Constantin Spille
Prediction of speech intelligibility with DNN-based performance measures
Mar 17, 2022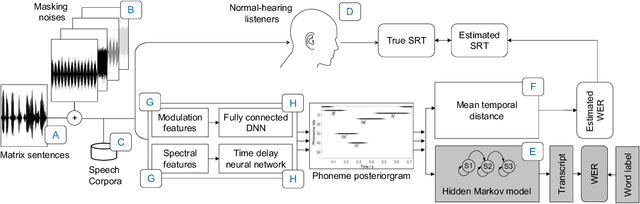


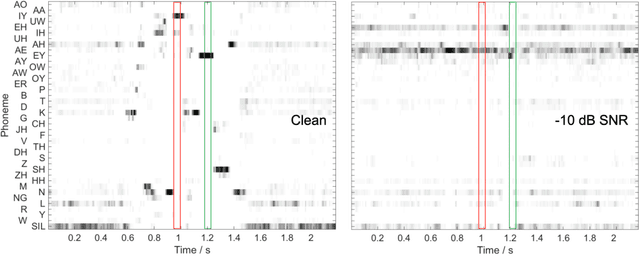
Abstract:This paper presents a speech intelligibility model based on automatic speech recognition (ASR), combining phoneme probabilities from deep neural networks (DNN) and a performance measure that estimates the word error rate from these probabilities. This model does not require the clean speech reference nor the word labels during testing as the ASR decoding step, which finds the most likely sequence of words given phoneme posterior probabilities, is omitted. The model is evaluated via the root-mean-squared error between the predicted and observed speech reception thresholds from eight normal-hearing listeners. The recognition task consists of identifying noisy words from a German matrix sentence test. The speech material was mixed with eight noise maskers covering different modulation types, from speech-shaped stationary noise to a single-talker masker. The prediction performance is compared to five established models and an ASR-model using word labels. Two combinations of features and networks were tested. Both include temporal information either at the feature level (amplitude modulation filterbanks and a feed-forward network) or captured by the architecture (mel-spectrograms and a time-delay deep neural network, TDNN). The TDNN model is on par with the DNN while reducing the number of parameters by a factor of 37; this optimization allows parallel streams on dedicated hearing aid hardware as a forward-pass can be computed within the 10ms of each frame. The proposed model performs almost as well as the label-based model and produces more accurate predictions than the baseline models.
Key Information Extraction From Documents: Evaluation And Generator
Jun 09, 2021
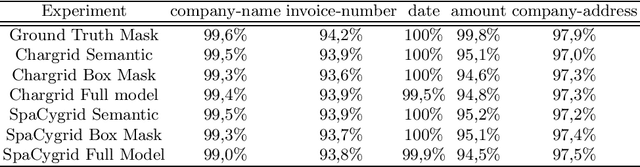
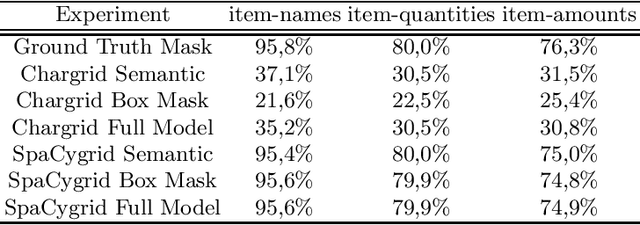
Abstract:Extracting information from documents usually relies on natural language processing methods working on one-dimensional sequences of text. In some cases, for example, for the extraction of key information from semi-structured documents, such as invoice-documents, spatial and formatting information of text are crucial to understand the contextual meaning. Convolutional neural networks are already common in computer vision models to process and extract relationships in multidimensional data. Therefore, natural language processing models have already been combined with computer vision models in the past, to benefit from e.g. positional information and to improve performance of these key information extraction models. Existing models were either trained on unpublished data sets or on an annotated collection of receipts, which did not focus on PDF-like documents. Hence, in this research project a template-based document generator was created to compare state-of-the-art models for information extraction. An existing information extraction model "Chargrid" (Katti et al., 2019) was reconstructed and the impact of a bounding box regression decoder, as well as the impact of an NLP pre-processing step was evaluated for information extraction from documents. The results have shown that NLP based pre-processing is beneficial for model performance. However, the use of a bounding box regression decoder increases the model performance only for fields that do not follow a rectangular shape.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge