Christian Hegeler
Teaching contact-rich tasks from visual demonstrations by constraint extraction
Apr 03, 2023Abstract:Contact-rich manipulation involves kinematic constraints on the task motion, typically with discrete transitions between these constraints during the task. Allowing the robot to detect and reason about these contact constraints can support robust and dynamic manipulation, but how can these contact models be efficiently learned? Purely visual observations are an attractive data source, allowing passive task demonstrations with unmodified objects. Existing approaches for vision-only learning from demonstration are effective in pick-and-place applications and planar tasks. Nevertheless, accuracy/occlusions and unobserved task dynamics can limit their robustness in contact-rich manipulation. To use visual demonstrations for contact-rich robotic tasks, we consider the demonstration of pose trajectories with transitions between holonomic kinematic constraints, first clustering the trajectories into discrete contact modes, then fitting kinematic constraints per each mode. The fit constraints are then used to (i) detect contact online with force/torque measurements and (ii) plan the robot policy with respect to the active constraint. We demonstrate the approach with real experiments, on cabling and rake tasks, showing the approach gives robust manipulation through contact transitions.
Model Predictive Impedance Control with Gaussian Processes for Human and Environment Interaction
Aug 15, 2022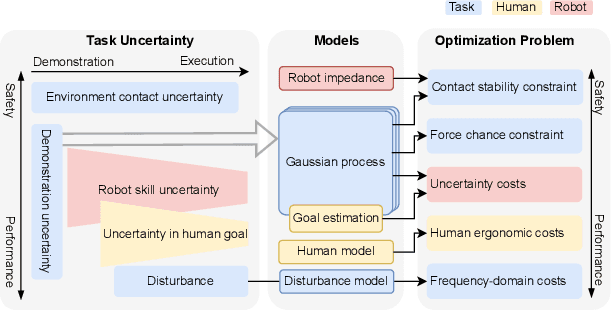
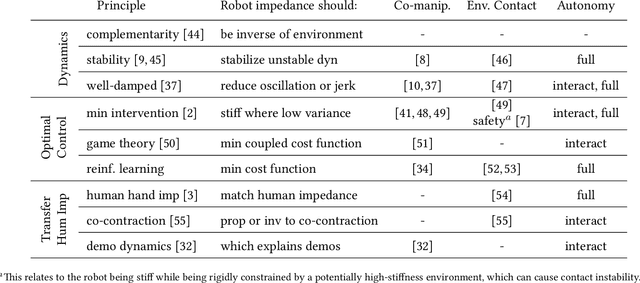
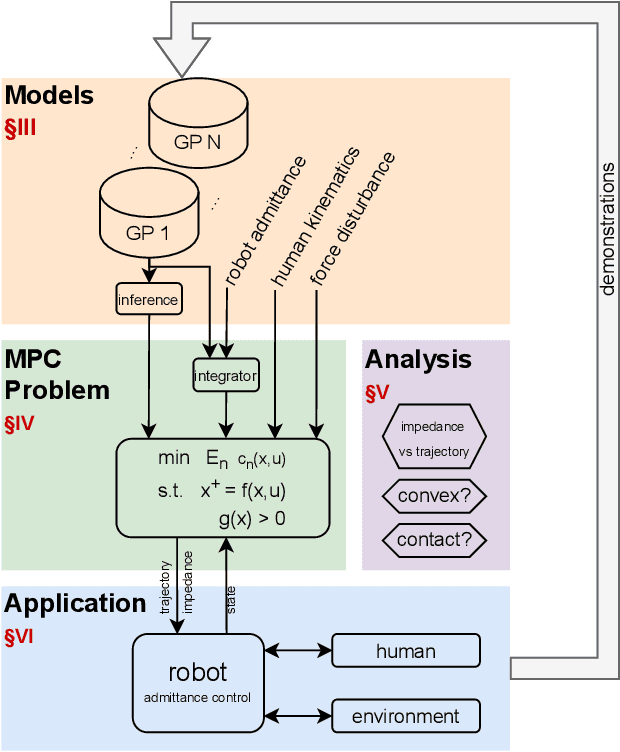
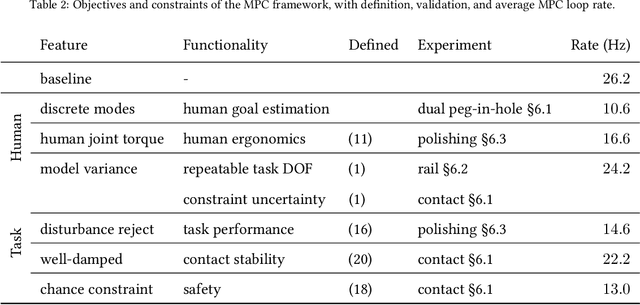
Abstract:In tasks where the goal or configuration varies between iterations, human-robot interaction (HRI) can allow the robot to handle repeatable aspects and the human to provide information which adapts to the current state. Advanced interactive robot behaviors are currently realized by inferring human goal or, for physical interaction, adapting robot impedance. While many application-specific heuristics have been proposed for interactive robot behavior, they are often limited in scope, e.g. only considering human ergonomics or task performance. To improve generality, this paper proposes a framework which plans both trajectory and impedance online, handles a mix of task and human objectives, and can be efficiently applied to a new task. This framework can consider many types of uncertainty: contact constraint variation, uncertainty in human goals, or task disturbances. An uncertainty-aware task model is learned from a few demonstrations using Gaussian Processes. This task model is used in a nonlinear model predictive control (MPC) problem to optimize robot trajectory and impedance according to belief in discrete human goals, human kinematics, safety constraints, contact stability, and frequency-domain disturbance rejection. This MPC formulation is introduced, analyzed with respect to convexity, and validated in co-manipulation with multiple goals, a collaborative polishing task, and a collaborative assembly task.
Model Predictive Control with Gaussian Processes for Flexible Multi-Modal Physical Human Robot Interaction
Oct 24, 2021
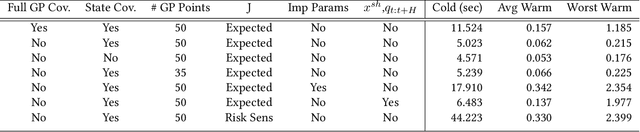
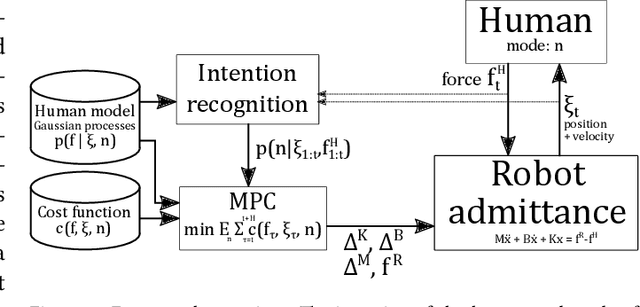

Abstract:Physical human-robot interaction can improve human ergonomics, task efficiency, and the flexibility of automation, but often requires application-specific methods to detect human state and determine robot response. At the same time, many potential human-robot interaction tasks involve discrete modes, such as phases of a task or multiple possible goals, where each mode has a distinct objective and human behavior. In this paper, we propose a novel method for multi-modal physical human-robot interaction that builds a Gaussian process model for human force in each mode of a collaborative task. These models are then used for Bayesian inference of the mode, and to determine robot reactions through model predictive control. This approach enables optimization of robot trajectory based on the belief of human intent, while considering robot impedance and human joint configuration, according to ergonomic- and/or task-related objectives. The proposed method reduces programming time and complexity, requiring only a low number of demonstrations (here, three per mode) and a mode-specific objective function to commission a flexible online human-robot collaboration task. We validate the method with experiments on an admittance-controlled industrial robot, performing a collaborative assembly task with two modes where assistance is provided in full six degrees of freedom. It is shown that the developed algorithm robustly re-plans to changes in intent or robot initial position, achieving online control at 15 Hz.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge