Claire Arthur
Survey on the Evaluation of Generative Models in Music
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Research on generative systems in music has seen considerable attention and growth in recent years. A variety of attempts have been made to systematically evaluate such systems. We provide an interdisciplinary review of the common evaluation targets, methodologies, and metrics for the evaluation of both system output and model usability, covering subjective and objective approaches, qualitative and quantitative approaches, as well as empirical and computational methods. We discuss the advantages and challenges of such approaches from a musicological, an engineering, and an HCI perspective.
Presenting the SWTC: A Symbolic Corpus of Themes from John Williams' Star Wars Episodes I-IX
Sep 06, 2023



Abstract:This paper presents a new symbolic corpus of musical themes from the complete Star Wars trilogies (Episodes I-IX) by John Williams. The corpus files are made available in multiple formats (.krn, .sib, and .musicxml) and include melodic, harmonic, and formal information. The Star Wars Thematic Corpus (SWTC) contains a total of 64 distinctive, recurring, and symbolically meaningful themes and motifs, commonly referred to as leitmotifs. Through this corpus we also introduce a new humdrum standard for non-functional harmony encodings, **harte, based on Harte (2005, 2010). This report details the motivation, describes the transcription and encoding processes, and provides some brief summary statistics. While relatively small in scale, the SWTC represents a unified collection from one of the most prolific and influential composers of the 20th century, and the under-studied subset of film and multimedia musical material in general. We hope the SWTC will provide insights into John Williams' compositional style, as well as prove useful in comparisons against other thematic corpora from film and beyond.
A Statistical Model for Melody Reduction
May 12, 2021



Abstract:A commonly-cited reason for the poor performance of automatic chord estimation (ACE) systems within music information retrieval (MIR) is that non-chord tones (i.e., notes outside the supporting harmony) contribute to error during the labeling process. Despite the prevalence of machine learning approaches in MIR, there are cases where alternative approaches provide a simpler alternative while allowing for insights into musicological practices. In this project, we present a statistical model for predicting chord tones based on music theory rules. Our model is currently focused on predicting chord tones in classical music, since composition in this style is highly constrained, theoretically making the placement of chord tones highly predictable. Indeed, music theorists have labeling systems for every variety of non-chord tone, primarily classified by the note's metric position and intervals of approach and departure. Using metric position, duration, and melodic intervals as predictors, we build a statistical model for predicting chord tones using the TAVERN dataset. While our probabilistic approach is similar to other efforts in the domain of automatic harmonic analysis, our focus is on melodic reduction rather than predicting harmony. However, we hope to pursue applications for ACE in the future. Finally, we implement our melody reduction model using an existing symbolic visualization tool, to assist with melody reduction and non-chord tone identification for computational musicology researchers and music theorists.
An Interdisciplinary Review of Music Performance Analysis
Apr 19, 2021
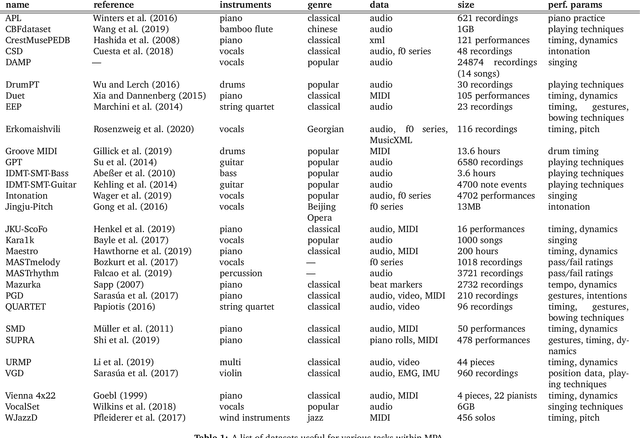
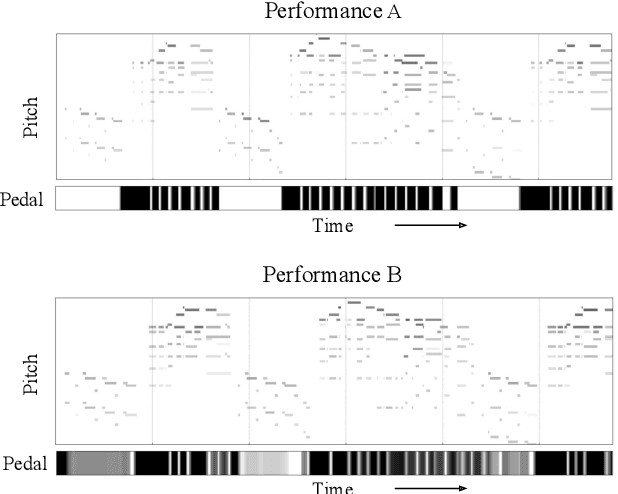
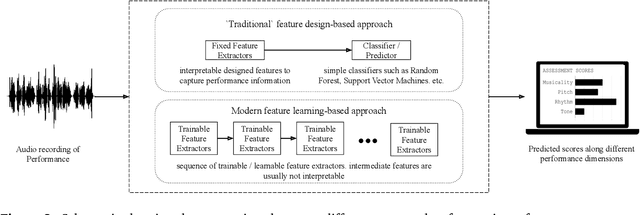
Abstract:A musical performance renders an acoustic realization of a musical score or other representation of a composition. Different performances of the same composition may vary in terms of performance parameters such as timing or dynamics, and these variations may have a major impact on how a listener perceives the music. The analysis of music performance has traditionally been a peripheral topic for the MIR research community, where often a single audio recording is used as representative of a musical work. This paper surveys the field of Music Performance Analysis (MPA) from several perspectives including the measurement of performance parameters, the relation of those parameters to the actions and intentions of a performer or perceptual effects on a listener, and finally the assessment of musical performance. This paper also discusses MPA as it relates to MIR, pointing out opportunities for collaboration and future research in both areas.
* arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:1907.00178
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge