Chenhan Lyu
MedSpeak: A Knowledge Graph-Aided ASR Error Correction Framework for Spoken Medical QA
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Spoken question-answering (SQA) systems relying on automatic speech recognition (ASR) often struggle with accurately recognizing medical terminology. To this end, we propose MedSpeak, a novel knowledge graph-aided ASR error correction framework that refines noisy transcripts and improves downstream answer prediction by leveraging both semantic relationships and phonetic information encoded in a medical knowledge graph, together with the reasoning power of LLMs. Comprehensive experimental results on benchmarks demonstrate that MedSpeak significantly improves the accuracy of medical term recognition and overall medical SQA performance, establishing MedSpeak as a state-of-the-art solution for medical SQA. The code is available at https://github.com/RainieLLM/MedSpeak.
DEMENTIA-PLAN: An Agent-Based Framework for Multi-Knowledge Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation in Dementia Care
Mar 26, 2025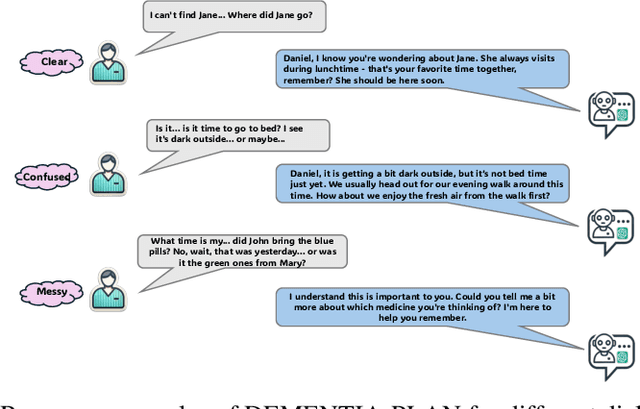

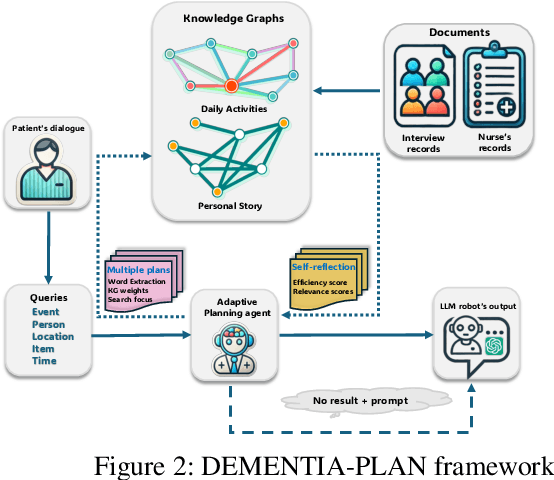
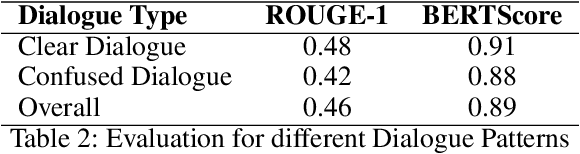
Abstract:Mild-stage dementia patients primarily experience two critical symptoms: severe memory loss and emotional instability. To address these challenges, we propose DEMENTIA-PLAN, an innovative retrieval-augmented generation framework that leverages large language models to enhance conversational support. Our model employs a multiple knowledge graph architecture, integrating various dimensional knowledge representations including daily routine graphs and life memory graphs. Through this multi-graph architecture, DEMENTIA-PLAN comprehensively addresses both immediate care needs and facilitates deeper emotional resonance through personal memories, helping stabilize patient mood while providing reliable memory support. Our notable innovation is the self-reflection planning agent, which systematically coordinates knowledge retrieval and semantic integration across multiple knowledge graphs, while scoring retrieved content from daily routine and life memory graphs to dynamically adjust their retrieval weights for optimized response generation. DEMENTIA-PLAN represents a significant advancement in the clinical application of large language models for dementia care, bridging the gap between AI tools and caregivers interventions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge