Christopher Collins
Computational Skills by Stealth in Secondary School Data Science
Oct 08, 2020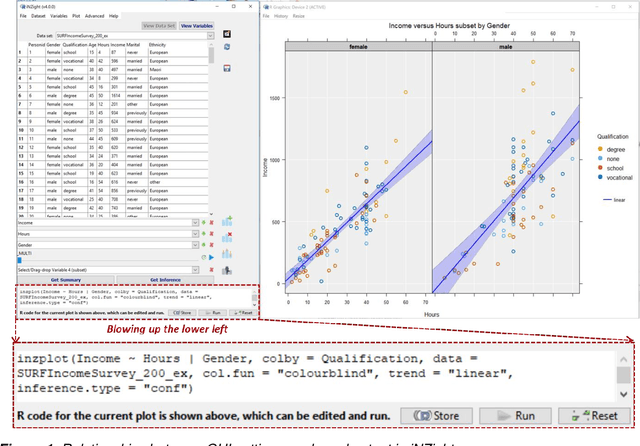
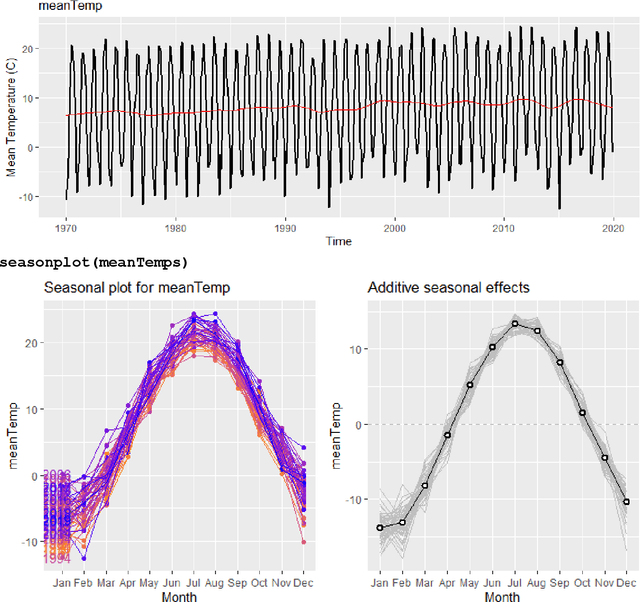
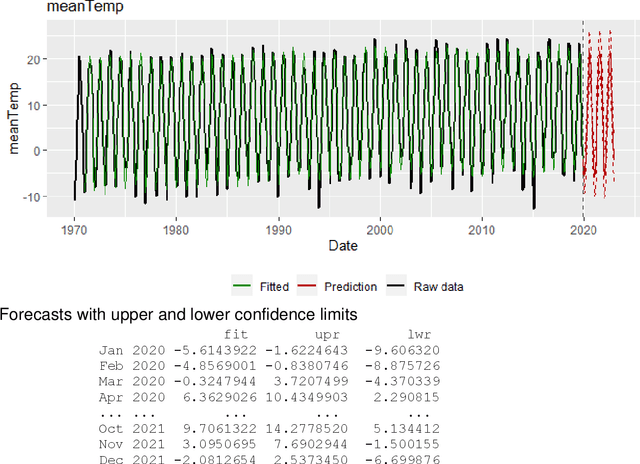
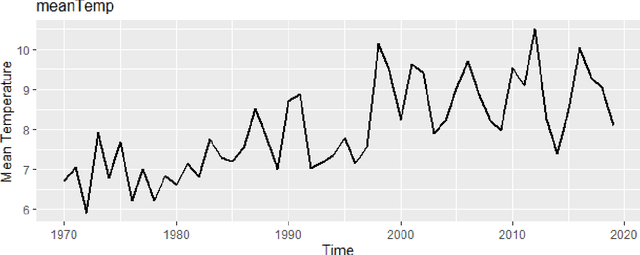
Abstract:The unprecedented growth in the availability of data of all types and qualities and the emergence of the field of data science has provided an impetus to finally realizing the implementation of the full breadth of the Nolan and Temple Lang proposed integration of computing concepts into statistics curricula at all levels in statistics and new data science programs and courses. Moreover, data science, implemented carefully, opens accessible pathways to stem for students for whom neither mathematics nor computer science are natural affinities, and who would traditionally be excluded. We discuss a proposal for the stealth development of computational skills in students' first exposure to data science through careful, scaffolded exposure to computation and its power. The intent of this approach is to support students, regardless of interest and self-efficacy in coding, in becoming data-driven learners, who are capable of asking complex questions about the world around them, and then answering those questions through the use of data-driven inquiry. This discussion is presented in the context of the International Data Science in Schools Project which recently published computer science and statistics consensus curriculum frameworks for a two-year secondary school data science program, designed to make data science accessible to all.
Semantic Concept Spaces: Guided Topic Model Refinement using Word-Embedding Projections
Aug 01, 2019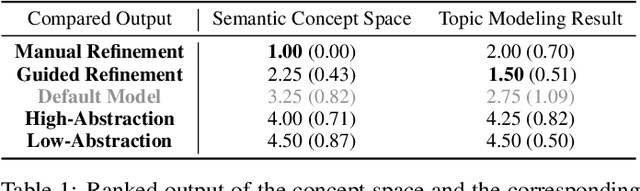
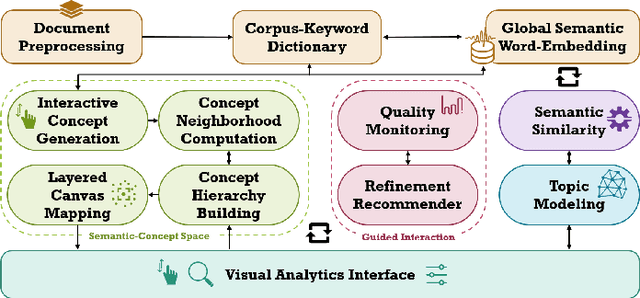
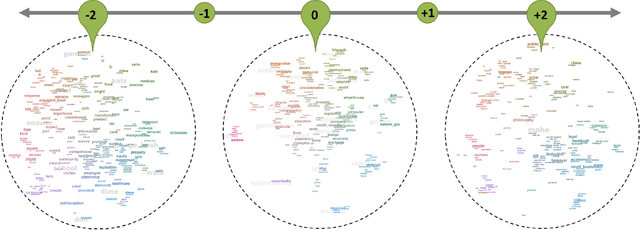

Abstract:We present a framework that allows users to incorporate the semantics of their domain knowledge for topic model refinement while remaining model-agnostic. Our approach enables users to (1) understand the semantic space of the model, (2) identify regions of potential conflicts and problems, and (3) readjust the semantic relation of concepts based on their understanding, directly influencing the topic modeling. These tasks are supported by an interactive visual analytics workspace that uses word-embedding projections to define concept regions which can then be refined. The user-refined concepts are independent of a particular document collection and can be transferred to related corpora. All user interactions within the concept space directly affect the semantic relations of the underlying vector space model, which, in turn, change the topic modeling. In addition to direct manipulation, our system guides the users' decision-making process through recommended interactions that point out potential improvements. This targeted refinement aims at minimizing the feedback required for an efficient human-in-the-loop process. We confirm the improvements achieved through our approach in two user studies that show topic model quality improvements through our visual knowledge externalization and learning process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge