Chien-Hung Chen
Compacting, Picking and Growing for Unforgetting Continual Learning
Oct 30, 2019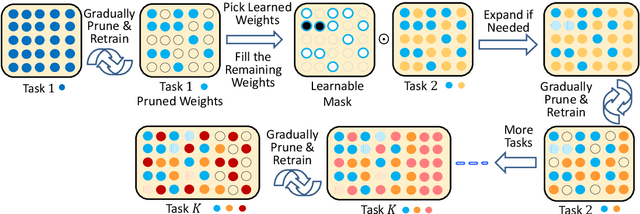
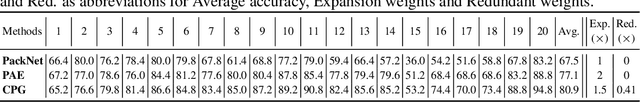
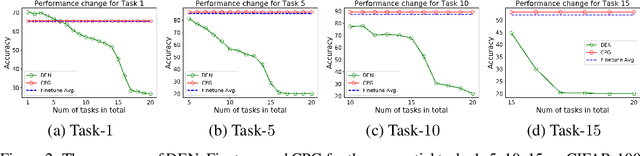
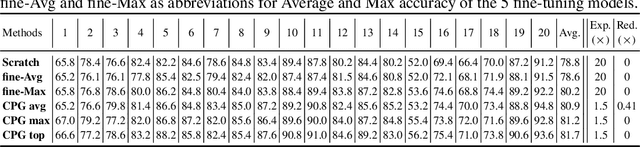
Abstract:Continual lifelong learning is essential to many applications. In this paper, we propose a simple but effective approach to continual deep learning. Our approach leverages the principles of deep model compression, critical weights selection, and progressive networks expansion. By enforcing their integration in an iterative manner, we introduce an incremental learning method that is scalable to the number of sequential tasks in a continual learning process. Our approach is easy to implement and owns several favorable characteristics. First, it can avoid forgetting (i.e., learn new tasks while remembering all previous tasks). Second, it allows model expansion but can maintain the model compactness when handling sequential tasks. Besides, through our compaction and selection/expansion mechanism, we show that the knowledge accumulated through learning previous tasks is helpful to build a better model for the new tasks compared to training the models independently with tasks. Experimental results show that our approach can incrementally learn a deep model tackling multiple tasks without forgetting, while the model compactness is maintained with the performance more satisfiable than individual task training.
IMMVP: An Efficient Daytime and Nighttime On-Road Object Detector
Oct 28, 2019

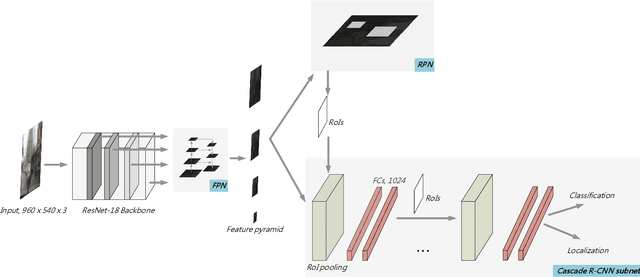

Abstract:It is hard to detect on-road objects under various lighting conditions. To improve the quality of the classifier, three techniques are used. We define subclasses to separate daytime and nighttime samples. Then we skip similar samples in the training set to prevent overfitting. With the help of the outside training samples, the detection accuracy is also improved. To detect objects in an edge device, Nvidia Jetson TX2 platform, we exert the lightweight model ResNet-18 FPN as the backbone feature extractor. The FPN (Feature Pyramid Network) generates good features for detecting objects over various scales. With Cascade R-CNN technique, the bounding boxes are iteratively refined for better results.
Stingray Detection of Aerial Images Using Augmented Training Images Generated by A Conditional Generative Model
Jun 25, 2018
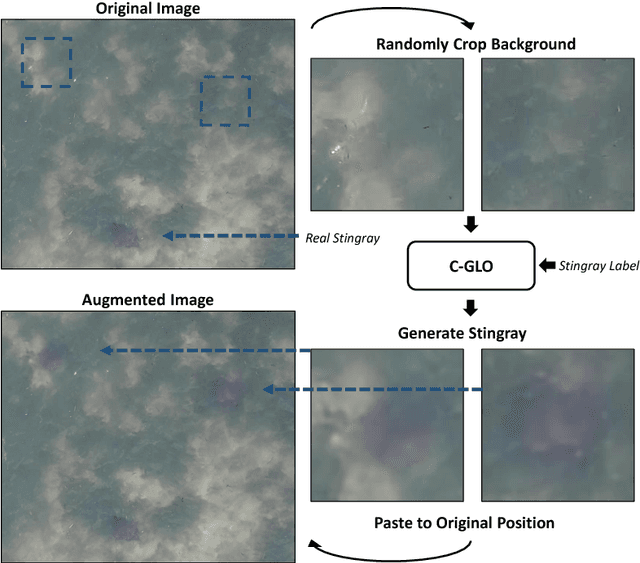
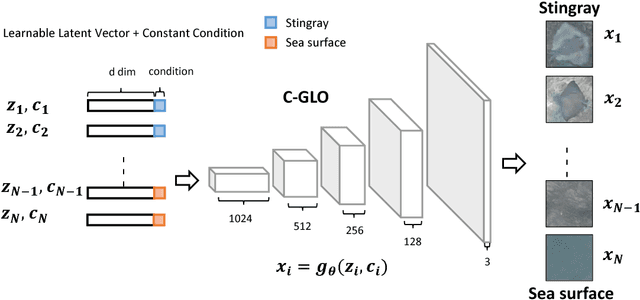
Abstract:In this paper, we present an object detection method that tackles the stingray detection problem based on aerial images. In this problem, the images are aerially captured on a sea-surface area by using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV), and the stingrays swimming under (but close to) the sea surface are the target we want to detect and locate. To this end, we use a deep object detection method, faster RCNN, to train a stingray detector based on a limited training set of images. To boost the performance, we develop a new generative approach, conditional GLO, to increase the training samples of stingray, which is an extension of the Generative Latent Optimization (GLO) approach. Unlike traditional data augmentation methods that generate new data only for image classification, our proposed method that mixes foreground and background together can generate new data for an object detection task, and thus improve the training efficacy of a CNN detector. Experimental results show that satisfiable performance can be obtained by using our approach on stingray detection in aerial images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge