Collin Farquhar
Distributed Transmission Control for Wireless Networks using Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
May 13, 2022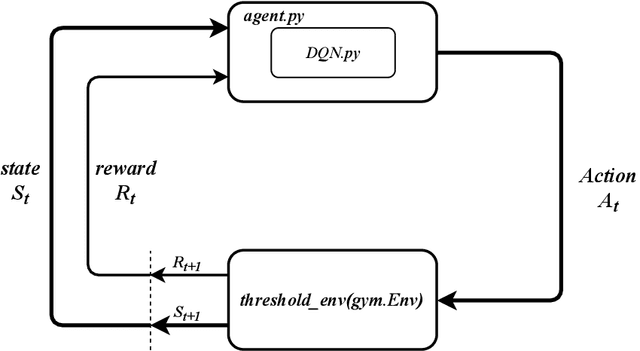
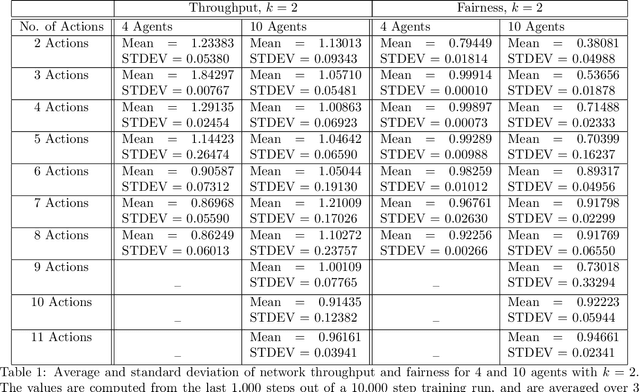
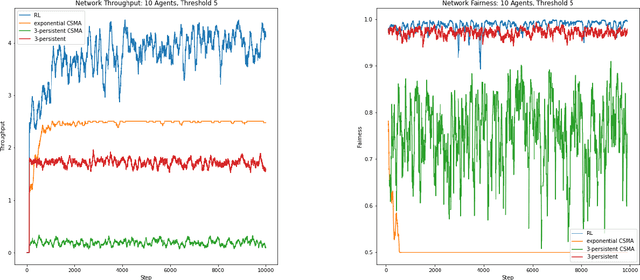
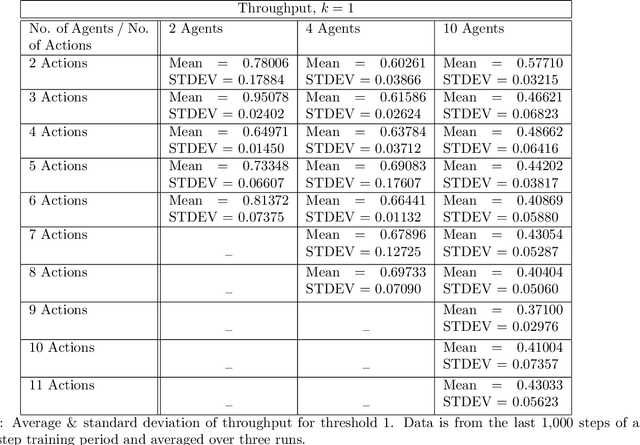
Abstract:We examine the problem of transmission control, i.e., when to transmit, in distributed wireless communications networks through the lens of multi-agent reinforcement learning. Most other works using reinforcement learning to control or schedule transmissions use some centralized control mechanism, whereas our approach is fully distributed. Each transmitter node is an independent reinforcement learning agent and does not have direct knowledge of the actions taken by other agents. We consider the case where only a subset of agents can successfully transmit at a time, so each agent must learn to act cooperatively with other agents. An agent may decide to transmit a certain number of steps into the future, but this decision is not communicated to the other agents, so it the task of the individual agents to attempt to transmit at appropriate times. We achieve this collaborative behavior through studying the effects of different actions spaces. We are agnostic to the physical layer, which makes our approach applicable to many types of networks. We submit that approaches similar to ours may be useful in other domains that use multi-agent reinforcement learning with independent agents.
MR-iNet Gym: Framework for Edge Deployment of Deep Reinforcement Learning on Embedded Software Defined Radio
Apr 09, 2022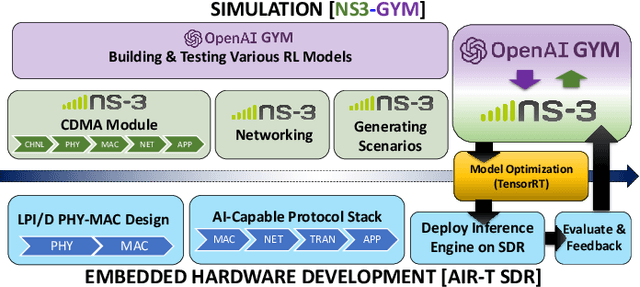
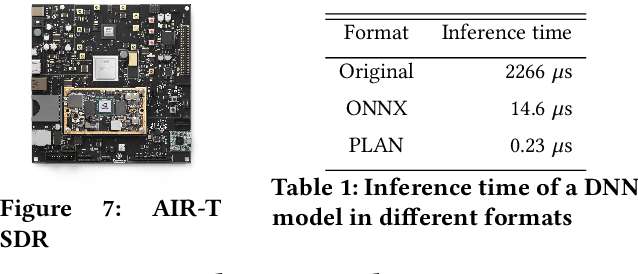
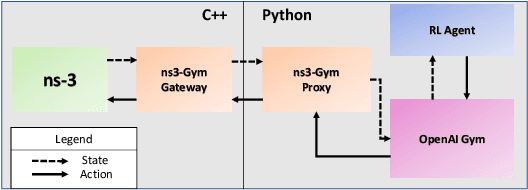
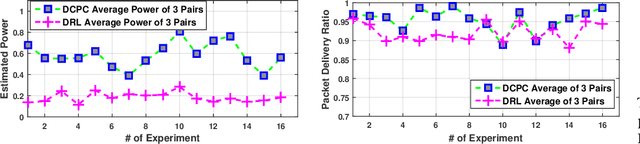
Abstract:Dynamic resource allocation plays a critical role in the next generation of intelligent wireless communication systems. Machine learning has been leveraged as a powerful tool to make strides in this domain. In most cases, the progress has been limited to simulations due to the challenging nature of hardware deployment of these solutions. In this paper, for the first time, we design and deploy deep reinforcement learning (DRL)-based power control agents on the GPU embedded software defined radios (SDRs). To this end, we propose an end-to-end framework (MR-iNet Gym) where the simulation suite and the embedded SDR development work cohesively to overcome real-world implementation hurdles. To prove feasibility, we consider the problem of distributed power control for code-division multiple access (DS-CDMA)-based LPI/D transceivers. We first build a DS-CDMA ns3 module that interacts with the OpenAI Gym environment. Next, we train the power control DRL agents in this ns3-gym simulation environment in a scenario that replicates our hardware testbed. Next, for edge (embedded on-device) deployment, the trained models are optimized for real-time operation without loss of performance. Hardware-based evaluation verifies the efficiency of DRL agents over traditional distributed constrained power control (DCPC) algorithm. More significantly, as the primary goal, this is the first work that has established the feasibility of deploying DRL to provide optimized distributed resource allocation for next-generation of GPU-embedded radios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge