Cornelius Glackin
Fraud detection in telephone conversations for financial services using linguistic features
Dec 10, 2019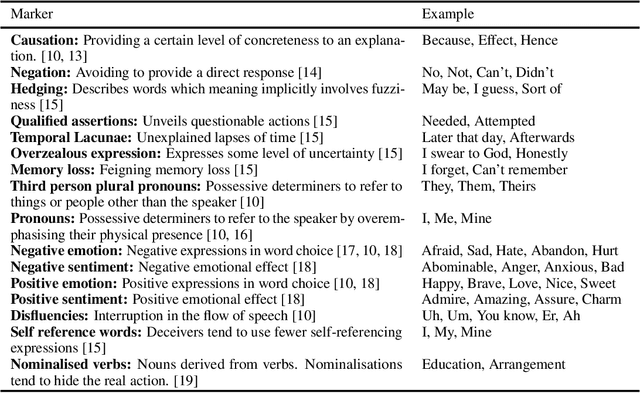

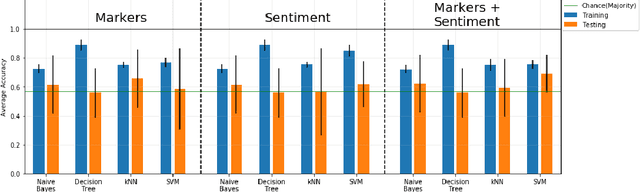
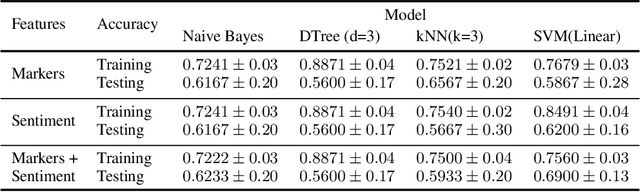
Abstract:Detecting the elements of deception in a conversation is one of the most challenging problems for the AI community. It becomes even more difficult to design a transparent system, which is fully explainable and satisfies the need for financial and legal services to be deployed. This paper presents an approach for fraud detection in transcribed telephone conversations using linguistic features. The proposed approach exploits the syntactic and semantic information of the transcription to extract both the linguistic markers and the sentiment of the customer's response. We demonstrate the results on real-world financial services data using simple, robust and explainable classifiers such as Naive Bayes, Decision Tree, Nearest Neighbours, and Support Vector Machines.
The Intelligent Voice 2016 Speaker Recognition System
Nov 02, 2016



Abstract:This paper presents the Intelligent Voice (IV) system submitted to the NIST 2016 Speaker Recognition Evaluation (SRE). The primary emphasis of SRE this year was on developing speaker recognition technology which is robust for novel languages that are much more heterogeneous than those used in the current state-of-the-art, using significantly less training data, that does not contain meta-data from those languages. The system is based on the state-of-the-art i-vector/PLDA which is developed on the fixed training condition, and the results are reported on the protocol defined on the development set of the challenge.
Changing the Environment Based on Empowerment as Intrinsic Motivation
Jun 03, 2014



Abstract:One aspect of intelligence is the ability to restructure your own environment so that the world you live in becomes more beneficial to you. In this paper we investigate how the information-theoretic measure of agent empowerment can provide a task-independent, intrinsic motivation to restructure the world. We show how changes in embodiment and in the environment change the resulting behaviour of the agent and the artefacts left in the world. For this purpose, we introduce an approximation of the established empowerment formalism based on sparse sampling, which is simpler and significantly faster to compute for deterministic dynamics. Sparse sampling also introduces a degree of randomness into the decision making process, which turns out to beneficial for some cases. We then utilize the measure to generate agent behaviour for different agent embodiments in a Minecraft-inspired three dimensional block world. The paradigmatic results demonstrate that empowerment can be used as a suitable generic intrinsic motivation to not only generate actions in given static environments, as shown in the past, but also to modify existing environmental conditions. In doing so, the emerging strategies to modify an agent's environment turn out to be meaningful to the specific agent capabilities, i.e., de facto to its embodiment.
* 31 pages, 8 figures, published in Entropy (http://www.mdpi.com/1099-4300/16/5/2789), much extended version of http://arxiv.org/abs/1310.3692
Empowerment -- an Introduction
Oct 08, 2013



Abstract:This book chapter is an introduction to and an overview of the information-theoretic, task independent utility function "Empowerment", which is defined as the channel capacity between an agent's actions and an agent's sensors. It quantifies how much influence and control an agent has over the world it can perceive. This book chapter discusses the general idea behind empowerment as an intrinsic motivation and showcases several previous applications of empowerment to demonstrate how empowerment can be applied to different sensor-motor configuration, and how the same formalism can lead to different observed behaviors. Furthermore, we also present a fast approximation for empowerment in the continuous domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge