Chuanjian Zheng
Single-shot quantitative differential phase contrast imaging combined with programmable polarization multiplexing illumination
Apr 13, 2023

Abstract:We propose a single-shot quantitative differential phase contrast (DPC) method with polarization multiplexing illumination. In the illumination module of our system, the programmable LED array is divided into four quadrants and covered with polarizing films of four different polarization angles. We use a polarization camera with polarizers before the pixels in the imaging module. By matching the polarization angle between the polarizing films over the custom LED array and the polarizers in the camera, two sets of asymmetric illumination acquisition images can be calculated from a single-shot acquisition image. Combined with the phase transfer function, we can calculate the quantitative phase of the sample. We present the design, implementation, and experimental image data demonstrating the ability of our method to obtain quantitative phase images of the phase resolution target, as well as Hela cells.
Robust full-pose-parameter estimation for the LED array in Fourier ptychographic microscopy
Jun 11, 2022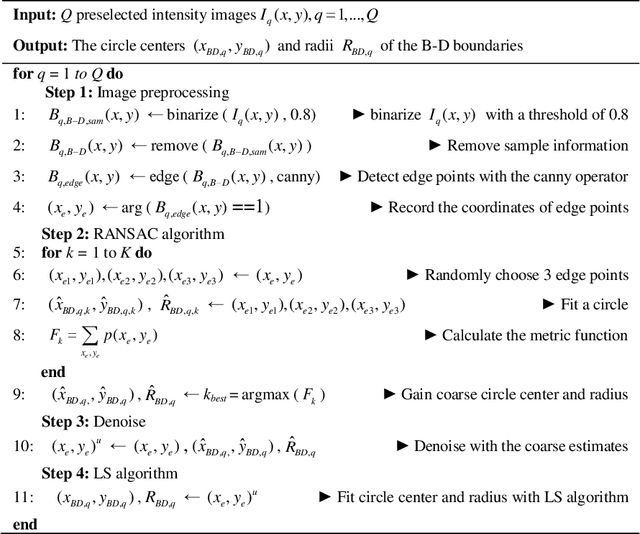
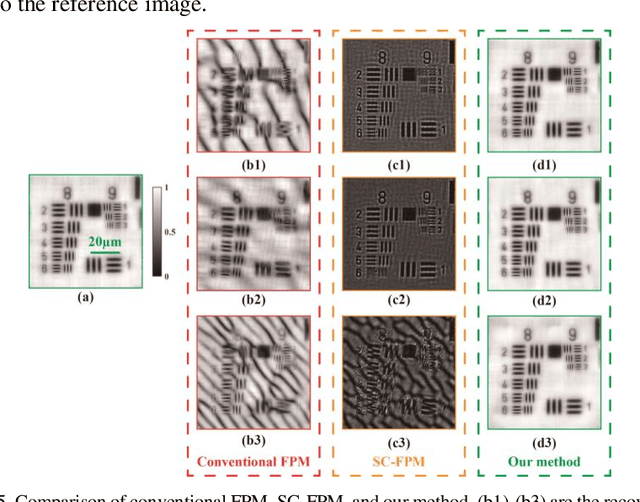

Abstract:Fourier ptychographic microscopy (FPM) can achieve quantitative phase imaging with a large space-bandwidth product by synthesizing a set of low-resolution intensity images captured under angularly varying illuminations. Determining accurate illumination angles is critical because the consistency between actual systematic parameters and those used in the recovery algorithm is essential for high-quality imaging. This paper presents a full-pose-parameter and physics-based method for calibrating illumination angles. Using a physics-based model constructed with general knowledge of the employed microscope and the brightfield-to-darkfield boundaries inside captured images, we can solve for the full-pose parameters of misplaced LED array, which consist of the distance between the sample and the LED array, two orthogonal lateral shifts, one in-plane rotation angle, and two tilt angles, to correct illumination angles precisely. The feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed method for recovering random or remarkable pose parameters have been demonstrated by both qualitative and quantitative experiments. Due to the completeness of the pose parameters, the clarity of the physical model, and the high robustness for arbitrary misalignments, our method can significantly facilitate the design, implementation, and application of concise and robust FPM platforms.
Fourier ptychography multi-parameter neural network with composite physical priori optimization
Feb 18, 2022



Abstract:Fourier ptychography microscopy(FP) is a recently developed computational imaging approach for microscopic super-resolution imaging. By turning on each light-emitting-diode (LED) located on different position on the LED array sequentially and acquiring the corresponding images that contain different spatial frequency components, high spatial resolution and quantitative phase imaging can be achieved in the case of large field-of-view. Nevertheless, FPM has high requirements for the system construction and data acquisition processes, such as precise LEDs position, accurate focusing and appropriate exposure time, which brings many limitations to its practical applications. In this paper, inspired by artificial neural network, we propose a Fourier ptychography multi-parameter neural network (FPMN) with composite physical prior optimization. A hybrid parameter determination strategy combining physical imaging model and data-driven network training is proposed to recover the multi layers of the network corresponding to different physical parameters, including sample complex function, system pupil function, defocus distance, LED array position deviation and illumination intensity fluctuation, etc. Among these parameters, LED array position deviation is recovered based on the features of brightfield to darkfield transition low-resolution images while the others are recovered in the process of training of the neural network. The feasibility and effectiveness of FPMN are verified through simulations and actual experiments. Therefore FPMN can evidently reduce the requirement for practical applications of FPM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge