Clodéric Mars
Human-AI Collaboration in Real-World Complex Environment with Reinforcement Learning
Dec 23, 2023Abstract:Recent advances in reinforcement learning (RL) and Human-in-the-Loop (HitL) learning have made human-AI collaboration easier for humans to team with AI agents. Leveraging human expertise and experience with AI in intelligent systems can be efficient and beneficial. Still, it is unclear to what extent human-AI collaboration will be successful, and how such teaming performs compared to humans or AI agents only. In this work, we show that learning from humans is effective and that human-AI collaboration outperforms human-controlled and fully autonomous AI agents in a complex simulation environment. In addition, we have developed a new simulator for critical infrastructure protection, focusing on a scenario where AI-powered drones and human teams collaborate to defend an airport against enemy drone attacks. We develop a user interface to allow humans to assist AI agents effectively. We demonstrated that agents learn faster while learning from policy correction compared to learning from humans or agents. Furthermore, human-AI collaboration requires lower mental and temporal demands, reduces human effort, and yields higher performance than if humans directly controlled all agents. In conclusion, we show that humans can provide helpful advice to the RL agents, allowing them to improve learning in a multi-agent setting.
Curriculum Learning for Cooperation in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Dec 19, 2023



Abstract:While there has been significant progress in curriculum learning and continuous learning for training agents to generalize across a wide variety of environments in the context of single-agent reinforcement learning, it is unclear if these algorithms would still be valid in a multi-agent setting. In a competitive setting, a learning agent can be trained by making it compete with a curriculum of increasingly skilled opponents. However, a general intelligent agent should also be able to learn to act around other agents and cooperate with them to achieve common goals. When cooperating with other agents, the learning agent must (a) learn how to perform the task (or subtask), and (b) increase the overall team reward. In this paper, we aim to answer the question of what kind of cooperative teammate, and a curriculum of teammates should a learning agent be trained with to achieve these two objectives. Our results on the game Overcooked show that a pre-trained teammate who is less skilled is the best teammate for overall team reward but the worst for the learning of the agent. Moreover, somewhat surprisingly, a curriculum of teammates with decreasing skill levels performs better than other types of curricula.
Human-Machine Teaming for UAVs: An Experimentation Platform
Dec 18, 2023Abstract:Full automation is often not achievable or desirable in critical systems with high-stakes decisions. Instead, human-AI teams can achieve better results. To research, develop, evaluate, and validate algorithms suited for such teaming, lightweight experimentation platforms that enable interactions between humans and multiple AI agents are necessary. However, there are limited examples of such platforms for defense environments. To address this gap, we present the Cogment human-machine teaming experimentation platform, which implements human-machine teaming (HMT) use cases that features heterogeneous multi-agent systems and can involve learning AI agents, static AI agents, and humans. It is built on the Cogment platform and has been used for academic research, including work presented at the ALA workshop at AAMAS this year [1]. With this platform, we hope to facilitate further research on human-machine teaming in critical systems and defense environments.
Cogment: Open Source Framework For Distributed Multi-actor Training, Deployment & Operations
Jun 21, 2021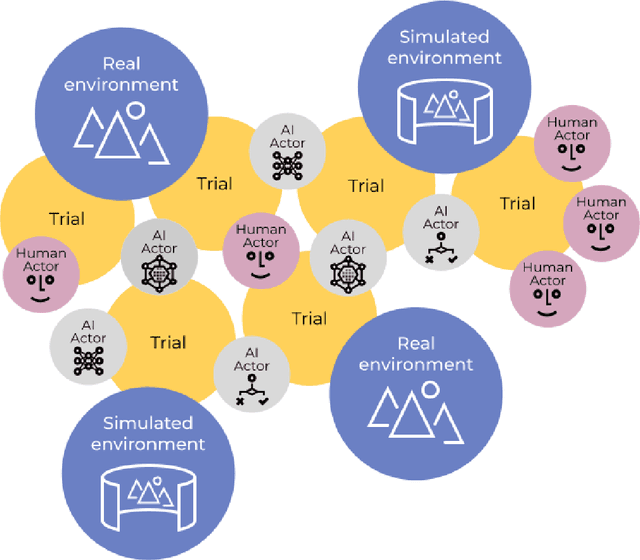
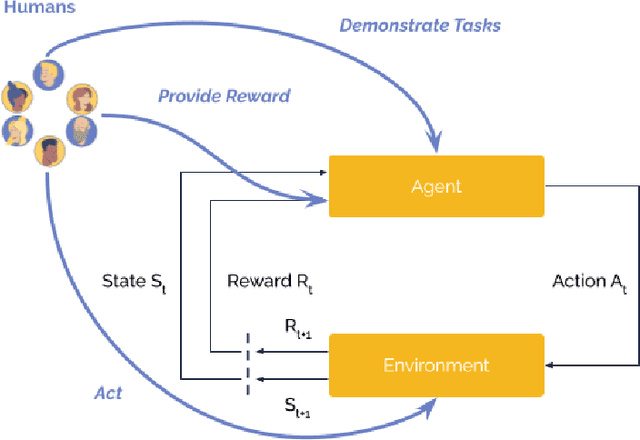
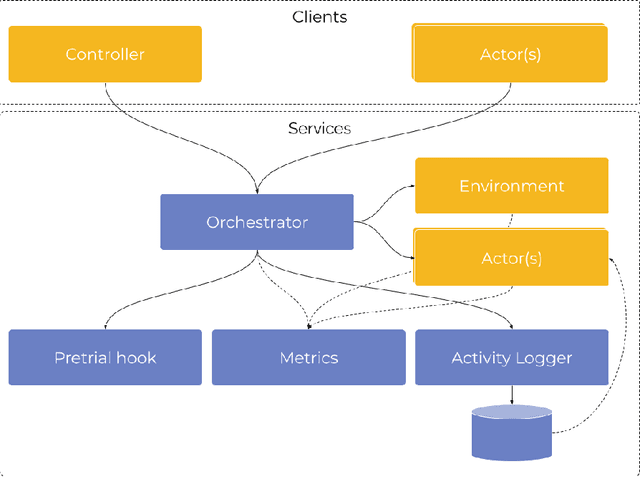
Abstract:Involving humans directly for the benefit of AI agents' training is getting traction thanks to several advances in reinforcement learning and human-in-the-loop learning. Humans can provide rewards to the agent, demonstrate tasks, design a curriculum, or act in the environment, but these benefits also come with architectural, functional design and engineering complexities. We present Cogment, a unifying open-source framework that introduces an actor formalism to support a variety of humans-agents collaboration typologies and training approaches. It is also scalable out of the box thanks to a distributed micro service architecture, and offers solutions to the aforementioned complexities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge