Anthony Miyaguchi
DS@GT at TREC TOT 2025: Bridging Vague Recollection with Fusion Retrieval and Learned Reranking
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:We develop a two-stage retrieval system that combines multiple complementary retrieval methods with a learned reranker and LLM-based reranking, to address the TREC Tip-of-the-Tongue (ToT) task. In the first stage, we employ hybrid retrieval that merges LLM-based retrieval, sparse (BM25), and dense (BGE-M3) retrieval methods. We also introduce topic-aware multi-index dense retrieval that partitions the Wikipedia corpus into 24 topical domains. In the second stage, we evaluate both a trained LambdaMART reranker and LLM-based reranking. To support model training, we generate 5000 synthetic ToT queries using LLMs. Our best system achieves recall of 0.66 and NDCG@1000 of 0.41 on the test set by combining hybrid retrieval with Gemini-2.5-flash reranking, demonstrating the effectiveness of fusion retrieval.
DINOv3 as a Frozen Encoder for CRPS-Oriented Probabilistic Rainfall Nowcasting
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes a competitive and computationally efficient approach to probabilistic rainfall nowcasting. A video projector (V-JEPA Vision Transformer) associated to a lightweight probabilistic head is attached to a pre-trained satellite vision encoder (DINOv3-SAT493M) to map encoder tokens into a discrete empirical CDF (eCDF) over 4-hour accumulated rainfall. The projector-head is optimized end-to-end over the Ranked Probability Score (RPS). As an alternative, 3D-UNET baselines trained with an aggregate Rank Probability Score and a per-pixel Gamma-Hurdle objective are used. On the Weather4Cast 2025 benchmark, the proposed method achieved a promising performance, with a CRPS of 3.5102, which represents $\approx$ 26% in effectiveness gain against the best 3D-UNET.
DS@GT AnimalCLEF: Triplet Learning over ViT Manifolds with Nearest Neighbor Classification for Animal Re-identification
Sep 15, 2025Abstract:This paper details the DS@GT team's entry for the AnimalCLEF 2025 re-identification challenge. Our key finding is that the effectiveness of post-hoc metric learning is highly contingent on the initial quality and domain-specificity of the backbone embeddings. We compare a general-purpose model (DINOv2) with a domain-specific model (MegaDescriptor) as a backbone. A K-Nearest Neighbor classifier with robust thresholding then identifies known individuals or flags new ones. While a triplet-learning projection head improved the performance of the specialized MegaDescriptor model by 0.13 points, it yielded minimal gains (0.03) for the general-purpose DINOv2 on averaged BAKS and BAUS. We demonstrate that the general-purpose manifold is more difficult to reshape for fine-grained tasks, as evidenced by stagnant validation loss and qualitative visualizations. This work highlights the critical limitations of refining general-purpose features for specialized, limited-data re-ID tasks and underscores the importance of domain-specific pre-training. The implementation for this work is publicly available at github.com/dsgt-arc/animalclef-2025.
Tile-Based ViT Inference with Visual-Cluster Priors for Zero-Shot Multi-Species Plant Identification
Jul 08, 2025Abstract:We describe DS@GT's second-place solution to the PlantCLEF 2025 challenge on multi-species plant identification in vegetation quadrat images. Our pipeline combines (i) a fine-tuned Vision Transformer ViTD2PC24All for patch-level inference, (ii) a 4x4 tiling strategy that aligns patch size with the network's 518x518 receptive field, and (iii) domain-prior adaptation through PaCMAP + K-Means visual clustering and geolocation filtering. Tile predictions are aggregated by majority vote and re-weighted with cluster-specific Bayesian priors, yielding a macro-averaged F1 of 0.348 (private leaderboard) while requiring no additional training. All code, configuration files, and reproducibility scripts are publicly available at https://github.com/dsgt-arc/plantclef-2025.
Annotation Techniques for Judo Combat Phase Classification from Tournament Footage
Dec 10, 2024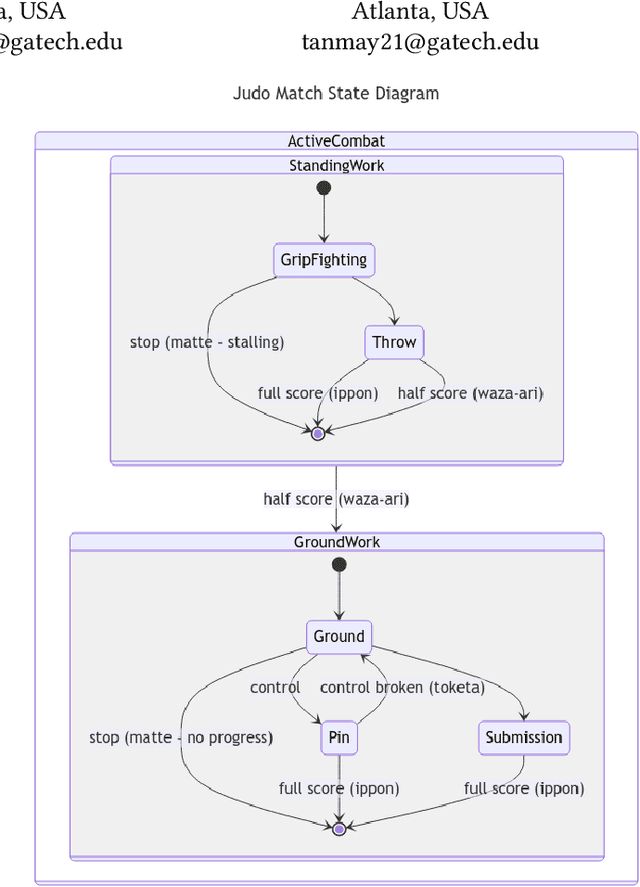
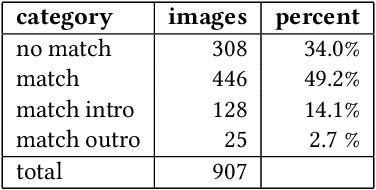
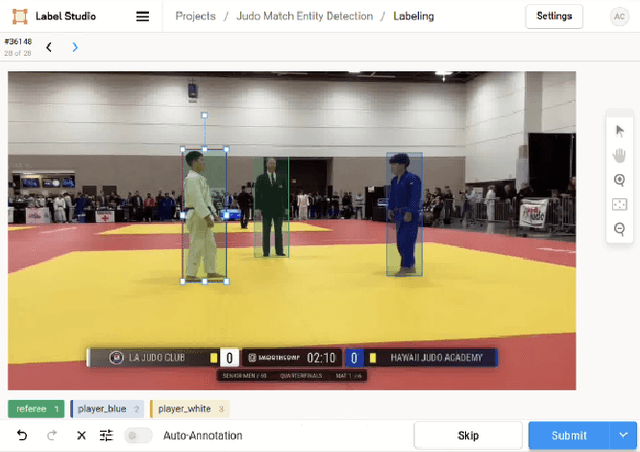
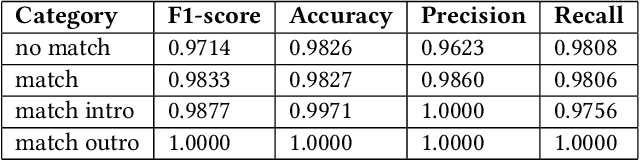
Abstract:This paper presents a semi-supervised approach to extracting and analyzing combat phases in judo tournaments using live-streamed footage. The objective is to automate the annotation and summarization of live streamed judo matches. We train models that extract relevant entities and classify combat phases from fixed-perspective judo recordings. We employ semi-supervised methods to address limited labeled data in the domain. We build a model of combat phases via transfer learning from a fine-tuned object detector to classify the presence, activity, and standing state of the match. We evaluate our approach on a dataset of 19 thirty-second judo clips, achieving an F1 score on a $20\%$ test hold-out of 0.66, 0.78, and 0.87 for the three classes, respectively. Our results show initial promise for automating more complex information retrieval tasks using rigorous methods with limited labeled data.
Fine-Grained Classification for Poisonous Fungi Identification with Transfer Learning
Jul 10, 2024



Abstract:FungiCLEF 2024 addresses the fine-grained visual categorization (FGVC) of fungi species, with a focus on identifying poisonous species. This task is challenging due to the size and class imbalance of the dataset, subtle inter-class variations, and significant intra-class variability amongst samples. In this paper, we document our approach in tackling this challenge through the use of ensemble classifier heads on pre-computed image embeddings. Our team (DS@GT) demonstrate that state-of-the-art self-supervised vision models can be utilized as robust feature extractors for downstream application of computer vision tasks without the need for task-specific fine-tuning on the vision backbone. Our approach achieved the best Track 3 score (0.345), accuracy (78.4%) and macro-F1 (0.577) on the private test set in post competition evaluation. Our code is available at https://github.com/dsgt-kaggle-clef/fungiclef-2024.
DS@GT eRisk 2024: Sentence Transformers for Social Media Risk Assessment
Jul 10, 2024Abstract:We present working notes for DS@GT team in the eRisk 2024 for Tasks 1 and 3. We propose a ranking system for Task 1 that predicts symptoms of depression based on the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI-II) questionnaire using binary classifiers trained on question relevancy as a proxy for ranking. We find that binary classifiers are not well calibrated for ranking, and perform poorly during evaluation. For Task 3, we use embeddings from BERT to predict the severity of eating disorder symptoms based on user post history. We find that classical machine learning models perform well on the task, and end up competitive with the baseline models. Representation of text data is crucial in both tasks, and we find that sentence transformers are a powerful tool for downstream modeling. Source code and models are available at \url{https://github.com/dsgt-kaggle-clef/erisk-2024}.
Transfer Learning with Self-Supervised Vision Transformers for Snake Identification
Jul 08, 2024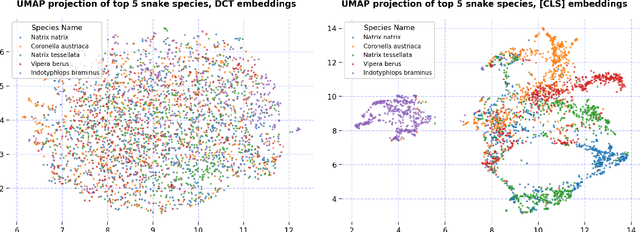
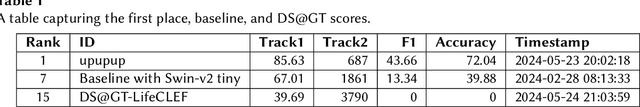
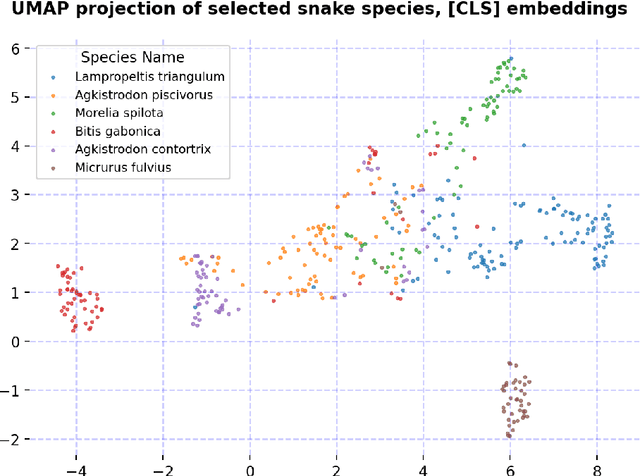
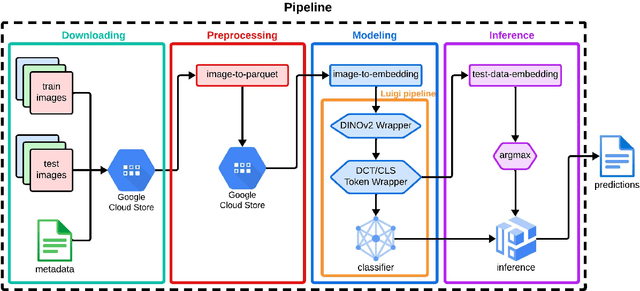
Abstract:We present our approach for the SnakeCLEF 2024 competition to predict snake species from images. We explore and use Meta's DINOv2 vision transformer model for feature extraction to tackle species' high variability and visual similarity in a dataset of 182,261 images. We perform exploratory analysis on embeddings to understand their structure, and train a linear classifier on the embeddings to predict species. Despite achieving a score of 39.69, our results show promise for DINOv2 embeddings in snake identification. All code for this project is available at https://github.com/dsgt-kaggle-clef/snakeclef-2024.
Tile Compression and Embeddings for Multi-Label Classification in GeoLifeCLEF 2024
Jul 08, 2024Abstract:We explore methods to solve the multi-label classification task posed by the GeoLifeCLEF 2024 competition with the DS@GT team, which aims to predict the presence and absence of plant species at specific locations using spatial and temporal remote sensing data. Our approach uses frequency-domain coefficients via the Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) to compress and pre-compute the raw input data for convolutional neural networks. We also investigate nearest neighborhood models via locality-sensitive hashing (LSH) for prediction and to aid in the self-supervised contrastive learning of embeddings through tile2vec. Our best competition model utilized geolocation features with a leaderboard score of 0.152 and a best post-competition score of 0.161. Source code and models are available at https://github.com/dsgt-kaggle-clef/geolifeclef-2024.
Multi-Label Plant Species Classification with Self-Supervised Vision Transformers
Jul 08, 2024Abstract:We present a transfer learning approach using a self-supervised Vision Transformer (DINOv2) for the PlantCLEF 2024 competition, focusing on the multi-label plant species classification. Our method leverages both base and fine-tuned DINOv2 models to extract generalized feature embeddings. We train classifiers to predict multiple plant species within a single image using these rich embeddings. To address the computational challenges of the large-scale dataset, we employ Spark for distributed data processing, ensuring efficient memory management and processing across a cluster of workers. Our data processing pipeline transforms images into grids of tiles, classifying each tile, and aggregating these predictions into a consolidated set of probabilities. Our results demonstrate the efficacy of combining transfer learning with advanced data processing techniques for multi-label image classification tasks. Our code is available at https://github.com/dsgt-kaggle-clef/plantclef-2024.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge