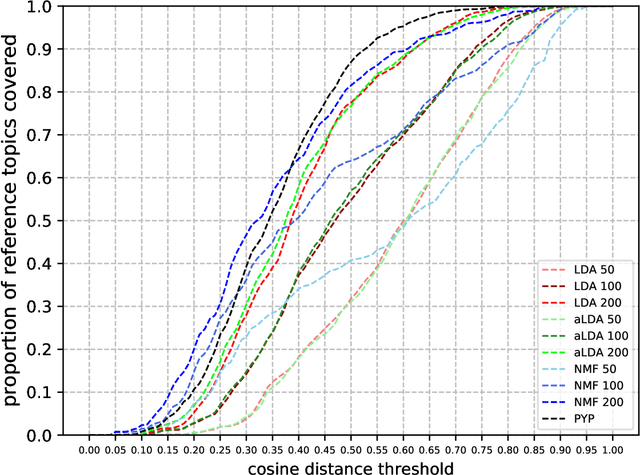
Abstract:When topic models are used for discovery of topics in text collections, a question that arises naturally is how well the model-induced topics correspond to topics of interest to the analyst. We investigate an approach to topic model evaluation based on measuring topic coverage, and propose measures of coverage based on matching between model topics and reference topics. We demonstrate the benefits of the approach by evaluating, in a series of experiments, different types of topic models on two distinct text domains. The experiments include evaluation of model quality, analysis of coverage of distinct topic categories, and the relation between coverage and other topic model evaluation methods. The contributions of the paper include the measures of coverage and the recommendations for the use of topic models for topic discovery.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge