Cunquan Qu
MGKAN: Predicting Asymmetric Drug-Drug Interactions via a Multimodal Graph Kolmogorov-Arnold Network
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Predicting drug-drug interactions (DDIs) is essential for safe pharmacological treatments. Previous graph neural network (GNN) models leverage molecular structures and interaction networks but mostly rely on linear aggregation and symmetric assumptions, limiting their ability to capture nonlinear and heterogeneous patterns. We propose MGKAN, a Graph Kolmogorov-Arnold Network that introduces learnable basis functions into asymmetric DDI prediction. MGKAN replaces conventional MLP transformations with KAN-driven basis functions, enabling more expressive and nonlinear modeling of drug relationships. To capture pharmacological dependencies, MGKAN integrates three network views-an asymmetric DDI network, a co-interaction network, and a biochemical similarity network-with role-specific embeddings to preserve directional semantics. A fusion module combines linear attention and nonlinear transformation to enhance representational capacity. On two benchmark datasets, MGKAN outperforms seven state-of-the-art baselines. Ablation studies and case studies confirm its predictive accuracy and effectiveness in modeling directional drug effects.
Logic-Guided Multistage Inference for Explainable Multidefendant Judgment Prediction
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Crime disrupts societal stability, making law essential for balance. In multidefendant cases, assigning responsibility is complex and challenges fairness, requiring precise role differentiation. However, judicial phrasing often obscures the roles of the defendants, hindering effective AI-driven analyses. To address this issue, we incorporate sentencing logic into a pretrained Transformer encoder framework to enhance the intelligent assistance in multidefendant cases while ensuring legal interpretability. Within this framework an oriented masking mechanism clarifies roles and a comparative data construction strategy improves the model's sensitivity to culpability distinctions between principals and accomplices. Predicted guilt labels are further incorporated into a regression model through broadcasting, consolidating crime descriptions and court views. Our proposed masked multistage inference (MMSI) framework, evaluated on the custom IMLJP dataset for intentional injury cases, achieves significant accuracy improvements, outperforming baselines in role-based culpability differentiation. This work offers a robust solution for enhancing intelligent judicial systems, with publicly code available.
Incorporating Legal Logic into Deep Learning: An Intelligent Approach to Probation Prediction
Aug 17, 2025Abstract:Probation is a crucial institution in modern criminal law, embodying the principles of fairness and justice while contributing to the harmonious development of society. Despite its importance, the current Intelligent Judicial Assistant System (IJAS) lacks dedicated methods for probation prediction, and research on the underlying factors influencing probation eligibility remains limited. In addition, probation eligibility requires a comprehensive analysis of both criminal circumstances and remorse. Much of the existing research in IJAS relies primarily on data-driven methodologies, which often overlooks the legal logic underpinning judicial decision-making. To address this gap, we propose a novel approach that integrates legal logic into deep learning models for probation prediction, implemented in three distinct stages. First, we construct a specialized probation dataset that includes fact descriptions and probation legal elements (PLEs). Second, we design a distinct probation prediction model named the Multi-Task Dual-Theory Probation Prediction Model (MT-DT), which is grounded in the legal logic of probation and the \textit{Dual-Track Theory of Punishment}. Finally, our experiments on the probation dataset demonstrate that the MT-DT model outperforms baseline models, and an analysis of the underlying legal logic further validates the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
Beyond Node Attention: Multi-Scale Harmonic Encoding for Feature-Wise Graph Message Passing
May 21, 2025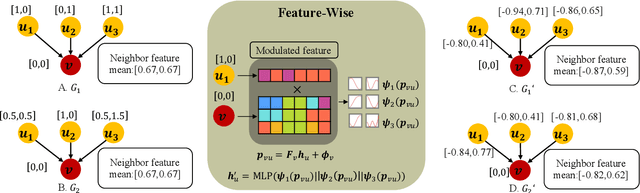
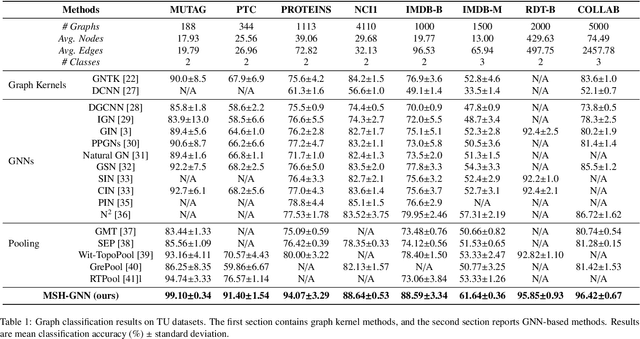
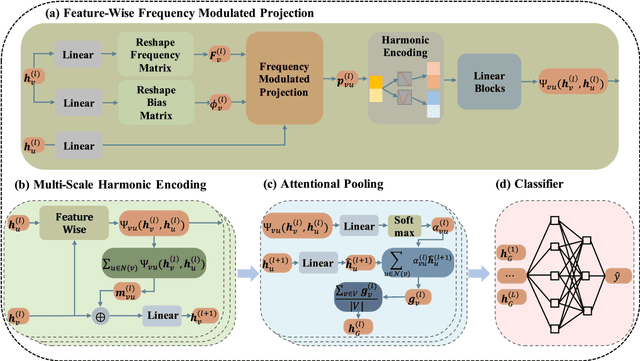
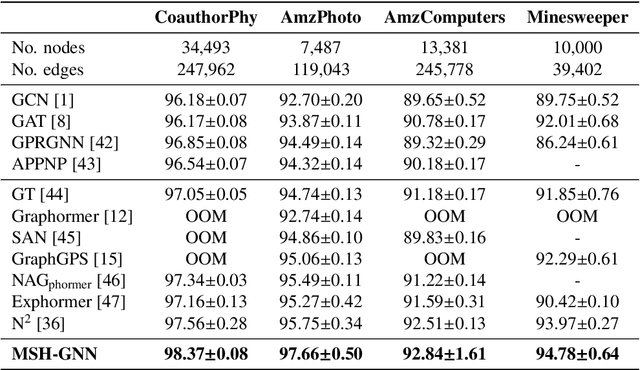
Abstract:Conventional Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) aggregate neighbor embeddings as holistic vectors, lacking the ability to identify fine-grained, direction-specific feature relevance. We propose MSH-GNN (Multi-Scale Harmonic Graph Neural Network), a novel architecture that performs feature-wise adaptive message passing through node-specific harmonic projections. For each node, MSH-GNN dynamically projects neighbor features onto frequency-sensitive directions determined by the target node's own representation. These projections are further modulated using learnable sinusoidal encodings at multiple frequencies, enabling the model to capture both smooth and oscillatory structural patterns across scales. A frequency-aware attention pooling mechanism is introduced to emphasize spectrally and structurally salient nodes during readout. Theoretically, we prove that MSH-GNN approximates shift-invariant kernels and matches the expressive power of the 1-Weisfeiler-Lehman (1-WL) test. Empirically, MSH-GNN consistently outperforms state-of-the-art models on a wide range of graph and node classification tasks. Furthermore, in challenging classification settings involving joint variations in graph topology and spectral frequency, MSH-GNN excels at capturing structural asymmetries and high-frequency modulations, enabling more accurate graph discrimination.
Atten-Transformer: A Deep Learning Framework for User App Usage Prediction
Feb 24, 2025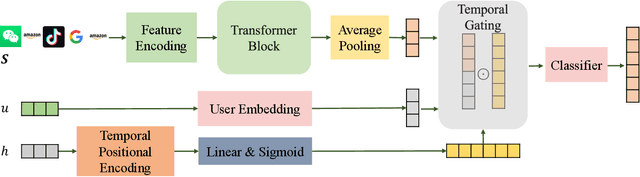
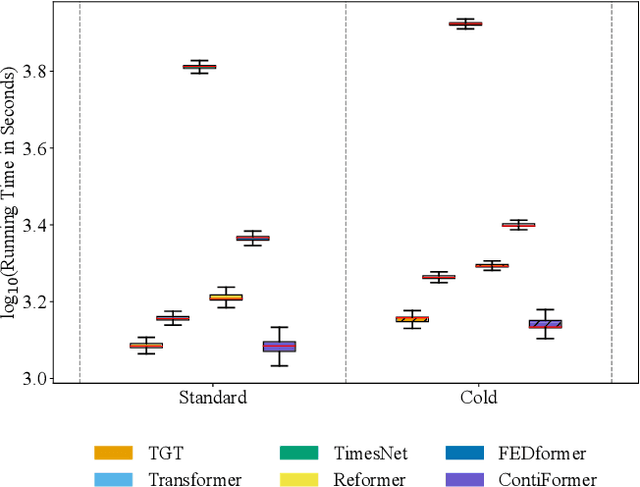
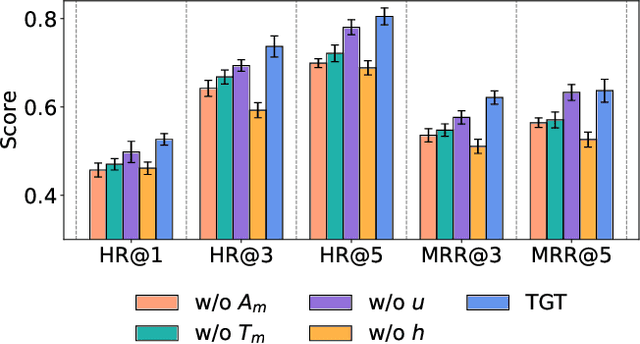
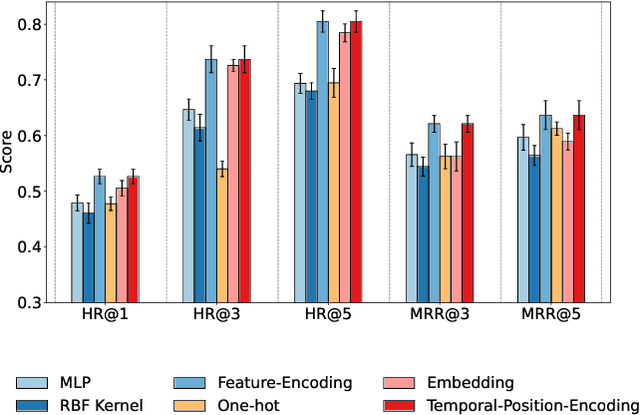
Abstract:Accurately predicting smartphone app usage patterns is crucial for user experience optimization and targeted marketing. However, existing methods struggle to capture intricate dependencies in user behavior, particularly in sparse or complex usage scenarios. To address these challenges, we introduce Atten-Transformer, a novel model that integrates temporal attention with a Transformer network to dynamically identify and leverage key app usage patterns. Unlike conventional methods that primarily consider app order and duration, our approach employs a multi-dimensional feature representation, incorporating both feature encoding and temporal encoding to enhance predictive accuracy. The proposed attention mechanism effectively assigns importance to critical app usage moments, improving both model interpretability and generalization. Extensive experiments on multiple smartphone usage datasets, including LSapp and Tsinghua App Usage datasets, demonstrate that Atten-Transformer consistently outperforms state-of-the-art models across different data splits. Specifically, our model achieves a 45.24\% improvement in HR@1 on the Tsinghua dataset (Time-based Split) and a 18.25\% improvement in HR@1 on the LSapp dataset (Cold Start Split), showcasing its robustness across diverse app usage scenarios. These findings highlight the potential of integrating adaptive attention mechanisms in mobile usage forecasting, paving the way for enhanced user engagement and resource allocation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge