Colin N Jones
Data-driven adaptive building thermal controller tuning with constraints: A primal-dual contextual Bayesian optimization approach
Oct 01, 2023



Abstract:We study the problem of tuning the parameters of a room temperature controller to minimize its energy consumption, subject to the constraint that the daily cumulative thermal discomfort of the occupants is below a given threshold. We formulate it as an online constrained black-box optimization problem where, on each day, we observe some relevant environmental context and adaptively select the controller parameters. In this paper, we propose to use a data-driven Primal-Dual Contextual Bayesian Optimization (PDCBO) approach to solve this problem. In a simulation case study on a single room, we apply our algorithm to tune the parameters of a Proportional Integral (PI) heating controller and the pre-heating time. Our results show that PDCBO can save up to 4.7% energy consumption compared to other state-of-the-art Bayesian optimization-based methods while keeping the daily thermal discomfort below the given tolerable threshold on average. Additionally, PDCBO can automatically track time-varying tolerable thresholds while existing methods fail to do so. We then study an alternative constrained tuning problem where we aim to minimize the thermal discomfort with a given energy budget. With this formulation, PDCBO reduces the average discomfort by up to 63% compared to state-of-the-art safe optimization methods while keeping the average daily energy consumption below the required threshold.
Violation-Aware Contextual Bayesian Optimization for Controller Performance Optimization with Unmodeled Constraints
Jan 28, 2023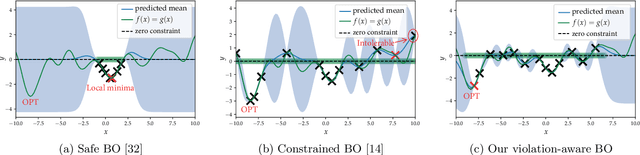



Abstract:We study the problem of performance optimization of closed-loop control systems with unmodeled dynamics. Bayesian optimization (BO) has been demonstrated to be effective for improving closed-loop performance by automatically tuning controller gains or reference setpoints in a model-free manner. However, BO methods have rarely been tested on dynamical systems with unmodeled constraints and time-varying ambient conditions. In this paper, we propose a violation-aware contextual BO algorithm (VACBO) that optimizes closed-loop performance while simultaneously learning constraint-feasible solutions under time-varying ambient conditions. Unlike classical constrained BO methods which allow unlimited constraint violations, or 'safe' BO algorithms that are conservative and try to operate with near-zero violations, we allow budgeted constraint violations to improve constraint learning and accelerate optimization. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed VACBO method for energy minimization of industrial vapor compression systems under time-varying ambient temperature and humidity.
VABO: Violation-Aware Bayesian Optimization for Closed-Loop Control Performance Optimization with Unmodeled Constraints
Oct 14, 2021
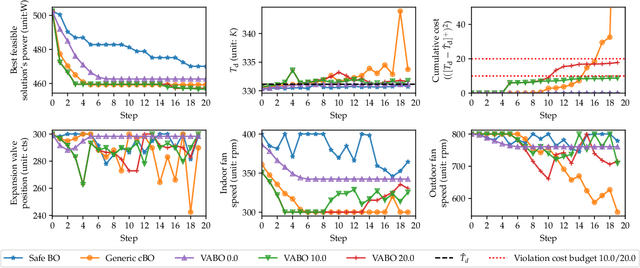
Abstract:We study the problem of performance optimization of closed-loop control systems with unmodeled dynamics. Bayesian optimization (BO) has been demonstrated effective for improving closed-loop performance by automatically tuning controller gains or reference setpoints in a model-free manner. However, BO methods have rarely been tested on dynamical systems with unmodeled constraints. In this paper, we propose a violation-aware BO algorithm (VABO) that optimizes closed-loop performance while simultaneously learning constraint-feasible solutions. Unlike classical constrained BO methods which allow an unlimited constraint violations, or safe BO algorithms that are conservative and try to operate with near-zero violations, we allow budgeted constraint violations to improve constraint learning and accelerate optimization. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed VABO method for energy minimization of industrial vapor compression systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge