Constantinos Patsakis
Assessing the Impact of Packing on Machine Learning-Based Malware Detection and Classification Systems
Oct 31, 2024



Abstract:The proliferation of malware, particularly through the use of packing, presents a significant challenge to static analysis and signature-based malware detection techniques. The application of packing to the original executable code renders extracting meaningful features and signatures challenging. To deal with the increasing amount of malware in the wild, researchers and anti-malware companies started harnessing machine learning capabilities with very promising results. However, little is known about the effects of packing on static machine learning-based malware detection and classification systems. This work addresses this gap by investigating the impact of packing on the performance of static machine learning-based models used for malware detection and classification, with a particular focus on those using visualisation techniques. To this end, we present a comprehensive analysis of various packing techniques and their effects on the performance of machine learning-based detectors and classifiers. Our findings highlight the limitations of current static detection and classification systems and underscore the need to be proactive to effectively counteract the evolving tactics of malware authors.
SoK: Cross-border Criminal Investigations and Digital Evidence
May 25, 2022



Abstract:Digital evidence underpin the majority of crimes as their analysis is an integral part of almost every criminal investigation. Even if we temporarily disregard the numerous challenges in the collection and analysis of digital evidence, the exchange of the evidence among the different stakeholders has many thorny issues. Of specific interest are cross-border criminal investigations as the complexity is significantly high due to the heterogeneity of legal frameworks which beyond time bottlenecks can also become prohibiting. The aim of this article is to analyse the current state of practice of cross-border investigations considering the efficacy of current collaboration protocols along with the challenges and drawbacks to be overcome. Further to performing a legally-oriented research treatise, we recall all the challenges raised in the literature and discuss them from a more practical yet global perspective. Thus, this article paves the way to enabling practitioners and stakeholders to leverage horizontal strategies to fill in the identified gaps timely and accurately.
Large-scale analysis of grooming in modern social networks
Apr 16, 2020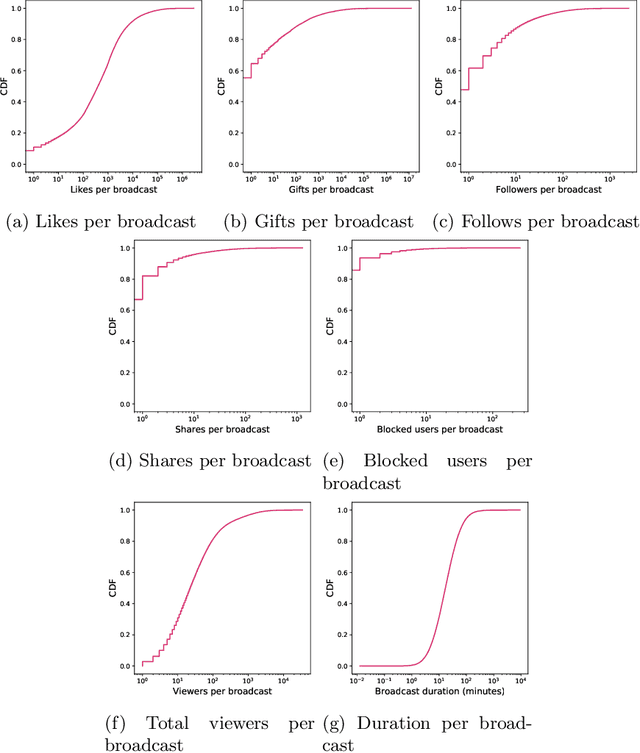
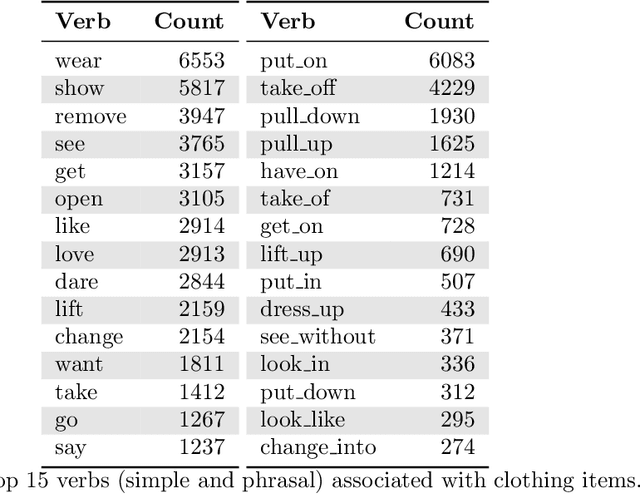
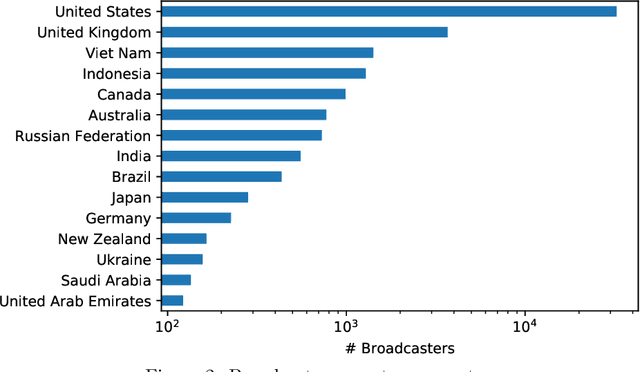
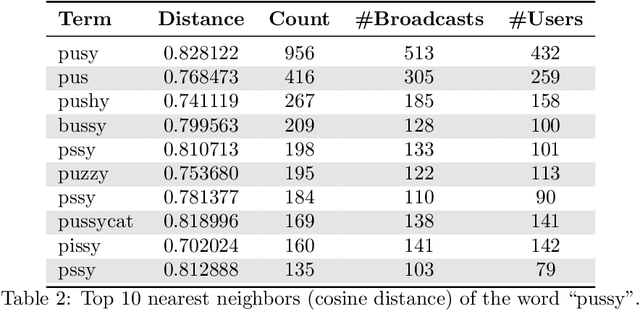
Abstract:Social networks are evolving to engage their users more by providing them with more functionalities. One of the most attracting ones is streaming. Users may broadcast part of their daily lives to thousands of others world-wide and interact with them in real-time. Unfortunately, this feature is reportedly exploited for grooming. In this work, we provide the first in-depth analysis of this problem for social live streaming services. More precisely, using a dataset that we collected, we identify predatory behaviours and grooming on chats that bypassed the moderation mechanisms of the LiveMe, the service under investigation. Beyond the traditional text approaches, we also investigate the relevance of emojis in this context, as well as the user interactions through the gift mechanisms of LiveMe. Finally, our analysis indicates the possibility of grooming towards minors, showing the extent of the problem in such platforms.
Technical Report: Implementation and Validation of a Smart Health Application
Jun 13, 2017



Abstract:In this article, we explain in detail the internal structures and databases of a smart health application. Moreover, we describe how to generate a statistically sound synthetic dataset using real-world medical data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge