Christopher Chiu
AgentScore: Autoformulation of Deployable Clinical Scoring Systems
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Modern clinical practice relies on evidence-based guidelines implemented as compact scoring systems composed of a small number of interpretable decision rules. While machine-learning models achieve strong performance, many fail to translate into routine clinical use due to misalignment with workflow constraints such as memorability, auditability, and bedside execution. We argue that this gap arises not from insufficient predictive power, but from optimizing over model classes that are incompatible with guideline deployment. Deployable guidelines often take the form of unit-weighted clinical checklists, formed by thresholding the sum of binary rules, but learning such scores requires searching an exponentially large discrete space of possible rule sets. We introduce AgentScore, which performs semantically guided optimization in this space by using LLMs to propose candidate rules and a deterministic, data-grounded verification-and-selection loop to enforce statistical validity and deployability constraints. Across eight clinical prediction tasks, AgentScore outperforms existing score-generation methods and achieves AUC comparable to more flexible interpretable models despite operating under stronger structural constraints. On two additional externally validated tasks, AgentScore achieves higher discrimination than established guideline-based scores.
Fine-Grained Classification for Poisonous Fungi Identification with Transfer Learning
Jul 10, 2024



Abstract:FungiCLEF 2024 addresses the fine-grained visual categorization (FGVC) of fungi species, with a focus on identifying poisonous species. This task is challenging due to the size and class imbalance of the dataset, subtle inter-class variations, and significant intra-class variability amongst samples. In this paper, we document our approach in tackling this challenge through the use of ensemble classifier heads on pre-computed image embeddings. Our team (DS@GT) demonstrate that state-of-the-art self-supervised vision models can be utilized as robust feature extractors for downstream application of computer vision tasks without the need for task-specific fine-tuning on the vision backbone. Our approach achieved the best Track 3 score (0.345), accuracy (78.4%) and macro-F1 (0.577) on the private test set in post competition evaluation. Our code is available at https://github.com/dsgt-kaggle-clef/fungiclef-2024.
On Real-time Image Reconstruction with Neural Networks for MRI-guided Radiotherapy
Feb 10, 2022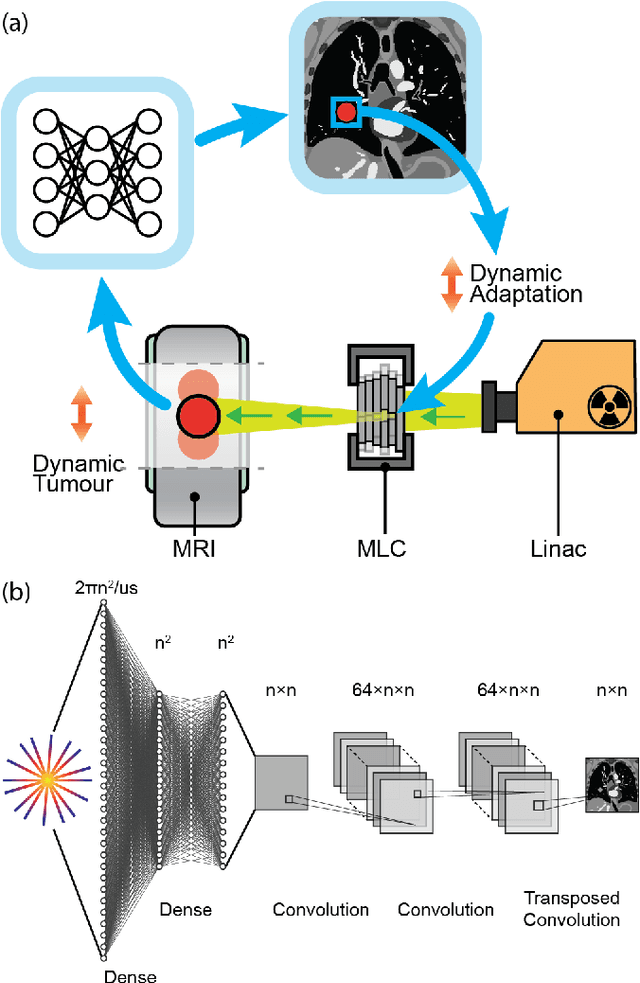
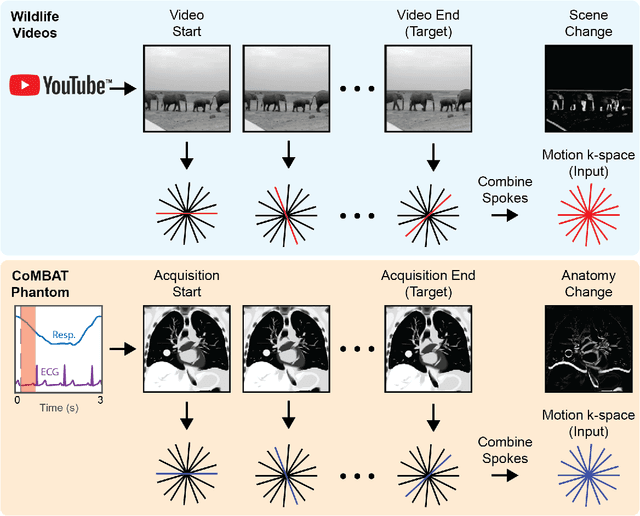
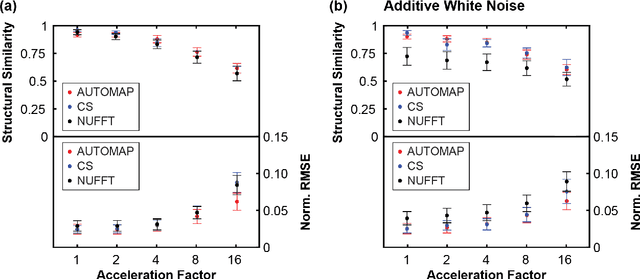
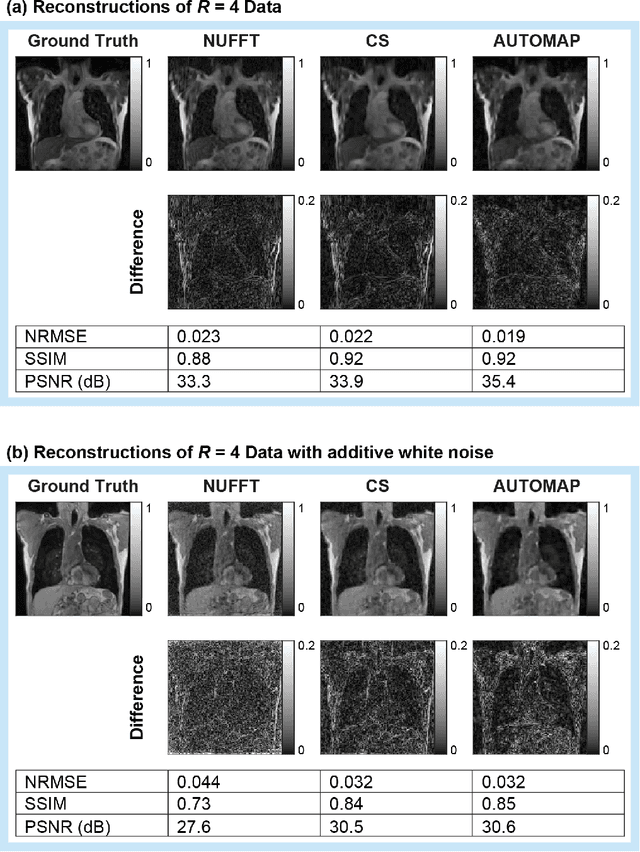
Abstract:MRI-guidance techniques that dynamically adapt radiation beams to follow tumor motion in real-time will lead to more accurate cancer treatments and reduced collateral healthy tissue damage. The gold-standard for reconstruction of undersampled MR data is compressed sensing (CS) which is computationally slow and limits the rate that images can be available for real-time adaptation. Here, we demonstrate the use of automated transform by manifold approximation (AUTOMAP), a generalized framework that maps raw MR signal to the target image domain, to rapidly reconstruct images from undersampled radial k-space data. The AUTOMAP neural network was trained to reconstruct images from a golden-angle radial acquisition, a benchmark for motion-sensitive imaging, on lung cancer patient data and generic images from ImageNet. Model training was subsequently augmented with motion-encoded k-space data derived from videos in the YouTube-8M dataset to encourage motion robust reconstruction. We find that AUTOMAP-reconstructed radial k-space has equivalent accuracy to CS but with much shorter processing times after initial fine-tuning on retrospectively acquired lung cancer patient data. Validation of motion-trained models with a virtual dynamic lung tumor phantom showed that the generalized motion properties learned from YouTube lead to improved target tracking accuracy. Our work shows that AUTOMAP can achieve real-time, accurate reconstruction of radial data. These findings imply that neural-network-based reconstruction is potentially superior to existing approaches for real-time image guidance applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge