Chenzhuo Zhu
Shape-independent Hardness Estimation Using Deep Learning and a GelSight Tactile Sensor
Apr 13, 2017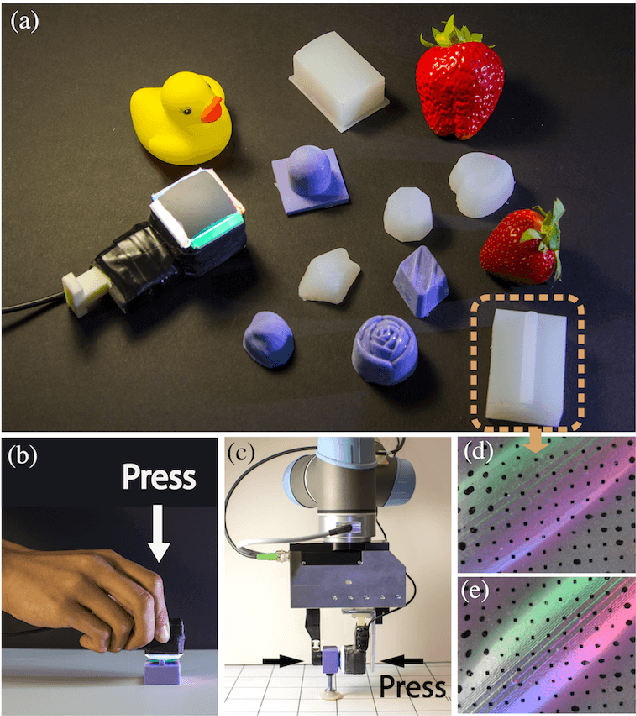
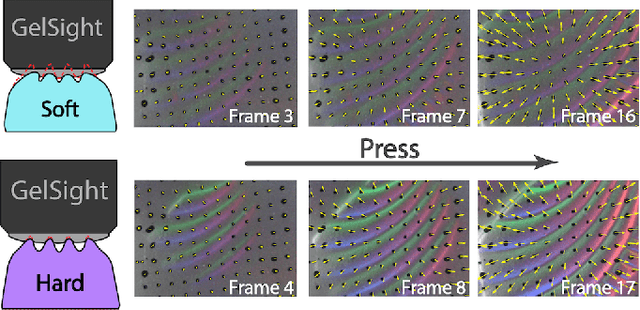
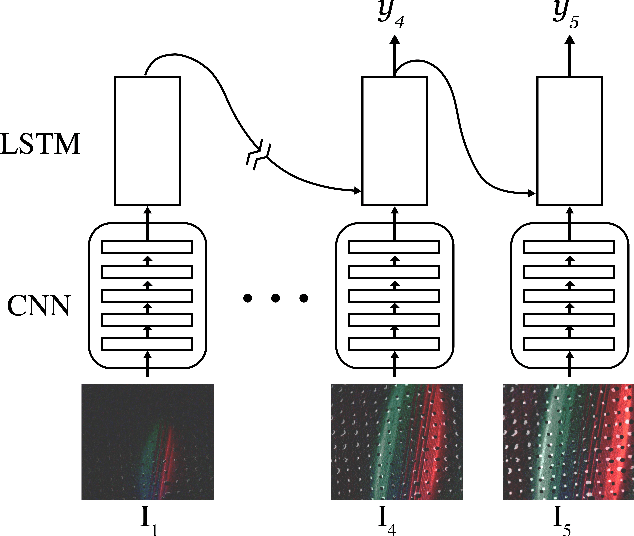
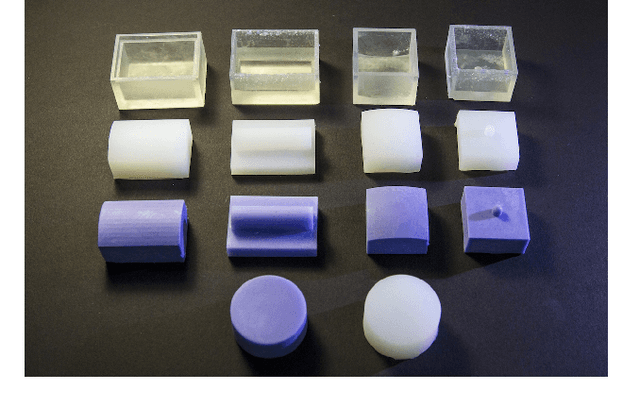
Abstract:Hardness is among the most important attributes of an object that humans learn about through touch. However, approaches for robots to estimate hardness are limited, due to the lack of information provided by current tactile sensors. In this work, we address these limitations by introducing a novel method for hardness estimation, based on the GelSight tactile sensor, and the method does not require accurate control of contact conditions or the shape of objects. A GelSight has a soft contact interface, and provides high resolution tactile images of contact geometry, as well as contact force and slip conditions. In this paper, we try to use the sensor to measure hardness of objects with multiple shapes, under a loosely controlled contact condition. The contact is made manually or by a robot hand, while the force and trajectory are unknown and uneven. We analyze the data using a deep constitutional (and recurrent) neural network. Experiments show that the neural net model can estimate the hardness of objects with different shapes and hardness ranging from 8 to 87 in Shore 00 scale.
Trained Ternary Quantization
Feb 23, 2017


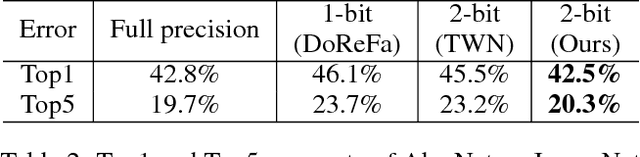
Abstract:Deep neural networks are widely used in machine learning applications. However, the deployment of large neural networks models can be difficult to deploy on mobile devices with limited power budgets. To solve this problem, we propose Trained Ternary Quantization (TTQ), a method that can reduce the precision of weights in neural networks to ternary values. This method has very little accuracy degradation and can even improve the accuracy of some models (32, 44, 56-layer ResNet) on CIFAR-10 and AlexNet on ImageNet. And our AlexNet model is trained from scratch, which means it's as easy as to train normal full precision model. We highlight our trained quantization method that can learn both ternary values and ternary assignment. During inference, only ternary values (2-bit weights) and scaling factors are needed, therefore our models are nearly 16x smaller than full-precision models. Our ternary models can also be viewed as sparse binary weight networks, which can potentially be accelerated with custom circuit. Experiments on CIFAR-10 show that the ternary models obtained by trained quantization method outperform full-precision models of ResNet-32,44,56 by 0.04%, 0.16%, 0.36%, respectively. On ImageNet, our model outperforms full-precision AlexNet model by 0.3% of Top-1 accuracy and outperforms previous ternary models by 3%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge